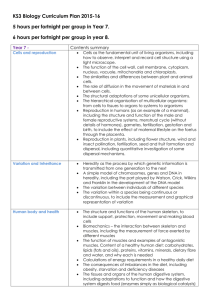
2.2.5 Respiration FMQuiz Homework Solution
advertisement

Follow-Me-Quiz Homework Solution Book Declan Finlayson Page 1 of 62 Contents 1.1.3 Sc. Method & Expt FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................................ 4 1.2.1 Life – 1.3.3 Food Structure Homework Solution ............................................................................. 6 1.3.3 Biomolecular Structures FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................................................... 7 1.3.4 Biomolecular Components FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................... 8 1.3.5 +1.3.6 Role of Biomolecules FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................. 9 1.3.8 Biomolecules & Minerals FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................................................ 10 1.4.2 - 1.4.6 Ecology FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................................................................. 11 1.4.6 - 1.4.7 Ecology FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................................................................. 12 1.4.8 + 9 Nutrient Recycling & Human Impact FMQuiz Homework Solution ........................................ 13 1.4.10 - 12 Relationships & Population Dynamics FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................... 14 1.5 Ecosystem Study FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................................................................ 15 2.1 Cell Structure & Microscopy 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution ........................................................... 16 2.1 Cell Structure & Microscopy 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution ........................................................... 17 2.2.3 Enzymes FMQuiz Homework Solution .......................................................................................... 18 2.2.4 Photosynthesis 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................................. 19 2.2.4 Photosynthesis 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................................. 20 2.2.5 Respiration FMQuiz Homework Solution ...................................................................................... 21 2.2.6 Movement through Membranes FMQuiz Homework Solution .................................................... 22 2.2.7 Enzymes FMQuiz Homework Solution .......................................................................................... 23 2.2.9 Photosynthesis FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................................................................ 24 2.2.10 Respiration FMQuiz Homework Solution .................................................................................... 25 2.3 Cell Continuity FMQuiz Homework Solution .................................................................................... 26 2.5.1 - 4 Genetics 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution .................................................................................. 27 2.5.5 + 2.5.15 Genetics 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution ......................................................................... 28 2.5.6 - 2.5.8 Genetics 3 FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................................ 29 2.5.9 - 2.5.14 Genetics 4 FMQuiz Homework Solution .......................................................................... 30 3.1.1 - 3.1.3 Monera Homework Solution .............................................................................................. 31 3.1.4 Fungi 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution............................................................................................. 32 3.1.4 Fungi 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution............................................................................................. 33 3.1.4, 6, 10 Fungi, Protista, Growth Curves FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................. 34 3.2.1 Plant Structure 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................................. 35 3.2.1 Plant Structure 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................................. 36 3.2.2 Blood & Circulation 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution ...................................................................... 37 3.2.2 Blood & Circulation 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution ...................................................................... 38 3.2.3 + 4 Blood Cells & Heartbeat FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................ 39 3.3.1 + 2 Nutrition & Storage in Plants FMQuiz Homework Solution .................................................... 40 Page 2 of 62 3.3.3 + 4 Human Nutrition & Digestion 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................................ 41 3.3.4 Digestion 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution ...................................................................................... 42 3.3.4 Digestion 3 FMQuiz Homework Solution ...................................................................................... 