CHEM PP2 MS
advertisement

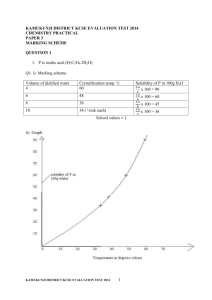
KAMUKUNJI DISTRICT KCSE EVALUATION TEST CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 233/2, MARKING SCHEME 1. (Q1) a) (i) By putting a few drops of the liquid to anhydrous copper(ii) sulphate, which would change from white to blue. Cobalt (II) chloride paper (anhydrous cobalt ii chloride changes from blue to pink on adding the liquid. (2mks) (ii) by determining its boiling point, has a b.p of 1000 at sea level / determining freezing point which is 00 at sea level / determining its density which is 1g/cm 3 (1mk) iii) Ca(s) + 2 H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) mole ratio 1: 1 40g - 22.4dm3 2.5g - ? 2.5 X 22.4 = 1.4dm3 40 Or Eqn – ½ mk 2.5 = 0.0625 moles 40 Moles of H2 produced are 0.0625 moles Vol. Of H2 is 0.0625 x 22.4 = 1.4dm3 b) i) Anhydrous calcium chloride/ concentrated sulphuric acid. (ii) Droplets of colourless liquid collects on cooler parts of the combustion tube. Black copper ii oxide turns brown. (iii) CUO(s) + H2(g) CU(s) + H2O(g) (1mk) (iv) To drive out air from the combustion tube because a mixture of air and hydrogen burns explosively (1mk) KAMUKUNJI DISTRICT KCSE EVALUATION TEST 2014 1 (v) 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) or (l) (1mk) (vi) Iron (iii) Oxide / Lead (ii) Oxide 2. a) i) D ii)F has smaller atomic radius than E, E has more protons (nuclear charge ) than F hence electron strongly attracted to nucleus decreasing the size. (2mks) iii) J is more reactive than A. Outer electrons in J are far away from nucleus / J has bigger atomic radius hence weakly attracted by the nucleus and can easily be lost iv) Halogens v) H – outer energy level full with electrons / cannot gain or lose electrons. b) i) XY2 3. a) i) Bubbles of a gas are produced / effervescence. Mg2+ and H+ ions move to the cathode. H+ ions are preferentially discharged because H+ ions have a greater tendency to gain electrons than Mg2+ ions . (2mks) 2H2O(l) + O2(g) + 4e- ii) 4OH(aq) iii) Concentration increases. Electrolysis of MgSO4(aq) discharges OH- ions at the anode and H+ ions at the cathode, this removes water from the solution making it to be more concentrated. (2mks) decrease in oxidation number. (reduction) b) 2Fe2+ + H2O2(aq) + 2H+(aq) +2 +1 -1 +1 2Fe3+ + 2H20(l) +3 +1 -2 Increase in oxidation number (oxidation) KAMUKUNJI DISTRICT KCSE EVALUATION TEST 2014 2 c ) i) Eθcell = EθFe - Eθ Al = - 0.44 - -1.66 = + 1.22V ii) Al(s) / Al3+(aq) Fe2+/ Fe(s) Eθ = + 1.22V iii) Al metal is a stronger reducing agent than F/e has a more negative Eθ value than Fe, it will be oxidised to Al3+ ions hence Aluminium container will react with Fe (NO3)2. d) Extraction of reactive metals purification of metals manufacture of sodium hydroxide, Chlorine and hydrogen from conc. NaCl. 4. a) i) H2(g) + Cl2 (g) 2 HCl (g) 1mk) ii) Mole ratio 1:1 Therefore 50dm3 reacts with50cm3 of Chlorine. Chlorine is in exess by 80 – 50 = 30dm3(2mks) iii) - From electrolysis of brine - cracking of long chains hydrocarbons - reacting methane (natural gas) with steam at high temperature. iv) hydrogen chloride gas in water ionises to form H+ ions which turns blue litmus paper red.while hydrogen chloride gas in methylbenzene do not have H+ ions, it is in molecule form (2mks) b) i) Acts as an Oxidising agent (1mk) ii) X – Concentrated hydrochloric acid (1mk) Y – Concentrated Sulphuric (vi) acid iii) Fe(s) + 3Cl2 (g) 2FeCl3(g) or (s) (1mk) iv) To absorb unreacted chlorine.(1mk) v) It sublimes (1mk) 5. a) KAMUKUNJI DISTRICT KCSE EVALUATION TEST 2014 3 b) i) E – ethylpropanoate M – polythene (polyethene) (2mks) ii) Nickel catalyst Temperature of 1500C – 2500C (1mk) hydrogen gas. 1mk) iii) – it is non- biodegradable hence it pollutes the environment - it produces poisonous gas when burnt (any 1mk) iv) Step 2 – esterification Step 3 – Substitution (2mks) c) B (1mk) magnesium sulphate makes water hard and B being a soapless detergent lathers easily with hard water. (1mk) 6. a)(i) Time 8.8 10.0 11.7 13.5 17.5 22.2 35.5 70.0 Rate = 0.114 0.1 0.085 0.074 0.057 0.044 0.044 0.014 1/time KAMUKUNJI DISTRICT KCSE EVALUATION TEST 2014 4 b) - surface area - Pressure - Temperature - Light (any two – 2mks) c) i) CrO42x + -2 x 4 = -2 x – 8 = -2 x = -2 = 8 x = +6 (1mk) Cr2O722x + -2 x 7 = -2 2x = -2 + 14 2x = +12 X = +6 (1mk) ii) Solution turns yellow/brown. Addition of NaOH(aq) reacts with H+ ions and removes them from solution. Equilibrium shifts to the left or backward reaction is favoured,Cr2O7 2- and water reacts to form more H+ ions.(2mks) ` 7. a) i) Bauxite (1mk) ii) Silicon (iv) Oxide iron(iii) Oxide.(2mks) iii) To lower the M.P of aluminium Oxide from 20150 to 8000C (1mk) iv) (1mk) v ) Because at high temperature about 800 0C Oxygen evolved at the anode reacts with the anode to form carbon (iv) Oxide gas making the anode to wear out b) Al3+(l) + 3e Al(s) 96500 x 3 = 27 Q= C x T = 7.5 x 3 x 60 x 60 = 81,000C 289500C = 27 KAMUKUNJI DISTRICT KCSE EVALUATION TEST 2014 5 81,000c = ? 81000 x 27 = 7.55g 289500 C) – construction of aircraft - cooking vessels - Car windows frames - Overhead cables - A reducing agent in the thermite process (any two correct 2mks) KAMUKUNJI DISTRICT KCSE EVALUATION TEST 2014 6