Plant Catalogue
advertisement

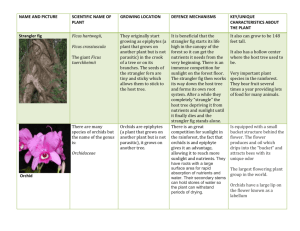
Leaf Catalogue of Central America NAME AND PICTURE Strangler Fig Orchid SCIENTIFIC NAME OF PLANT Ficus aurea Orchidaceae GROWING LOCATION DEFENCE MECHANISMS KEY/UNIQUE CHARACTERISTICS ABOUT PLANT The parasitic The fig has a symbiotic The Strangler fig fig can be relationship with the fig produces fruit found on trees wasp, both species several times a in any tropical relying on the other to year, and is the climate, survive. main source of food usually The fig wasp’s life cycle is for hundreds of rainforests tied directly with that of species and islands. the Strangler fig’s A fully grown flowers. Strangler fig will The inside of a “bulb” is appear to be tall carpeted with male and canopy tree, part of female flowers, as well as which will be freshly laid Fig wasp wrapped around a eggs. The maturing of dead “host” tree both the flowers and the which the fig wasps are tightly linked, “strangled” in order so that when the female to steal its sunlight wasps are inseminated and nutrients by the male wasps and The Strangler fig hatch, the males die and has waxy leaves to the females, now covered protect it from with pollen from the moisture-wicking flowers, burry out of the winds and sunlight. bulb and fly off in search of another bulb to burry into, lay her eggs, and then die, thus continuing the life cycle of both species. The flower One species of Orchid, Orchids are pretty can often be called Coryanthes, are flowers found found the fastest growing growing from the growing on orchids (one year to bark of trees. Most the bark of a bloom!). It is believed of the fruits tree, but is not that this adaptation is a produced by an parasitic. defense mechanism to orchid are edible There are the frequent forest fire. (ex. Vanilla) over 1400 species of orchids on Costa Rica Pitcher plant Nepenthes The tropical pitcher plant is usually grown on the rainforest floor, where there is humidity, water and varying levels of sunlight. Teak tree Tectona Grandis The tree grows on the forest floor, and prospers in soil that is slightly basic (high pH) Calabash Lagenaria siceraria This leafy vine can be found wrapped around a tree, and are usually found in a warm climate. The pitcher plant originated from a place where the soil was inadequate to support their life (high acidity, low nutrients). The plant adapted a new way of getting the nutrients it needed, by developing an attractive, sweet smelling exterior and a tubular structure is slippery, so insects can’t escape once they’ve entered. Eventually, the insect falls and is digested by the plant’s various enzymes. Teak trees produce oil, called Teak oil, in their wood. This oil can be very beneficial, as it a waterproofing agent and it helps to prevent the wood from aging. Therefore, if part of its bark was ripped off and its wood exposed, the tree could still live, impervious to weather. The pitcher plant has a tubular structure, and a sweet smelling, insect-enticing exterior. The calabash vine produces gourds that, when mature, harden and are very difficult to smash or open, protecting it from the elements. It is believed, however, that horses were able to, and would, smash mature gourds with their hooves, eat the insides and disperse the calabash seeds in their fecal matter. The vine produces a green gourd. The gourds can be harvested while they are young, and cooked like squash. When mature, the gourds dry out and harden, and can be fashioned into drinking gourds. The leaves can be used to treat headaches, diarrhea and hypertension. Teak trees can grow up to 40 meters, dominated by small and fragrant white flowers, and large leaves that are papery to the touch. Air plants Catoosa’s berteroniana Grows on trees and rocks in tropical climates, where strong light is available. Air plants such as Catoosa’s berteroniana are insectivorous. They tend to grow on branches above the foliage, where they are visible to insects. They are secured to their respective branches by a thick and tangled root system (the root system doesn’t pull nutrients from the host tree) The yellow leaves have a waxy, powdery coating, which makes it appear that the flower is glowing. This waxy coating also helps to ensnare different insects, which are then pulled into the flower’s interior and digested. Resurrection fern Pleopeltis polypodioide s This fern grows on rocks, logs or tree trunks in warm climates. The Resurrection fern gets its name from its unique reaction to droughts. When a drought occurs, the leaf curls up and appears grey and dead. Then, when only a little water the fern unfurls and appears to come back to life within 24 hours. This adaptation allows it to survive long periods of drought. The fern is about 25cm in height and 5cm in width, and the extremities of the long, thin leaves are dotted with brown spots. The fern attaches itself to braches of large trees, and gather nutrients from both the water on the tree’s bark and in the air. Angel’s trumpet trees grow best in a partly shaded area within humid regions like rainforests. To avoid being eaten, an Angel’s trumpet tree produces a toxin, a hallucinogen called Scopolamine. This toxin interferes with the nervous system, causing problems with body temperature, heart rate, motor control and mental processes. The tree has hanging, colorful, sweet smelling flowers with long, green stems. The tree has large leaves as well. Angel’s Trumpet tree Brugmansia Coconut Cocos nucifera Coconut trees grow in warm, tropical climates. Coconut trees tend to grow on beaches, and areas where there are violent gusts of wind. The trunk of the coconut tree has developed an elastic quality, which allows it to bend instead of break. Sensitive plant Mimosa pudica This plant is found on the forest floor of tropical regions such as South and Central America. The Sensitive plant was aptly named. When it is touched, the leaves of the plant curl in methodically, protecting itself from predators. SOURCES OF INFORMATION http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/strangler_figs.htm http://www.wikihow.com/Grow-Pitcher-Plants http://www.evergreenseeds.com/calgouropo.html http://www.sarracenia.com/faq/faq5110.html http://hort.ufl.edu/database/documents/pdf/shrub_fact_sheets/brusppa.pdf http://www.gardenguides.com/129263-brugmansia-poisoning.html While the coconut itself is difficult to get at and to crack (the hard-shelled exterior can be 2030m in the air), it contains water and potassium, and its milk is a good source of fat as well. The Sensitive plant has a pink flower head, which resembles fiber optics with a bright red center. The leaves of the plant resemble those of the resurrection fern.