Earth Science – Chapter 15 – Rocks and Fossils – Notes
advertisement

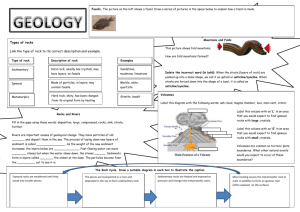
Chapter 15 - Rocks and Fossils o 15A Introduction to Rocks How should a Christian look at the fossils and rock layers that we find? o God’s power o God’s Judgment o __________________________ o God’s mercy o Reminds us we desperately need God 15A Introduction to Rocks What is a Rock? o __________________________________ formed from one or more minerals or organic materials Petrology o Study of _________________ 3 Main Types of Rocks o Sedimentary o ______________________ o Metamorphic Sedimentary Rocks o Rocks consisting of particles of sediment that have been bonded together by natural cements, solids that have precipitated from water solutions Igneous Rocks o Any of several kinds of rock that appear to have _________________________ Metamorphic o Rock that has been altered in its basic characteristics by heat, pressure, and/or by hydrothermal chemical action since it was formed or created What are some cyclic processes we have talked about? There are many cyclic processes God produced in the earth Water cycle / ____________________ Nutrient Cycle Day / night _______________ Uniformitarinanists o See the Rock Cycle as something you would expect to take millions and billions of years to occur Creationists o Restricted to few locations o Insufficient time to complete most of cycle o _______________________________ 15 B Sedimentary Rocks Creation – Turbulent waters of Genesis Flood responsible for most strata Can contain fossils Strata o Sedimentary rock layers 2 Classifications o Clastic - ___________________ o Nonclastic - chemical 15 B Sedimentary Rocks Clastic Rocks o Formed from ________________________ o Assorted sized particles o May contain fossils or fragments of fossils Conglomerate o Pebbles and gravel sized particles cemented together o “________________________” o 2mm or greater in diameter Breccia o Similar to Conglomerate but it’s fragments are angular o ______________________ o Not the movie Material in which something else is embedded in or _________________ Breccia and Conglomerate o Deposited by ________________ flowing waters or winds o Slow flow cannot support large particles Sandstone o Between 2mm and .0625mm particle size o Typically have air spaces in between particles o High ________________ o Usually form a permeable layer Siltstone and Shale(flagstone) o .0625mm or less in particle size o Smaller spaces in between particles o Most layers of this rock are _______________________ Non-clastic sediments o From minerals dissolved in water Precipitate o Minerals crystalize out of a solution Evaporite o Evaporating water leaves behind minerals o Limestone – ______________ o Precipitates directly out of salt water Extensive limestone deposits on all continents o Good evidence for continents under water o During the Flood Volcanic activity and high level of ____________________________________ Large amounts of Carbonate precipitates Halite – Rock Salt o Formed by o Evaporation and ____________________ o During o ___________ o Or Created that way o We find extensive beds From 1m to over 60m thick 15 B Sedimentary Rocks Salt Domes o Cylindrical masses of Halite o Forced upward by great pressure Usually collect oil and gas Gulf of __________________ Remember the BP oil spill? Fossils o Any trace or remains of a living creature that has been preserved by natural means o From micro fossils to dinosaurs Paleontology o Study of fossils Is this what we see today? o No, we do not see fish on the sea floor waiting to be buried by sediment o Nor any other animal…. Fossils and Evolution – Where are the Missing Links? o Evolutionists and Creationists all have the same evidence o ________________ are different o _______________ are different o Evolution – biological organism went through gradual changes from one kind to another Fossils don’t have ____________ on them o Soft tissue fossilization o Animals giving birth while being fossilized o Animals eating lunch while being fossilized Good indication of_____________ burial Ichthyosaur giving birth Darwin—soft creature preservation Hoaxes o “__________________” o People have been searching for them for years o People have also made a lot of false claims, only to be proved wrong