View
advertisement

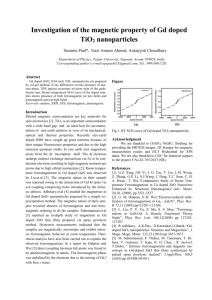
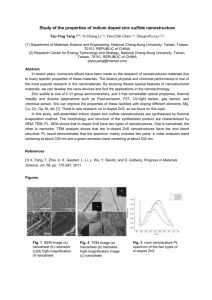
ICMAGMA 2014 Anti-ferromagnetic ordering in Mn doped copper oxide nanosheet at low temperature F. Winfred Shashikanth1, S. Ravi1* 1 * Department of Physics, Mepco Schlenk Engineering College, Sivakasi 626005, India Corresponding author’s e-mail:sravi@mepcoeng.ac.in, Tel.: +91-9360534894; Fax: +91-4562-235111 Abstract We report the anti-ferromagnetic ordering of Mn doped CuO nanosheet at low temperature. This material exhibit ferromagnetic behavior at room temperature and at 77 K it changes to weak ferromagnetism with antiferromagnetic ordering dominates. This may be due to the suppression of ferromagnetic ordering at 77 K and Morin temperature lies close of 77 K. Keywords: Dilute magnetic semiconductor, copper oxide nanosheet, Mn doping, anti-ferromagnetic ordering Introduction Ferromagnetic semiconductors or dilute magnetic semiconductors (DMS) are key materials for spin injection in electronic and optoelectronic semiconductor devices that can be controlled by weak magnetic field [1]. Generally, oxide based semiconductors are of much interest since they have wide bandgap [2]. In the present study, we synthesized Mn doped copper oxide nanosheet using a simple chemical route. Their morphological, optical and magnetic study were present and discussed. Experimental Fig 1 SEM image of Mn doped CuO Fig 2 Magnetic study of Mn doped CuO at room temperature and 77 K In a typical synthesis, appropriate amount of Cu(NO3)2.3H2O and 0.5% of Mn(NO3)2 were mixed to obtain a homogenous solution and heated to 220 C for 1 h. To this mixture, appropriate amount of glycine (0.05 M) is added, which serves as a surfactant and template. The precipitate was centrifuged and dried at 60 C to obtain the powder. The magnetic study reveals a hysteresis loop at room temperature. But at 77 K, the hysteresis pattern collapses and anti-ferromagnetic ordering dominates and Morin temperature lies in the range of 77 K. Further investigation is in progress. Result and Discussion References XRD and EDS (not shown) confirm the phase pure formation of Mn doped copper oxide nanosheet. The SEM image is presented in the Figure 1, which shows the formation of nanosheets. It also reveals that the length to width ratio are high confirming the formation of the 2-D nanostructure. The magnetic study was performed using Lakeshore VSM 7410. Figure 2 shows the magnetic study of Mn doped copper oxide nanosheet for room temperature and at 77 K. [1] S. G. Yang et al. Ferromagnetism in Mn-doped CuO, App. Phys. Lett. 83 (2003) 3746–3748 [2] S. Ravi, V.S. Prabvin, Nanostructured Copper Oxide Synthesizedby a Simple Bio-Molecule Assisted Route with Wide Bandgap, Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett.5 (2013) 879–882.