File
advertisement

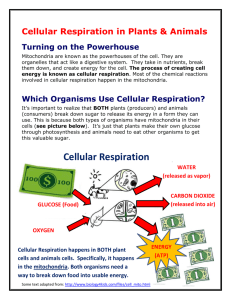
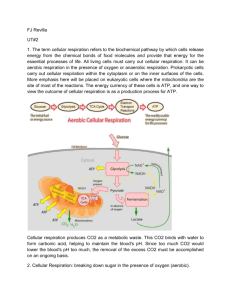
Biology 20 – Unit C Cellular Respiration Chapter 7.1 Pages 202-209 Learner Outcomes: To explain the role of cellular respiration in releasing potential energy from organic compounds To summarize and explain the role of ATP in cellular metabolism - active transport, cytoplasmic streaming, phagocytosis, biochemical synthesis, muscle contraction, heat production To distinguish, in general terms, between aerobic and anaerobic respiration and fermentation in plants, animals and yeast The Importance of Cellular Respiration When cells require energy for a particular process, it must be supplied in _______________________________________________________________ The cells of both animals and plants release the energy stored in the ____________________________________________________________through the process of ____________________________________________________________________ Cellular Respiration ________________________________________ ___________________________________________ _______________________________________ __________________________________________ 1 Biology 20 – Unit C Electron Carriers _________________________is a reduced form of _________________(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) _______________________ is the reduced form of___________________(flavin adenine dinucleotide) These compounds serve as __________________________________________________________________________________ The transfer of electrons from one reactive atom to another produces more stable ions or compounds Energy is _____________________________________________________ This energy can be used to _________________________ ______________________ __________________ Questions 1. What is the primary function of cellular respiration? 2. How do the oxidation and reduction reactions in electron transfer help form ATP? Energy, Cells and ATP ________________________________________moves substances _________________________________________________into or out of the cell using ___________________and _____________________________________often referred to as ‘pumps’. Example: sodium-potassium pump 2 Biology 20 – Unit C Other Processes that Require ATP Chromosome movements during __________________________________ Movement of organelles such as ______________________________________ ________________________________________________ Formation of _____________________________________ Beating of ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles __________________________________________________in protein synthesis Building new strands of __________________________________________________ Switches certain _________________________________________________ Produces _____________________________________________________________such as glow-worms and fireflies Glucose and ATP Virtually________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________. ___________________________________________be used directly by cells Glucose has the equivalence of ________________________________________________________________ Glucose must be ____________________________________________so it can be used by the cell Vending Machine Analogy Cells are like vending machines – they can only accept one dollar coins _____________________ Glucose is like $100 bill – we need to get change in the form of dollar coins (ATP) before the vending machine ___________________________can use it. 3 Biology 20 – Unit C Questions: 3. Active transport involves carrier proteins imbedded in the membranes of cells. How do these carrier proteins use ATP to transport molecules across the membrane? 4. How is ATP used in muscle contraction? 5. One glucose molecule has 100 times more stored energy than one ATP molecule. Explain why cells can’t use glucose to run their processes. Releasing Energy During cellular respiration, energy is ________________________as the high energy glucose molecule is ______________________________________________________________ In accordance with the Second Law of Thermodynamics,________________________________________________________________ ___________________________– cellular respiration is ________________________________________at converting glucose into the ___________________________________________ The remaining___________________________________________, which in the case of______________________________________________, maintains our constant body temperature Two Types of Cellular Respiration Aerobic Cellular Respiration – ______________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ The end products of aerobic cellular respiration are___________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ______________________________ 4 Biology 20 – Unit C Aerobic Cellular Respiration Stages Stage 1: __________________________________ Stage 2: __________________________________________ Stage 3: __________________________________________ Stage 4: ______________________________________________________________________ Anaerobic Cellular Respiration ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ There are two types of anaerobic cellular respiration: _____________________________________ ____________________________________________ _____________________________________ ____________________________________________ Anaerobic Cellular Respiration Stages Stage 1: ______________________________________________ Stage 2:______________________________________________ * Aerobic cellular respiration produces ____________________________________than either anaerobic cellular respiration Assignment: Do 7.1 Questions #1 – 5 Page: 209 5