later! Nebraska man o Only evidence was a _______________ o Ended up being a ____________ tooth o Yet they put him in the succession of “primate evolution” (had to take him out later) Neanderthals o Are just really old people o Fossilized from flood o 500+ year old humans o As we age our skulls Deforms What about Dinosaurs! I could do a whole chapter just on them! 6 F’s of Dinosaurs _____________Created on day 6 _____________Fall of Man – Fall of Animals _____________Not on the boat – you die _____________Truth becomes Legends _____________Dinosaur – Modern Word _____________Made up stories – lures Children How do you fit dinosaurs? o In the Ark Creationist think about ____________ biblical Kinds of dinosaurs Most dinosaurs are the size of turkeys All dinosaurs were small at one point Young and ______________ dinosaurs o In the Bible? You don’t “Dinosaur” is a modern word, not in scripture “______________” Job 40:15-24 “_______________” Job 41 Most Bibles have men’s opinions at the bottom, not Scripture! 15 B Sedimentary Rocks The Geologic Column o Layers of strata _________ through history Superposition principle o Lower layers of strata were deposited before the layers in the strata above. o Lower layers older than the above layers 15 B Sedimentary Rocks Attempt to use fossils to link layers of strata o Index fossils o Same fossil in layer a and layer b, both must be the same age… Circular reasoning o How old is the rock layer? As old as the __________ o How old is the fossil? As old as the ____________ 15 B Sedimentary Rocks Geologic Column Sequence of rock units and layers Supposedly extends through time Earliest rock, Earliest______________ – till today 15 B Sedimentary Rocks Assumptions o #1 The ______________ of fossils of a creature in a particular geological formation is evidence of the non-existence of that creature when the sedimentary layer was deposited o No fossil evidence Living Fossils – 1938 coelacanth – “_____________” Wollemi pine – 150 mya 1994 living in Australia Rock rat –____________ – meat market in SE Asia Slit shell – 500 mya discovered 1855 Horseshoe crab – 190 mya and 445 mya “The Fossil record of the very earliest plants is very poor. Fossils of mosses, generally considered the most primitive of the living land plants, have been found from the Devonian period, but surely they existed earlier but did not fossilize.” Ernst Mayr, What Evolution is (New York: Basic Books, 2001), p.63. 15 B Sedimentary Rocks Assumption #2 - Fossil deposits represent _________________________ - Cumberland Bone Cave, Maryland Australia – muskrat and whale ________________ Polystrate fossils o Fossilized trees extending ______________ layers o Good contrary evidence for layers taking ‘millions’ of years o Polystrate coal seams What else we find in sedimentary Rocks o Fossil fuels o Coal o __________ o Natural Gas 15C Igneous Rocks Molten in the _____________ Magma o Molten rock found anywhere beneath the earth’s surface Lava o Molten rock that flows out onto earth’s surface 15C Igneous Rocks Extrusive Rocks o Lava solidifies ________________ earth’s surface Intrusive Rocks o Lava squeezes into another rock, intruding the rock layer Pluton – intrusive rock formation Batholith – largest intrusive structure – ___________ of square km2 15C Igneous Rocks Granite – intrusive ____________ rock Mixture of ___________, feldspars, and quartz Extrusive rocks o Lava plateau o Thick rock formation from a _____________ o Magma Volcanic neck o Eroded volcano 15C Igneous Rocks Obsidian – “_____________” Pumice Basalt – ocean floor 15D Metamorphic Rocks Rocks that appear to have changed in their structure or chemical composition since their creation Magma ________________ the rock, then it is solidified 2 kinds of metamorphic processes o Local metamorphism Intrusive or extrusive magma heats and compresses _________________ rocks o ______________l Metamorphism o Pushing of Continental Plates over large areas effecting large volumes of rock Usually previous rock was sedimentary Classified into 2 types of Rocks o Foliated Flattened mineral crystals aligned in parallel layers Looks ________________ Slate(__________), Schist(slate), Gneiss(schist) o Nonfoliated rocks No banding Layers or will break in sharp angular pieces _____________ – metamorphosed limestone