Chapter 3 Study Guide
advertisement

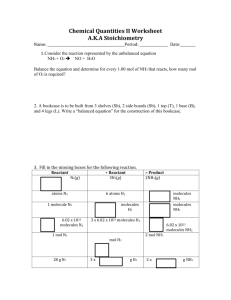
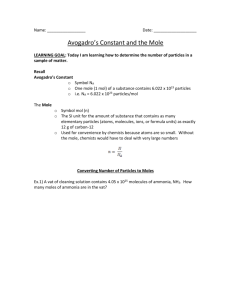
Chapter 3 Study Guide STP- Pressure= 1 ATM Temp= 0 degrees Celcius , or 273 degrees Kelvin R= Constant= .0821 atm/mol or 8.3145 j/mol Sublimation Melt. Boil Solid. Liquid. Gas Freezing. Condense Deposition Solid-closely packed vibrating particles Definite shape and volume Liquid- more energy; further apart Compressible Definite shape No definite volume Gas- highest energy; furthest apart Highly compressible No shape or volume What's between air molecules? Answer: NOTHING. Physical Properties- Observe property without changing atom or molecules -Color, texture, BP, MP, solubility Chemical Properties- How substance reacts -Flammability, reactivity with oxygen, acid, or base, corrosiveness Intensive Properties- Don't change no matter what size - Color, density Extensive Properties- Changes when size or substance changes - Mass, volume Density Ex) A rock has a mass of 6.37 grams. What is its density if its volume is 8.21 mL??? D=M/V D= 6.37/8.21 = .776 g/mL Ex) A sample of a liquid has a density of 1.75 g/cm^3. What is the mass of 35.5 cm^3 of this metal. 1.75 g/mL = M/ 35.5 35.5 x 1.75 = M M= 62.1 Physical Changes- do not affect structure- only properties- Melting point, freezing point, boiling point Chemical Changes- Changes how elements of molecules are arranged - When salt is dissolved and separated back out - Fire! - Rusting Ex) What is the mass of a piece of flesh from Mrs. Yard if it has a density of 42.25 grams and a density of 3.80 g/mL??? 3.50 = 42.25 / V V= 12.9 What is the difference between melting and dissolving? Answer: Melting is a phase changes from the solid state into the liquid state of a substance. Dissolving refers to the addition of a solute into a solution and having the solute completely “disappear” or dissociate. Pressure: Mole increase= Pressure increase Temperature increase= Pressure increase Volume decrease= pressure increase Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Matter is made up of particles that contain a certain mass The distance separating gas molecules is so big that the size of the molecules of gas is insignificant Gas particles move constantly, fast, and randomly No kinetic energy is lost during collisions Temperature is directly proportional to kinetic energy Particles exert no force on each other (neither attract nor repel) However, real gases do deviate from KMT. They are not perfectly elastic; they can exert forces on each other. A gas is most ideal at a low pressure and high temperature. Diffusion- Spread of particles into a bigger space -Ex) Producing H₂S in the classroom. And crying while it diffuses into your nostrils. Effusion- Escape of particles through tiny holes -Ex) Balloons deflating over periods of time Avagadro- Molecules are too many to count, so Avagadro discovered the “mole”, no not the one that lives underground, the kind of SCIENCE. A mole is 6.02 x 1023 molecules. Ex) How many molecules of water in 10 grams? 10 g 1 mol 6.02 x 1023 = 3.346 x 1023 molecules 18.02g/mol 1 mol Find the molecular mass: CaCl2 Ca= 40.08 g/mol Cl= 2 x 35.45 g/mol CaCl2 = 110.98 g/mol Can convert this into grams if given moles….. Ex) How many grams in 10 moles? 10 mol= 110.98/1 mol = 1109.8 grams! Pressure Conversions 1 atm=760 Torr= 760 mm Hg= 101.3 kPa Avagadro’s Law P1/n1=P2/n2 (n=moles) Charles’ Law Combined V1/T1=V2/T2 P1V1/n1T1=P2V2/n2T2` Boyle’s Law P1V1=P2V2 Ideal Gas Law PV=nRT R-Constant given This equation can happen at any temperature or pressure. Plug in all values given and solve for missing piece. If finding n, moles, you can then convert to grams or molecules if needed.