43 3.3.5 Blood Transport of Nutrients FMQuiz Homework Solution .......................................................... 44 3.4.1 - 3.4.4 Homeostasis, Plant Exchange, Breathing System FMQuiz HW Solution ........................... 45 3.4.4 + 3.4.7 Breathing System FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................................................ 46 3.4.6 Excretory System 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution ......................................................................... 47 3.4.6, 8 Excretory System 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution ..................................................................... 48 3.5.2 Plant Responses FMQuiz Homework Solution .............................................................................. 49 3.5.3 + 7 Defence System FMQuiz Homework Solution ........................................................................ 50 3.5.3 Endocrine & Musculoskeletal System FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................ 51 3.5.3 Eye & Ear FMQuiz Homework Solution ......................................................................................... 52 3.5.3 Musculoskeletal System FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................................................. 53 3.5.3 Nervous System FMQuiz Homework Solution .............................................................................. 54 3.6.1 Asexual, Flower Structure, Gamete Formation FMQuiz Homework Solution .............................. 55 3.6.1 Dormancy & Germination FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................... 56 3.6.1 Fruit Formation & Dispersal FMQuiz Homework Solution............................................................ 57 3.6.1 Pollination & Fertilisation FMQuiz Homework Solution ............................................................... 58 3.6.2 Birth, Breastfeeding, Infertility & Birth Control FMQuiz Homework Solution .............................. 59 3.6.2 Structures & Hormones FMQuiz Homework Solution .................................................................. 60 3.6.4 + 5 Embryo Development & Menstrual Cycle FMQuiz Homework Solution ................................ 61 Page 3 of 62 1.1.3 Sc. Method & Expt FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is a hypothesis? A. Educated guess based on observation A. Hypothesis can develop into a theory or explained Q. True or False. In science, a hypothesis is an educated guess based on observations. A. TRUE Q. What might an hypothesis develop into? A. A Theory Q. Why is a control important in an experiment? A. Standard for comparison Q. State two ways in which the results of an experiment may be presented. A. Table / Graph Q. Explain the term Data in relation to the scientific method. A. Measurements or observations or information gathered from an experiment Q. Explain the term Replicate in relation to the scientific method. A. Make a duplicate(s) of an experiment or procedure Q. Explain the importance of double-blind testing in scientific experimentation. A. Avoidance of bias Q. Why is it a good idea to repeat an experiment? A. To verify results /(statistical) reliability/ minimise error Q. True or False. In experiments the factor that is changed is called the dependent variable. A. FALSE Q. When investigating the effect of a mineral on wheat growth. Suggest a reason why the seeds used were all taken from one parent plant. A. To minimise (genetic) variation Q. Explain the term Theory in relation to the scientific method. A. A proven hypothesis Q. The compost was sterilised at the start of the investigation. Suggest a way in which this may have been achieved. A. Heat (or method of heating) or named chemical or irradiation Q. As a result of observations a scientist may formulate a … A. Hypothesis Q. After formulating an hypothesis a scientist will then progress her investigation by devising a series of … and then carefully analysing the resulting … A. Experiments / Data Q. Suggest where a scientist may publish the results of her investigations A. Scientific journal / Internet Q. Why were the young wheat plants divided into two equal groups? A. As experiment and control Q. During the investigation the two groups of plants were kept under identical conditions. Why was this? A. To have only one variable (or explained) Q. Name two conditions you think they would have kept constant during the investigation. A. Temperature / Light / pH / CO2 / humidity / other minerals / H2O Q. In relation to the scientific method, explain the term experiment. A. Test of hypothesis or test of prediction Q. Why was the investigation repeated several times before the results were published? A. To ensure (statistical) reliability Q. In relation to the scientific method, explain the term theory. A. Hypothesis supported (by experiment) Q. How does a hypothesis differ from a theory? Q. What is meant by metabolism? A. All the chemical reactions taking place in living organisms Page 4 of 62 Page 5 of 62 1.2.1 Life – 1.3.3 Food Structure Homework Solution Q. What is meant by metabolism? A. The sum of all the chemical reactions in an organism OR catabolism + anabolism Q. What is a disaccharide? A. Carbohydrate made