PACING GUIDE: chemistrY ESSENTIAL STANDARDS OBJECTIVES
advertisement
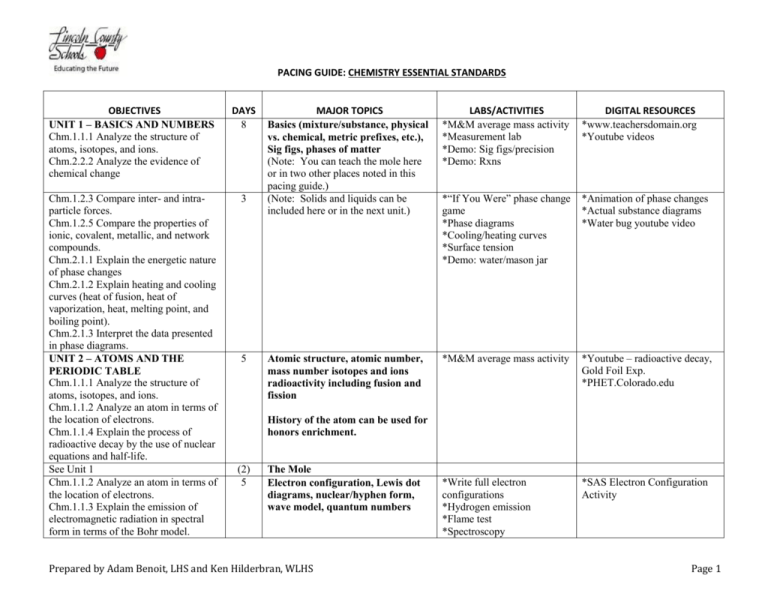
PACING GUIDE: CHEMISTRY ESSENTIAL STANDARDS OBJECTIVES UNIT 1 – BASICS AND NUMBERS Chm.1.1.1 Analyze the structure of atoms, isotopes, and ions. Chm.2.2.2 Analyze the evidence of chemical change DAYS 8 Chm.1.2.3 Compare inter- and intraparticle forces. Chm.1.2.5 Compare the properties of ionic, covalent, metallic, and network compounds. Chm.2.1.1 Explain the energetic nature of phase changes Chm.2.1.2 Explain heating and cooling curves (heat of fusion, heat of vaporization, heat, melting point, and boiling point). Chm.2.1.3 Interpret the data presented in phase diagrams. UNIT 2 – ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Chm.1.1.1 Analyze the structure of atoms, isotopes, and ions. Chm.1.1.2 Analyze an atom in terms of the location of electrons. Chm.1.1.4 Explain the process of radioactive decay by the use of nuclear equations and half-life. See Unit 1 Chm.1.1.2 Analyze an atom in terms of the location of electrons. Chm.1.1.3 Explain the emission of electromagnetic radiation in spectral form in terms of the Bohr model. 3 5 MAJOR TOPICS Basics (mixture/substance, physical vs. chemical, metric prefixes, etc.), Sig figs, phases of matter (Note: You can teach the mole here or in two other places noted in this pacing guide.) (Note: Solids and liquids can be included here or in the next unit.) LABS/ACTIVITIES *M&M average mass activity *Measurement lab *Demo: Sig figs/precision *Demo: Rxns DIGITAL RESOURCES *www.teachersdomain.org *Youtube videos *“If You Were” phase change game *Phase diagrams *Cooling/heating curves *Surface tension *Demo: water/mason jar *Animation of phase changes *Actual substance diagrams *Water bug youtube video Atomic structure, atomic number, mass number isotopes and ions radioactivity including fusion and fission *M&M average mass activity *Youtube – radioactive decay, Gold Foil Exp. *PHET.Colorado.edu *Write full electron configurations *Hydrogen emission *Flame test *Spectroscopy *SAS Electron Configuration Activity History of the atom can be used for honors enrichment. (2) 5 The Mole Electron configuration, Lewis dot diagrams, nuclear/hyphen form, wave model, quantum numbers Prepared by Adam Benoit, LHS and Ken Hilderbran, WLHS Page 1 OBJECTIVES (See note in Unit 1) Chm.2.1.5 Explain the relationships between pressure, temperature, volume, and quantity of gas both qualitative and quantitative. Chm.3.1.2 Explain the conditions of a system at equilibrium Chm.1.3.1 Classify the components of a periodic table (period, group, metal, metalloid, nonmetal, transition). Chm.1.3.2 Infer the physical properties (atomic radius, metallic and nonmetallic characteristics) of an element based on its position on the Periodic Table. Chm.1.3.3 Infer the atomic size, reactivity, electronegativity, and ionization energy of an element from its position in the Periodic Table. UNIT 3 – COMPOUNDS/NAMING Chm.1.2.1 Compare (qualitatively) the relative strengths of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds Chm.1.2.2 Infer the type of bond and chemical formula formed between atoms. Chm.1.2.3 Compare inter- and intraparticle forces. Chm.1.2.4 Interpret the name and formula of compounds using IUPAC convention. DAYS (3) MAJOR TOPICS (Solids and liquids can be taught here or above in Unit 1) 5 Gas Laws – Ideal, Dalton, Combined, Le Chatlier 6 Periodic table - trends, main group representative elements, individual elements 7 Nomenclature (IUPAC names) for Ionic compounds, polyatomic ions, distinguish between types of bonds, diatomic molecules LABS/ACTIVITIES DIGITAL RESOURCES *Molar mass calculation using bic lighter *Water bottle in freezer *Can shrink and collapse *Demo: balloon in different temp environments *SAS crossword puzzle *Project: students generate lists of element uses *Ingredient list activity *Kitchen chemistry *SAS Gas Lab *Ohio State Virtual lab *Liquid Nitrogen/CO2 bottle bombs *MythBusters video *Making compound kinesthetic activity *Samples under microscope *Salt solution conductivity *Youtube – water formation, sodium chloride *Brainiacs videos (IA) *Element videos *Show trends for activity on Smart Board First 9 weeks can end here or include the first section of