Cavity Quantum Electrodynamics of Semiconductor Quantum Dots
advertisement

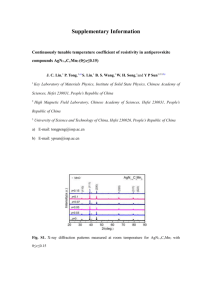
Session <Sample> Cavity Quantum Electrodynamics of Semiconductor Quantum Dots for Quantum Photonics Applications Wen-Hao Chang Department of Electrophysics, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, 300 Taiwan Semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) coupled to an optical microcavity, known as a cavity quantum electrodynamics (QED) system, have been a research field of intense investigations. It offers a solid-state system not only for exploring the fundamentals of light-matter coupling, but also for applications in quantum information processing, such as single photon sources for quantum cryptography, entangled photon sources for quantum teleportation, and quantum networks for quantum computations. In this talk, I will give a review of our recent studies on the solid-state cavity QED system based semiconductor QDs in monolithic microcavities. In particular, a new tuning scheme based on externally applied stress to the QDs has been developed for the control of cavity-QD coupling. The excitonic transitions and cavity modes can be brought into resonance due to their different energy shift rates with the applied strain. Spectral signatures of both strong and weak couplings are clearly observed. The strain tunable device can be used to tune the exciton wavelength bidirectionally at constant temperatures without affecting the emission rate and line width of excitons. Figure 1. The stress tuning device and the signature of strong QD-cavity coupling. References: 1. W.-H. Chang, W.-Y. Chen, H.-S. Chang, T. M. Hsu, T.-P. Hsieh and J.-I. Chyi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 117401 (2006). 2. H. S. Chang, W. Y. Chen, T. M. Hsu, T. P. Hsieh, J. I. Chyi, and W.-H. Chang, 3. M.-F. Tsai, H. Lin, C.-H. Lin, S.-D. Lin, S.-Y. Wang, S.-J. Cheng, M.-C. Lee, W.-H. Chang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 267402 (2008). 4. Y. J. Fu, S. D. Lin, M. F. Tsai H. Lin, C. H. Lin, S. Y. Wang, S. J. Cheng, and W.-H. Chang, Phys. Rev. B 81, 113307 (2009). 5. T.-C. Lin, C.-H. Lin, H.-S. Ling, Y.-J. Fu, W.-H. Chang, S.-D. Lin, C.-P. Lee, Phys. Rev. B 80, Rapid Com. 081304(R) (2009). 6. H. Lin, J.-H. Chen, S.-S. Chao, M.-C. Lo, S.-D. Lin and W.-H. Chang, Optics Express 18, 23948 (2010). 7. C.-H. Lin, W.-T. You, H.-Y.Chou, S.-J. Cheng, S.-D. Lin and W.-H. Chang, Phys. Rev. B 83 075317 (2011). 8. H. Lin, C.-H. Lin, W.-C. Lai, Y.-S. Li, S.-D. Lin and W.-H. Chang, Phys. Rev. B Rapid Com. (accepted). 1 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 163111 (2009).
![[1]. In a second set of experiments we made use of an](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006848904_1-d28947f67e826ba748445eb0aaff5818-300x300.png)