Classroom Practices Checklist
advertisement
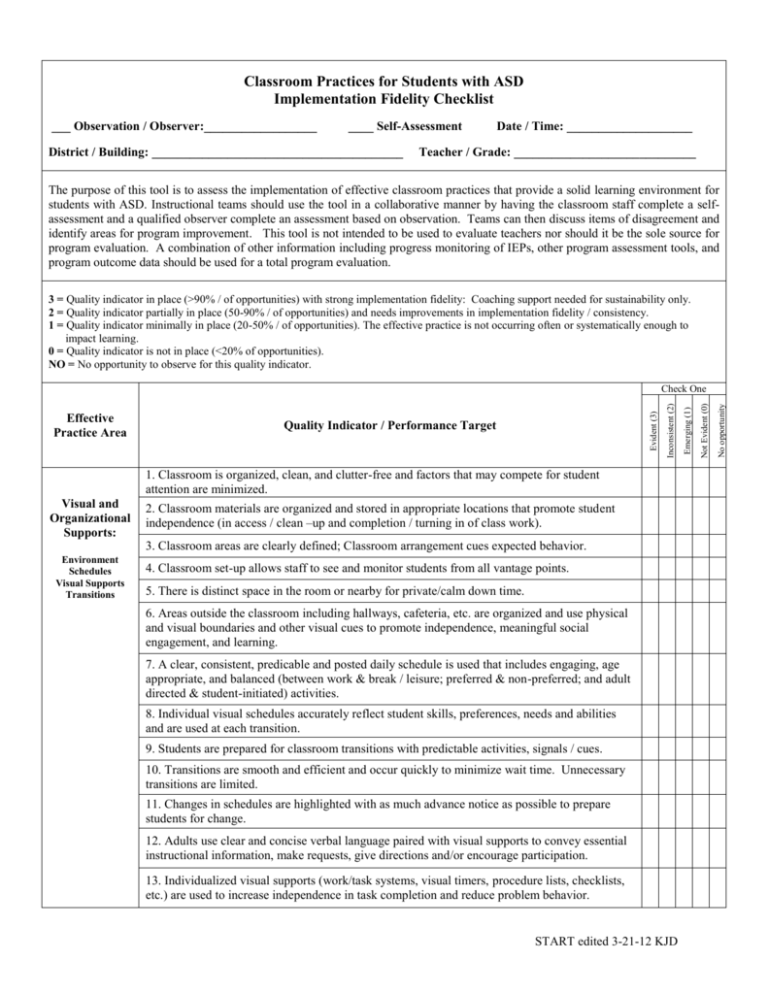
Classroom Practices for Students with ASD Implementation Fidelity Checklist ___ Observation / Observer:__________________ ____ Self-Assessment District / Building: ________________________________________ Date / Time: ____________________ Teacher / Grade: _____________________________ The purpose of this tool is to assess the implementation of effective classroom practices that provide a solid learning environment for students with ASD. Instructional teams should use the tool in a collaborative manner by having the classroom staff complete a selfassessment and a qualified observer complete an assessment based on observation. Teams can then discuss items of disagreement and identify areas for program improvement. This tool is not intended to be used to evaluate teachers nor should it be the sole source for program evaluation. A combination of other information including progress monitoring of IEPs, other program assessment tools, and program outcome data should be used for a total program evaluation. 3 = Quality indicator in place (>90% / of opportunities) with strong implementation fidelity: Coaching support needed for sustainability only. 2 = Quality indicator partially in place (50-90% / of opportunities) and needs improvements in implementation fidelity / consistency. 1 = Quality indicator minimally in place (20-50% / of opportunities). The effective practice is not occurring often or systematically enough to impact learning. 0 = Quality indicator is not in place (<20% of opportunities). NO = No opportunity to observe for this quality indicator. 1. Classroom is organized, clean, and clutter-free and factors that may compete for student attention are minimized. Visual and Organizational Supports: 2. Classroom materials are organized and stored in appropriate locations that promote student independence (in access / clean –up and completion / turning in of class work). 3. Classroom areas are clearly defined; Classroom arrangement cues expected behavior. Environment Schedules Visual Supports Transitions 4. Classroom set-up allows staff to see and monitor students from all vantage points. 5. There is distinct space in the room or nearby for private/calm down time. 6. Areas outside the classroom including hallways, cafeteria, etc. are organized and use physical and visual boundaries and other visual cues to promote independence, meaningful social engagement, and learning. 7. A clear, consistent, predicable and posted daily schedule is used that includes engaging, age appropriate, and balanced (between work & break / leisure; preferred & non-preferred; and adult directed & student-initiated) activities. 8. Individual visual schedules accurately reflect student skills, preferences, needs and abilities and are used at each transition. 9. Students are prepared for classroom transitions with predictable activities, signals / cues. 10. Transitions are smooth and efficient and occur quickly to minimize wait time. Unnecessary transitions are limited. 11. Changes in schedules are highlighted with as much advance notice as possible to prepare students for change. 12. Adults use clear and concise verbal language paired with visual supports to convey essential instructional information, make requests, give directions and/or encourage participation. 13. Individualized visual supports (work/task systems, visual timers, procedure lists, checklists, etc.) are used to increase independence in task completion and reduce problem behavior. START edited 3-21-12 KJD No opportunity Emerging (1) Not Evident (0) Quality Indicator / Performance Target Inconsistent (2) Effective Practice Area Evident (3) Check One Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports Instructional / Educational Strategies Functional Communication Systems & Supports 14. Clear, positively stated expectations for student behavior are posted and taught, reviewed, pre-taught and prompted when behavioral errors occur. 15. Positive feedback for acceptable behavior is provided 7-10 times more frequently than negative / corrective feedback. 16. Positive reinforcers are used as appropriate to promote student engagement and motivation in task completion and routines. 