of two sugar units or monosaccharides Q. A sex cell is also known as a ... A. Gamete Q. Removal from the body of the waste products of metabolism is called ... A. Excretion Q. Give two reasons why living things need energy. A. For movement / heat / making products / internal transport / etc. Q. Name a polysaccharide that has a different role to cellulose. A. Starch, glycogen Q. Describe a test for a named polysaccharide. A. Iodine & Blue/Black colour Q. True or False. Nutrition is the way living organisms get rid of waste. A. FALSE Q. Name the reagent(s) used when testing for a protein. A. Biuret OR Copper sulphate and sodium hydroxide Q. Give an example of a trace element in the human diet. A. Iron OR copper OR zinc Q. What is the initial colour of the reagent(s) used in the test for a reducing sugar? A. Blue Q. In relation to the human diet, what is meant by a trace element? A. Small amount needed Q. True or False. Nitrogen is a trace element. A. FALSE Q. Does the test for reducing sugar require heat? A. Yes Q. What colour indicates a positive result in the test for reducing sugar? A. Brick red Q. True or False. Polysaccharide molecules contain many sugar units. A. TRUE Q. What is the initial colour of the reagent(s) used in the test for a protein? A. Blue Q. True or False. Glucose is a monosaccharide. A. TRUE Q. Does the test for protein require heat? A. No Q. Calcium and iron are examples of essential … A. Minerals / elements Q. Name a monosaccharide. A. Glucose, lactose, ribose, deoxyribose Q. Cellulose is a polysaccharide. What is it formed from? A. Glucose or monosaccharides units Q. What colour indicates a positive result in the test for protein? A. Violet Q. What is the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in a carbohydrate? A. 2:1 Page 6 of 62 1.3.3 Biomolecular Structures FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Vitamins are either water-soluble or __________-soluble. A. Fat Q. Cellulose is a polysaccharide. Explain the term polysaccharide. A. Made up of many sugar units Q. Fats are composed of oxygen, hydrogen and ... A. Carbon Q. When an iodine solution is added to a food sample and remains red-brown in colour, ___________ is absent. A. Starch Q. When two monosaccharides unite they form a ... A. Disaccharide Q. Vitamin … is an example of a water-soluble vitamin. A. Vitamin C / Vitamin B Q. State a use of the Biuret test (copper sulphate and sodium hydroxide solutions) in the biology laboratory A. Test for protein Q. Give an example of a fat-soluble vitamin. A. Vitamin A or D or E or K Q. State a use of Benedict’s (or Fehling’s) test in the biology laboratory. A. Test for reducing sugar Q. Give an example of a reducing sugar. A. Glucose or Maltose Q. In the test for reducing sugar which of the following is correct? 1. No heat needed; 2. Heat but do not boil; 3. Boil. A. Heat but do not boil Q. 1. Name a monosaccharide. 2. Give its formula. 3. Name a polysaccharide that can be formed from it. A. 1. Glucose; 2. C6H12O6; 3. Starch Q. State a good source of a fat-soluble vitamin in the human diet. A. A – Carrots, D – Dairy products, E – Oils, nuts, K – Liver Q. Fats are composed of fatty acids and … A. Glycerol Q. What name is given to fats that are liquid at room temperature? A. Oils Q. Name a chemical element found in proteins that is not found in carbohydrates. A. Nitrogen Q. State two good sources of protein in the human diet. A. Lean meat, fish, eggs Q. Proteins are digested to simpler substances. What are these simpler substances called? A. Amino acids Q. Give an example of a polysaccharide. A. Cellulose or Starch or Glycogen or Chitin Q. Biomolecules of the general formula Cx(H2O)y are examples of … A. Carbohydrate or Sugar or Saccharide Q. In carbohydrates, which two elements are in the ratio 2:1? A. Hydrogen and Oxygen Q. Name the elements found in Carbohydrate. A. Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen Q. Name the elements found in Fat. A. Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen Q. Apart from Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen name one other element that may be present in protein. A. Sulphur Page 7 of 62 1.3.4 Biomolecular Components FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Give two good sources of protein in the human diet. A. Lean meat, fish, eggs A. Contains N or contains –NH2 or contains – COOH (group) Q. How may one fat differ from another, in terms of chemical composition? A. Different fatty acids or some are phosphorylated (have phosphate) Q. Name a test or the solution(s) that is (are) used to detect protein in a food source. A. Biuret or Copper sulphate and sodium hydroxide Q. True or False. Lipids are made of amino acids. A. FALSE Q. Glucose is an example of which type of biomolecule? A. Carbohydrate / monosaccharide / sugar Q. True or False. All vitamins are fat soluble. A. FALSE Q. The same elements are found in carbohydrates and fats. Name these elements. A. Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen Q. True or False. Eggs are a good source of fat in the diet. A. TRUE Q. State one way in which carbohydrates differ from fats. A. Hydrogen and oxygen not in 2:1 ratio Q. What food in a student’s lunch (a tuna and sweetcorn sandwich, an apple and a bag of crisps) is a good source of protein? A. Tuna Q. How do phospholipids differ from other lipids? A. They have one of the three fatty acids replaced with a phosphate group Q. What food in a student’s lunch (a tuna and sweetcorn sandwich, an apple and a bag of crisps) is a good source of fat? A. Crisps / “Butter” (on bread) Q. State one way in which an oil differs from a fat. A. Oil is liquid at room temperature or fat is solid or oils are unsaturated or explained Q. Suggest one food in the lunch (a tuna and sweetcorn sandwich, an apple and a bag of crisps) that contains a water-soluble vitamin. A. Bread or Sweetcorn / Apple Q. What is a triglyceride? A. Fat (or lipid or oil) unit (or molecule) or glycerol and three fatty acids Q. Name one water-soluble vitamin. A. B or C Q. For which purpose did you use Brown paper or Sudan III in food testing? A. Test for fat (or lipid or oil) Q. Proteins always contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and … A. Nitrogen Q. How many common amino acids are found in proteins? A. 20 Q. An example of a fat-soluble vitamin is … A. A or D or E or K Q. State a use for a water bath in biological investigations. A. Keep temperature constant / to vary temperature / denaturing enzyme / heating Q. A solution used to test for the presence of glucose is … A. Benedict’s or Fehling’s Q. Was heat necessary to test a food for starch? A. No Q. Give one way in which an amino acid differs from a monosaccharide, in terms of chemical composition. Page 8 of 62 1.3.5 +1.3.6 Role of Biomolecules FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What term is used to describe a cellular reaction in which large molecules are broken down to smaller ones? A. Catabolic Q. Give an example of a protein that has a structural role. A. Keratin or myosin or elastin or collagen Q. Give an example of a catabolic reaction in an animal. A. Respiration or digestion or deamination Q. Give an example of an anabolic reaction in a plant. A. Photosynthesis or protein synthesis or replication Q. Is energy release a feature of anabolic or catabolic reactions? A. Catabolic Q. What is the role of the polysaccharide starch or glycogen? A. Energy storage Q. Where precisely in a plant cell would you expect to find cellulose? A. Cell wall Q. Give a role of lipids in cells. A. Component of cell membranes or phospholipid or lipoprotein or energy storage Q. Is protein synthesis an anabolic or catabolic process? A. Anabolic Q. Name the protein found in human hair, nails and skin. A. Keratin Q. Is the conversion of ADP to ATP an anabolic or catabolic process? A. Anabolic Q. Are the reactions in which product molecules are larger than substrate molecules anabolic or catabolic processes? A. Anabolic Q. Name a monosaccharide and state a role for it in living organisms. A. Glucose or lactose or ribose / Energy Q. Cellulose is a polysaccharide. What is it formed from? A. Glucose or monosaccharide molecules Q. State two functions of fats in the human body. A. Insulation / energy / storage / cell membrane / structural Q. Give one structural function of proteins in living organisms. A. Growth and repair of muscle (myosin), hair (keratin), nails, etc. Q. Give one metabolic function of proteins in living organisms. A. Enzymes or immunity (antibodies) Q. An example of a water-soluble vitamin is … A. B or C Q. State a role for cellulose in living organisms. A. Cell wall formation Q. True or False. Anabolism is the breaking down of large molecules. A. FALSE Q. Name a polysaccharide that has a different role to cellulose. A. Starch or Glycogen Q. Cellulose is an example of a structural … A. Carbohydrate or Polysaccharide Q. What reagent or chemicals did you use to test for protein? A. Biuret or Copper sulphate and sodium hydroxide Q. In the test for protein what colour change occurred if protein was present? A. Purple or violet. Page 9 of 62 1.3.8 Biomolecules & Minerals FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Name two monosaccharides. A. Glucose and ribose Q. Give a function of carbohydrates other than a structural one. A. Energy or storage Q. Name a disorder associated with a deficiency of Vitamin A in the human diet. A. Night blindness Q. Give one role for magnesium in plants. A. Chlorophyll formation Q. To which group of biomolecules do enzymes belong? A. Proteins Q. Name two minerals required by the human body. A. Iron & Calcium Q. Name a fat-soluble vitamin. A. A or D Q. What is the function of iron in the body? A. Needed for haemoglobin formation Q. Name a disorder associated with a deficiency of Vitamin C in the human diet. A. Scurvy Q. What is the function of calcium in the body? A. Needed for bone and teeth development Q. Give two functions of water in a living organism. A. Solvent / transport / reaction medium / reactant / turgidity Q. State a good source of Vitamin A in the human diet. A. Carrots Q. Name a disorder associated with a deficiency of Vitamin D in the human diet. A. Rickets Q. True or False. Nitrogen is a trace element. A. FALSE Q. True or False. Polysaccharide molecules contain many sugar units. A. TRUE Q. State a good source of Vitamin D in the human diet. A. Dairy products Q. State two functions of fats in the human body. A. Insulation / energy storage / cell membrane / myelin sheath Q. State a role of carbohydrates other than a structural one. A. Energy store or release Q. True or