Algebra Section 1-4, 1-5, & 1-6 Notes
advertisement

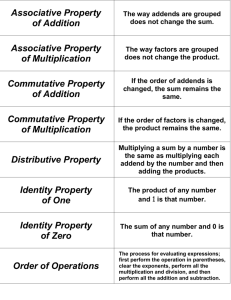
Section 1-4 Notes: Identity and Equality Properties (pgs. 21-22 of textbook) Used in comparing data There are two Identity Properties: Additive and Multiplicative -Additive Identity: states that adding 0 to any number or expression does not change its value -Multiplicative Identity: states that multiplying a number or expression by 1 does not change its value The product of any number and 0 is equal to 0; this is called the multiplicative property of zero Two numbers whose product is 1 are called multiplicative inverses or reciprocals; zero has no reciprocal because any number times 0 is 0 Properties of equality preserve equality between the two sides of an equation; these properties can be used to solve equations -Reflexive: any quantity is equal to itself -Symmetric: if one quantity equals a second quantity, then the second quantity equals the first -Transitive: if one quantity equals a second quantity and the second quantity equals a third quantity, then the first quantity equals the third quantity -Substitution: a quantity may be substituted for its equal in any expression Section 1-5 Notes: The Distributive Property (pgs. 26-28 of textbook) Distributive Property: a term outside the parentheses is distributed by multiplication to each term inside the parentheses -apply the Distributive Property when simplifying expressions and solving equations -combine like terms Section 1-6 Notes: Commutative and Associative Properties (pgs. 32-33 of textbook) Commutative Property: the order in which you add or multiply numbers does not change their sum or product Associative Property: the way you group three or four numbers when adding or multiplying does not change their sum or product These properties cannot be applied to subtraction or division