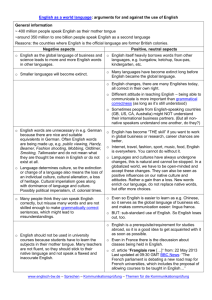
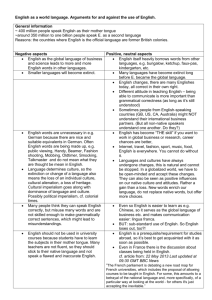
Imperialism: Nation States Look Beyond Europe What were the
advertisement

Imperialism: Nation States Look Beyond Europe What were the motives of Europeans for Imperialism? (P/S/E) What type of reactions surfaced in regards to the practice of imperialism? What are the lasting impacts of European expansion and imperialism? Date 2/3 2/4-5 2/6 2/9 2/10 2/11-12 2/13 Topic Motives for Imperialism Document Study Intro to Trial of Queen Victoria Trial work Scramble for Africa Homework: Read textbook pages at your own pace and take notes for your role. Focus on the information in relation to your trial role. Also pay attention to the key terms as you read. Trial Work Trial of Queen Victoria Trial of Queen Victoria Continue to read the textbook and research for your role Finish any textbook reading in preparation for your MC test Finish any textbook reading in preparation for your MC test. Write Trial Reflection Study for test. Write Trial Reflection Continue to read the textbook and research for your role DBQ MC Test: Imperialism DUE: Trial Reflection Textbook Pages: PP701-702, PP 743-745, PP759-768, PP 817-820, PP822-824 While reading, take notes that focus on 1) your role 2) overarching questions (above) and 3) key terms Terms for Multiple Choice Test The Suez Canal Scramble For Africa/ Congress of Berlin White Man’s Burden Indian National Congress Cecil Rhodes Sepoy Rebellion Boxer Rebellion Boer War (South Africa) French Imperialism Belgian Imperialism (King Leopold) Japanese Imperialism Benjamin Disraeli Young Turks Financial and Civilizing Motives for Imperialism Social Darwinism East India Company Opium War German Imperialism Italian Imperialism William Gladstone The Trial of Queen Victoria Trial: Monday 2/9, Reflection DUE Friday 2/13 th Imperialism was a driving force in Europe in the late 19 century. With the balance of power upset by the recently developed states of Germany and Italy and most of the continent realizing industrial might, the new nationalistic states sought ways to increase their power and prestige. Colonies were the solution. Industrial powers sought new sources of raw materials, new markets and cheap sources of labor. These possessions came at a high price to the native populations who were subjected to Social Darwinism. European nations took it upon themselves to “civilize” the world, wiping out native culture, governing systems of economies. Great Britain led the way with Queen Victoria as their head of state. In 1850 the saying was; “The Sun Never Sets on the British Empire.” In 1880 about 20% of Africa was controlled by an outside power, by 1914 almost 95% of Africa was under the domination of another nation. Procedures: The class will be divided into two groups: prosecution and defense. The “trial” will proceed as a debate. Each side will choose two trial captains who will organize the team, divide up labor and assign specific roles and area of content. The debate will mimic a bench trial where each side will try to convince the judge (me) the righteousness of their point of view. The Charges: Queen Victoria is accused of promoting the practice of Imperialism to build wealth and power for the British Empire and therefore inflicting political, social and economic harm to large segments of the global population. Debate process: The format for the trial will be in debate format and specific rules and policies will be provided prior to the trial date. Opening-each side will briefly present their side (think – thesis statement). Trial Teams: The people listed under each side are suggestions for research. This by no means is an exhaustive list, but rather a list to get you thinking about where and how to form an appropriate argument. Team captains should consider who will make opening statements and closing statements. Defense Prosecution 2 Team captains 2 team captains Queen Victoria William Gladstone Prince Albert E. D. Morel Benjamin Disraeli Gandhi Cecil Rhodes Boer Farmer Rudyard Kipling King LoBengula Gen. Charles George Gordan Anti-Imperialist league member British East India Company official Missionary (anti) Missionary-pro Member of the Xhosa tribe Bismarck Member of the Zulu tribe Jules Ferry Vladimir Lenin King Leopold of Belgium Belgian Rubber Farmer William Gladstone Sepoy Soldier Japanese Emperor Boxer Revolutionary (China) What to turn in? Pre Debate: Each person is responsible for finding one primary source document that supports his or her specific point of view. With the primary source document you will answer the following questions in a one-page response with the source attached: (These can be answered all together or as separate questions) DUE: Monday 2/9 1. What is the main idea or focus of the document? What did you learn? 2. How does this document help you understand your role or your focus? 3. What is the point of view or bias of the author of the document? Post Debate: Each class member must hand in a one page, typed reflection of the debate to include: 1. Who you were and an explanation of y our position on imperialism 2. An evaluation of your own as well as your team’s performance during the debate 3. Your personal reflection of the pros and cons of imperialism Reflection: 10 points Debate Grade: In addition to the above assignments, you will receive a separate grade that will be based on the following: 1. Did you use the class time that was provided in a productive way? 2. Did you use specific evidence and examples in your arguments? 3. Was your argument and participation well prepared, clear and focused? 10 points TOTAL POINTS FOR DEBATE: 20 POINTS