False. Glucose is a monosaccharide. A. TRUE Q. What is the initial colour of the reagent(s) used in the test for a protein? A. Blue Q. What colour indicates a positive result in the test for reducing sugar? A. Brick red Q. State one function of protein in the human body. A. Growth, repair, enzymes Q. What term is given to a protein which changes metabolic rate? A. Enzyme Q. What colour indicates a positive result in the test for protein? A. Violet Page 10 of 62 1.4.2 - 1.4.6 Ecology FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is an ecosystem? A. A community of living organisms interacting with one another and their environment Q. Explain the term biosphere. A. The part of the planet where life occurs A. The position of an organism in a food chain Q. What is a food web? A. Interconnected food chains or more than one species at each trophic level Q. True or False. Herbivores normally live long lives. A. False Q. What is a habitat? A. The place where an organism lives Q. In ecological studies what are abiotic factors. A. Non-living features that influence the distribution of organisms Q. Organisms capable of making their own food are known as … A. Producers Q. Where in a food chain are primary producers found? A. First (level) Q. Explain the term edaphic. A. Relating to the soil Q. True or False. The term abiotic refers to the living factors in an ecosystem. A. FALSE Q. Give an example of an abiotic factor that influences the distribution of a named plant in an ecosystem. A. e.g. Climatic, edaphic, etc. Q. Give an example of an edaphic factor. A. Particle size or Soil type or pH or Air content or Water content or Mineral content or Humus content Q. In ecological studies what are biotic factors. A. Living features that influence the distribution of organisms Q. What is meant by a pyramid of numbers? A. The numbers of organisms at each trophic level Q. Give an example of a biotic factor that influences the distribution of a named animal. A. Predator (fox) influences distribution of rabbits Q. What term is used by ecologists to describe the organisms that form the base of a pyramid of numbers? A. Producers or autotrophs Q. Why are most food chains short i.e. only consist of a few trophic levels? A. Large energy loss from one level to next or small energy transfer Q. What term is used to describe organisms that feed on primary producers? A. Primary consumer(s) or herbivore(s) Q. What deduction may be made if the organisms at the start of the chain are less numerous than those that feed upon them? A. Producers are large or primary consumers are parasites Q. Can a parasite be the first member of a food chain? A. No. They are not producers Q. Energy enters food chains in the form of light. In which form do you think most energy is lost from food chains? A. Heat Q. Name the process that takes place in plants in which the sun’s energy is converted to a usable form. A. Photosynthesis Q. What is the source of energy for the earth’s ecosystems? A. The sun Q. In ecology what is meant by a trophic level? Page 11 of 62 1.4.6 - 1.4.7 Ecology FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What substance do plants possess that allows them to carry out photosynthesis? A. Chlorophyll Q. Name a primary producer. A. Any autotroph, i.e. plant that makes food Q. Position in a pyramid of numbers. A. Trophic level Q. If all the tertiary consumers were removed (e.g. by disease) what would happen to the secondary consumers? A. Their number would increase Q. What are secondary consumers? A. An organism which feeds on the primary consumer Q. Name one herbivore. A. Caterpillar, Mouse, Greenfly, etc. Q. Explain the term consumer. A. An organism that eats another organism / heterotroph Q. What would happen to the number of caterpillars if all the thrushes died? A. Increase in number Q. What is a pyramid of numbers? A. The numbers of organisms at each trophic level Q. Name one carnivore. A. Hawk, Spider, Ladybird, etc. Q. What does the animal plankton feed on? A. Plant plankton (phytoplankton) Q. True or False. Grazing food chains begin with animals. A. FALSE Sparrow hawk. The primary consumer in this food chain is … A. Caterpillar Q. Name one omnivore. A. Human, thrush, etc. Q. Hawtho Sparrow hawk. If the sparrow hawks’ numbers increase, the number of blue tits may … A. Decrease Sparrow hawk. The hawthorn leaves represent the … A. Producer / Autotroph Q Sparrow hawk. Name a carnivore from this food chain. A. Blue tit / Sparrow hawk Q. The number of trophic (feeding) levels in a food chain is limited by the small transfer of … from one level to the next. A. Energy Q. Explain the term niche. A. The functional role of an organism in an ecosystem Q. Explain the term edaphic. A. Relating to the soil Q. What is the biosphere? A. The part of the planet where life occurs Q. Energy enters food chains in the form of light. In which form do you think most energy is lost from food chains? A. Heat Q. What term is used to describe organisms that feed on primary producers? A. Primary consumer(s) or herbivore(s) Q. Organisms capable of making their own food are known as … A. Producers Page 12 of 62 1.4.8 + 9 Nutrient Recycling & Human Impact FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is meant by nitrogen fixation? A. The conversion of nitrogen into nitrates Q. State