QUIZ ON TOPIC TWO: GO#2a and 2b (S)
advertisement

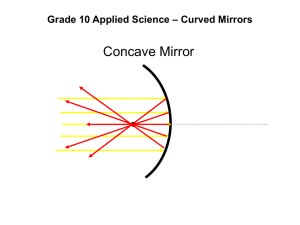
LAB M: 2.3 REFLECTING LIGHT WITH CURVED MIRRORS (page 197) 1. A mirror that is curved inwards like a bowl is called a ________________ mirror. 2. Look at the inside of a spoon. Describe what you see. 3. Look at the concave mirror supplied. What does the reflection look like? 4. What happens when you move far away from the mirror? 5. What happens when you are very close to the mirror? 6. Sketch a ray diagram of a concave mirror that has a light source hitting it. Page 197. Note that the rays follow the Law of Reflection! 7. The place where the light rays all head to a common point is called the __________________ __________________. 8. Because of the shape of a concave mirror they are very good at ___________ ____________ and ________________ it to a ______________ __________________. 9. Explain where concave mirrors are used and why. 10. Make a ray diagram using a light bulb at the focal point of a concave mirror, such as a flashlight or car headlight. Watch the direction of the light rays! 11. Explain what an image looks when the object is outside the focal point and what happens as the object approaches the focal point. 12. When using a concave mirror, explain when you get an image that is upright and enlarged? LAB N: REFLECTING LIGHT WITH CURVED MIRRORS: (page 199) 1. A mirror with the surface curved outwards is called a ____________ ________. 2. Look at the outside of a spoon. Describe what you see. 3. Look at the convex mirror supplied. What happens when you move far away from the mirror? 4. What happens when you move very close to the mirror? 5. Sketch a ray diagram of a convex mirror that has a light source hitting it. Page 199. Note that the rays follow the Law of Reflection! 6. Describe what type of image you get when using a convex mirror. 7. List a couple of places where convex mirrors are used. 8. What warning message do some convex mirrors have on them? TRY LOOKING AT THE LARGE CONCAVE AND CONVEX MIRRORS a) Which mirror gives you a large viewing area? ____________________ b) Which mirrors gives you a large image? ________________________ Explain where you need to be in relationship to the mirror to get the large image. *QUESTIONS: page 193-all, page 196-#1, 3, 4, page 199-#1, 2, 3 (F) QUIZ ON TOPIC TWO: GO#2a and 2b (S) GO#2c: Investigate, measure and describe the refraction of light through different materials LAB O: WHY IS THE FISH IN A DIFFERENT PLACE? 2.4 Transparent Substances Refract Light: (page 200-203) 1. How do transparent substances affect light rays? 2. Shine a laser through the colored water. Now shine the laser at an angle from the air above the water lever into the water. Look at the laser from the side. Explain what you see. 3. Explain why grizzlies have problems catching fish that are under water? 4. What is the scientific name given to light bending? 5. What is the reason for light bending? 6. Remember the term “density”? What does it mean? 7. a) What substance is denser? water or air b) Which substance (water or air) would you be able to run the fastest through? 8. STEPS FOR REFRACTION: 1. Density of substances (more dense into less dense of vise versa) 2. Is light going to speed up or slow down? a. Speeds up light refracts moves _________________ the normal. b. Slows down light refracts ________________ the normal. 3. Draw the normal line 4. Extend the light ray where it would go without a medium change 5. Refract the ray either towards the normal (slows down) or away from the normal (speed up) 9. Use a ruler to sketch how a fish would look to you when you are on the shore. Draw the normal: (it should be 90° to where the light beam hits the water surface). Label the incidence ray, the ray of refraction, the normal, the angle of incidence and angle of refraction. NOTE: INCIDENT RAY HAS TO BE AT AN ANGLE TO THE NEW MEDIUM 10. As the incidence ray of the fish changed from the water to the air the ray bent __________________ ____________the normal, because the speed of light ___________________. (dense to less dense matter) 11. The light will refract towards the normal when the ray goes from a ___________ dense matter into a _________________ dense matter, because the speed of light ____________________. 12. Diagram out how light would refract if it went from air into diamond. Show the normal. Air Diamond 12. Mirages are optical illusions caused by ____________________________. 13. Diagram out how light would refract if it went from glycerol into water Show the normal. Glycerol (1.2g/mL) Water (1.0g/mL). 14. Continue the light ray until it goes from the glass to the baby oil and finally into the air. Glass Baby oil Air 15. This diagram shows the path of light traveling from baby oil into an unknown substance. Is the unknown substance more or less dense than baby oil? Hint: draw the normal! 16. In the diagram below, is substance X more or less dense than the air? How can you tell? 17. Below is a diagram of light going from the left side into the right-side. Which side has the largest density? LAB P: 2.5 Lenses Refract and Focus Light: page 204-208 1. Draw the shape of a concave lens and describe it in words. 2. Look through the concave lens at a sheet of graph paper. What happens to the distance between the lines when you move the lens further away? What happens to the distance between the lines when you move the lens closer to the paper? 3. Describe and diagram out what happens to light as it passes through a concave lens. 4. Will light rays meet after they pass through a concave lens to make a focal point? Explain how the light is refracted. LAB Q: 2.5 Lenses Refract and Focus Light: (page 204-208) 1. Draw the shape of a convex lens and describe it in words. 2. Look through the convex lens at a sheet of graph paper. What happens to the distance between the lines when you move the lens further away? What happens to the distance between the lines when you move the lens closer to the paper? 3. If a lens is curved out on both sides, it is called a _______________________. 4. Describe and diagram out what happens to light as it passes through a convex lens. 5. List the two reasons why convex lenses are useful. 6. What are some uses of a convex lens? 7. What type of telescopes use convex lenses? 8. What is one drawback of convex lenses? 9. What type of lens would be useful for the following items? a) magnifying glass b) overhead projector c) eye piece in a telescope d) lens in microscope (objective) 10. How is the image of a double convex lens similar to that seen in a concave mirror? (distance, size, orientation) QUESTIONS: page 203-all, page 208-#2, 3, 5; page 211- #1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8 (F) TOPIC TWO TEST: ALL GO#2 outcomes and GO#3a outcome (S)