Unit 4 if you are giving a test after each section. Prepared by Adam Benoit, LHS and Ken Hilderbran, WLHS Page 2 OBJECTIVES UNIT 4 - REACTIONS Chm.1.2.2 Infer the type of bond and chemical formula formed between atoms. Chm.1.2.3 Compare inter- and intraparticle forces. Chm.2.2.1 Explain the energy content of a chemical reaction. Chm.2.2.2 Analyze the evidence of chemical change Chm.2.2.3 Analyze the Law of Conservation of Matter and how it applies to various types of chemical equations (synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, and combustion). Chm.2.2.5 Analyze quantitatively the composition of a substance (empirical formula, molecular formula, percent composition, and hydrates). Chm.2.2.4 Analyze the stoichiometric relationships inherent in a chemical reaction. UNIT 5 - SOLUTIONS Chm.3.1.3 Infer the shift in equilibrium when a stress is applied to a chemical system (Le Chatelier’s Principle). Chm.3.2.3 Infer the quantitative nature of a solution (molarity, dilution, and titration with a 1:1 molar ratio). Chm.3.2.4 Summarize the properties of solutions. Chm.3.2.5 Interpret solubility diagrams. Chm.3.2.6 Explain the solution process. Chm.2.2.4 Analyze the stoichiometric relationships inherent in a chemical reaction. DAYS 5 MAJOR TOPICS Covalent compounds, polarity, shapes of molecules – can be taught with unit 3 LABS/ACTIVITIES *Models lab DIGITAL RESOURCES *Molecules video of shape and formation *Hybridization and shape variations 8 Reactions – types, prediction of products, solubility rules, net ionic equations % composition, empirical formula, molecular formula (stoichiometry) *Demo: all 5 types of rxns *Vinegar/baking soda in a bag – if citric acid is used can tie to next unit and heat of sol’n *Microscale rxn lab *Prediction of products lab *% hydrate lab *9 solutions lab *Youtube videos – type of rxns *MythBuster thermite video *SAS balancing lab 8 Solutions – Molarity, molality, % by mass and volume, dilution, colligative properties *Solution kinesthetic activity *Sugar vs salt demo (conductivity) *Demo: “How to create” *Demo: Heat of Solutions *Salt dissolution video *Ice cream lab *Titration video *Making orange juice from concentrate 6 (Stoichiometry) can be taught here as a stand alone section or integrated in the reaction section of Unit 4 Limiting reagent can be honors enrichment. *Theoretical yield lab (can be a demo) *Ice cream production/sandwich production (PHET) Prepared by Adam Benoit, LHS and Ken Hilderbran, WLHS Page 3 OBJECTIVES Chm.3.2.1 Classify substances using the hydronium and hydroxide ion concentrations. Chm.3.2.2 Summarize the properties of acids and bases. Chm.3.2.3 Infer the quantitative nature of a solution (molarity, dilution, and titration with a 1:1 molar ratio). UNIT 6 – ENERGY, RATE, AND EQUILIBRIUM Chm.2.1.3 Interpret the data presented in phase diagrams Chm.2.1.4 Infer simple calorimetric calculations based on the concepts of heat lost equals heat gained and specific heat. Chm.2.2.1 Explain the energy content of a chemical reaction. Chm.3.1.1 Explain the factors that affect the rate of a reaction (temperature, concentration, particle size and presence of a catalyst). Chm.3.1.2 Explain the conditions of a system at equilibrium. Chm.1.1.4 Explain the process of radioactive decay by the use of nuclear equations and half-life REVIEW AND EXAM DAYS DAYS 7 MAJOR TOPICS Acid/Base LABS/ACTIVITIES *Titration *Demo: Indicators *Demo: Water/wine/milk/OJ DIGITAL RESOURCES *Industrial use videos *Cabbage juice 5 Energy (H, Hess’s Law, E, specific heat) *Caloric content of food *Specific heat lab *Video of calorie determination *Gibbs Free Energy *Hess’s Law *MythBusters – “Is the box more nutritious than the cereal” video *candle relighting video – youtube – (amazing five) 4 Rate of reaction, equilibrium *Mg/HCl change concentration and mass lab or demo *Ice bath vs room temp rxns *Soft drinks *Mentos/diet coke (temp) *Equilibrium calculations *Video of CO2 escape 4 Redox/Nuclear – either honors enrichment or a good time to cover nuclear if not done with Rutherford early in the semester *Titration *Elephant toothpaste *Geiger counter *Video of elephant toothpaste/titration *Fission/Fusion *Battery animation 4 Prepared by Adam Benoit, LHS and Ken Hilderbran, WLHS Page 4