AP Review Chapter 1 with pictures
advertisement

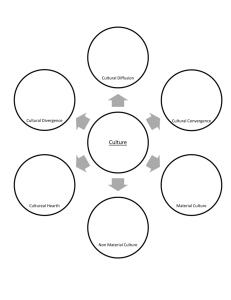
AP Review Chapter 1 *Some of the blanks for the vocab words are used in the back of the text book Human geography focuses on how _____ make _____, how people act with______ _______in _____ and across _____, and how we make ______ of others and ourselves in our _____, regions, and the world. Understanding and explain ______ is the mission of ______ ______ Globalization Is a set of ______ that are increasing ______, deepening ______, and heightening ______without regard to country ______. It is also a set of _____ that are felt from these ______ processes. What happens at a _____ scale affects the _____but it also affects the _____, _____ and _____, and similarly the processes at these scales _____ the ____ . A human phenomenon includes ____, religion, and _____. Physical phenomena include _____,______, and environmental changes Human geography is the study of _____ _____ on earth Physical geography is the study of _____ phenomena on Earth. Both human geography and physical geographers use _____ Mapping the_____ ______ of a phenomena is usually the ____ step in understanding it Pandemics – A _______ outbreak of dieses. Example; Cholera was an ancient dieses in India until the beginning of the 19th century when it spread to China, Japan, East Africa and Mediterranean Epidemic- A _______ regional outbreak of dieses. Example; Europe had its first reappearance of cholera in Naples. Spatial perspective can _____ from political elections and urban shantytowns to gay neighborhoods and folk music Observing variations in ______ phenomena across ______ is known as ______ perspective _____ ______ are derived from the spatial perspective of geography The first theme, _______, highlights how the geographical _______ of people and ______ on the earth’s surface _______ what happens and why Predicting where things are likely to occur fostered an interest in ______ ______ This helps geographers predict the ______ location for a specific thing The second of the 5 themes is ______ ________ interactions. This is the reciprocal _________ between _______ and ________. Phenomena are not evenly _______ on the earth’s surface. Instead, features to be _________ in ________areas, which we call regions. All places on the surface of the earth have ______ characteristics With place, Sense of place is created by infusing a place with meaning and emotion , by ________important events that occurred or by _______ a place with a certain character. _______ ___ ______ also develop through place. This is the ______ or understanding about a place _______ through books, movies, or stories. The fifth theme, movement, refers to the _______ of people, _______, and ideas across the surface of the planet. Movement is an expression of the ___________ of places. Spatial interaction between paces depends on the ______ among places, the accessibility (ease of reaching places), and the transportation and communication ________ (the degree of ______ between locations in a network) among places. Geographers use the term ________ to refer to the material character of a place, the complex of _______ features, human structures, and other ______ objects that give a place a particular form Cultural landscape, the visible _______ of human activity on the __________. We can see the cultural landscape in ______ of buildings, roads, memorials, churches etc. Any cultural landscape has layers of imprints form ______ of ________ _________. Sequent occupance refers to these sequential imprints of ______, whose impacts are _______ one on top of the other ___________ is the art and science of making maps. While ________ ______ show locations of places and geographic phenomena. __________ _______ tell stories, typically showing the degree of some attribute or the movement of a geographic phenomena Global positioning system (GPS) allows us to ______ things on the surface of the earth with _________ accuracy Geocaching uses their GPS units to play a ________ ________ game all over the world We carry maps in our ______ of places we have been we merely ______ of; these are called _______ ______. Our mental maps of the places within our _______ _______, those places we travel to routinely in our rounds of daily activity, are _______ accurate and _______ then places we’ve never been ________ ______ help us see general trends, but we cannot see all cases of a given phenomena Remote sensing is using technology that is a _______ away from the _____ being studied. It is collected by _______ and _______ (airplanes, balloons). Usually used after a ______ weather event. Remote sensed data show us ______ areas of ______. Use _______ ________ ________ (GIS) to compare variety of ______ data by creating digitized representation of the environment, combining _______ of ______ data, and creating maps in which ______ and _______ are superimposed. Geographers also use GIS to ______ data, which can give us ____ insight into geographic ______ and relationships Scales have two meanings in geography: the first is the ________ on a map ________ to the distance in the ______, and the second is the ________ extent of something. We see different ______ in different scales Region constitutes an area that share ______ characteristics. Criteria we use to define a region can be ______, _______, ________, or ________. A formal region has a ______ trait – it can be a shared ______ trait or a ______ trait. It is homogenous A functional region is defined by a particular set of ______ or _______ that occur within it. A functional region is a _______ system; its _______ are defined by the _______ of that system ________ ________ are intellectual constructs designed to _____ us understand the nature and ________ of phenomena in human geography At the hearth of human geography lies the concept of _______. It is the sum total _______, attitudes, and habitual ______ patterns sheared and _________ by members of a society Cultural geographers identify a single attribute of a culture as a _________ _______. Example; the wearing of a turban can be a ______ _______ of certain Muslim societies. Culture traits are not necessarily confined to a ________ culture. More than one _______ may exhibit a particular cultural trait, but each will consist of a _______ combination of ______. This is referred to as _______ ______. Example; in many cultures, the herding of cattle is a ______. However, cattle are regarded to and used in ________ ways by _______ cultures. Cultural hearth is a _____ where cultural traits _____ and form which the cultural traits _____. The process of dissemination, the spread of an idea or innovation from its hearth to other places is known as ________ _______. Whether diffusion of a cultural trait occurs depends, in part, on ______ and _______ from the ______. The ______ of an innovation becomes ____ likely the longer it takes to reach its potential _____. Time and distance cause _____ _______ ______. _______ _______ can also work against diffusion. Certain innovations, _____, or practices are not acceptable or ______ in particular cultures In the case of expansion diffusion, an innovation or ____ develops in a _____ and remains strong there while also spreading _______ The spread of Islam is an example of ________ ______, a form of expansion diffusion in which nearly all ______ individuals and _____ are affected. A dieses can spread in this way *I hope the pictures below help you remember some of the vocab words! - Sequent occupance -Hearth I like to think it of it as your heart is the organ that without it you couldn’t survive, same thing with hearth, without the hearth the idea couldn’t have spread Stimulus diffusion -Cultural landscape -Relocation Diffusion As people move and go to new places, so do their ideas Contagious diffusion Hierarchical diffusion Expansion Diffusion Environmental determinism thinks that the environment “controls” us Functional region- how connected a place is, going to work can be a a big factor of this Possibilism Thinks we control our environment Formal region Connected by a major trait, English and being American in this case GIS Theamtic map Perceptual region Exsist in our minds Remote sensed Image GPS