17. Proactive strategies used to prevent negative behaviors are evident. 18. Break cards are used to teach students to exit appropriately when necessary. 19. Adults consistently and promptly follow-through with planned / scripted responses for inappropriate behavior. 20. Responses / scripts to address inappropriate behavior are non-verbal, non-emotional, and non-punitive. 21. Adults limit / eliminate talking when students are stressed / agitated. 22. Implementation of positive behavioral intervention and support plans and crisis plan strategies are evident (use a checklist of strategies identified in available behavior plan(s)). 23. Students with ASD have daily core-content academic opportunities in general education. 24. All time is structured with clear instructional objectives. 25. Accommodations / modifications to support access to, participation in, and progress in the general education curriculum are evident in all content areas. 26. Student attention is consistently captured and directed to instruction, and staff responds to off-task behavior in a timely manner. 27. Multiple strategies, including differentiated instruction, embedded preferred interests, and accommodations / modifications, are used to enhance student engagement and active learning. 28. IEP goals are embedded within daily activities and are evident in multiple environments to promote generalization and maintenance. 29. Classroom activities and materials are age-appropriate (compared to typical peers). 30. Students spend the school day engaged in meaningful instructional activities that promote communication, independence, social engagement, daily-living skills, and academic progress. 31. Students are expected to perform routine tasks with minimal assistance. 32. Intentional teaching is evident in all activities / routines and learning opportunities are maximized at all times in all activities. 33. Instructional methods consist primarily of evidence-based practices. 34. Intentional use of a prompt hierarchy is evident in all teaching. 35. Instruction demonstrates intentional, systematic fading of prompts to reduce prompt / adult dependency and increase independence. 36. Functional communication systems are available across all environments and partners. 37. Adults create opportunities for conversation and other communicative interactions. 38. Adults consistently respond to both conventional and unconventional (e.g., yelling) communication attempts. 39. Unconventional communication attempts are paired with a functional communication equivalent. 40. Active teaching of various forms of communication is evident including initiation, responding, requesting, and answering “yes” / “no”. 41. Interactions promote expansion of students’ communication repertoires. 42. Frequent choice-making opportunities are provided throughout the day. START edited 3-21-12 KJD No opportunity Emerging (1) Quality Indicator / Performance Target Not Evident (0) Evident (3) Effective Practice Area Inconsistent (2) Check One Peer to Peer & Social Supports Adult / Student Interactions 43. Typical peers are present, prompted & supported to appropriately engage and support students with ASD. 44. Students with ASD have daily, meaningful interactions with typical peers in instructional and non-instructional settings. 45. Mediums of exchange (use of preferred interests for students with ASD) are evident and used to promote effective interaction with typical peers. 46. Adults communicate respect for students by interacting graciously & enthusiastically in an chronological age-appropriate manner demonstrating high academic and behavioral expectations. 47. Adults do not talk about students in front of them as if they are not there, but rather include them or have their conversations in private. 48. Unnecessary conversation between adults is minimal. 49. All interactions with students are treated as an opportunity to teach, practice and/or reinforce an instructional targets / outcomes. 50. Adults actively teach and promote independence in all routines and activities. NOTES / Recommendations: START edited 3-21-12 KJD No opportunity Emerging (1) Quality Indicator / Performance Target Not Evident (0) Evident (3) Effective Practice Area Inconsistent (2) Check One