one conservation practice from agriculture. A. e.g. control of fertiliser usage Q. Name an important group of biomolecules that plants make from nitrates. A. Proteins Q. The term used to describe micro-organisms and other organisms that return nutrients to the environment by decay is … A. Decomposers Q. Explain the term ectoparasite. A. Organism living on host (or explained) / causing damage Q. Suggest two reasons for conserving wild species. A. Recreational / food supplies / possible sources of drugs / prevent extinction / biodiversity Q. State one conservation practice from fisheries. A. e.g. control of mesh size Q. Outline the problems associated with the disposal of waste. A. Toxicity / non-biodegradable / pollute rivers / availability of land-fill / incineration causes toxins Q. What is meant by nitrification? A. The process of converting ammonia into nitrites and/or nitrites to nitrates Q. Farmers add nitrates as fertilizers to the soil, but not when heavy rain is forecast. Why not? A. Fertiliser may be washed off the land / eutrophication Q. Name a group of organisms involved in nitrogen fixation. A. Bacteria / Monera / Lichens/ Clover / Legumes Q. Explain the term decomposition. A. Decaying / rotting Q. State one conservation practice from forestry. A. e.g. plant trees Q. Suggest two ways of minimising waste. A. Reduce or Recycle or Re-use Q. Give an example of the use of microorganisms in waste management. A. Landfill sites / sewage treatment plants / digesters / compost heaps Q. Give an advantage for the incineration of domestic waste. A. Amount of waste greatly reduced or Useable heat or Reduced landfill Q. Why are elements recycled in nature? A. Limited supply or words to that affect or reused Q. What is meant by pollution? A. The harmful addition to the environment by humans Q. Suggest why continual monitoring of the environment is valuable. A. To detect change(s) early or To remedy effect of change or To detect levels of pollutants Q. Give an example of a human activity that results in the pollution of air. A. e.g. burning fossil fuels Q. Give a disadvantage for the incineration of domestic waste. A. Harmful products produced Q. Explain conservation in relation to wild plants and animals. A. The protection, preservation and wise management of endangered plants and animals Q. Give an example of a human activity that results in the pollution of water. A. e.g. fertiliser run-off Q. Why is waste management becoming an increasingly difficult problem? A. Increasing population & consumption; Too little recycling; Shortage of landfill sites Page 13 of 62 1.4.10 - 12 Relationships & Population Dynamics FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Comment on the relative sizes of an individual producer and an individual primary consumer in a pyramid of numbers. A. Producer larger or consumer smaller Q. Where one organism lives in or on a second species, feeding on it and causing it harm is called … A. Parasitism Q. What is a predator? A. An animal which kills and eats another animal for food Q. Name a factor, other than competition, that controls wild populations. A. Disease or Parasitism or Predation or Hunting Q. What does an ecologist mean by competition? A. When two or more organisms fight for a resource that is in short supply Q. Mortality levels resulting from infection by a particular virus tend to decline over the years. Why? A. Host immunity develops or natural selection or vaccination Q. What term is used to describe an animal that is killed and eaten? A. Prey Q. True or False. Competition is generally more intense between members of the same species than between members of different species. A. True Q. Suggest possible effects of the disappearance of a plant species on the populations of other plants and animals in the ecosystem. A. Consumers of this plant may decrease; numbers of other plant species may increase; new species may appear to fill the niche. Q. What is contest competition? A. One organism loses the resource Q. What term do ecologists use to describe an animal which kills and eats other animals? A. Predator Q. If the population of prey declines suggest two possible consequences for the predators. A. Starvation or death; Migration; Decline in population; Change food source Q. Suggest a role for parasites in the overall scheme of nature. A. Population control Q. Name a predator and give one adaptive technique. A. Fox, Speed and sharp canine teeth Q. Suggest an effect on human population of an increased availability of contraception. A. Decrease (no increase) in population; Improved social conditions; Reduced STIs Q. All the members of a species living in an area is referred to as … A. Population Q. Give four factors that influence the size of the human population. A. Famine; Birth control; War; Disease; Birth rate; Death rate or longevity; Degree of medical care Q. Mortality levels tend to be higher in the migratory animal species. Why? A. Hazards encountered on migration Q. What is scramble competition? A. Each organism gets some of resource Q. Apart from competition, state another factor that limits population growth. A. Disease or Parasitism or Food availability or Pollution Q. Give an example of predation by naming a predator and its prey. A. e.g. Fox, Chicken, Hawk, Rabbit, etc. Q. Marking an animal might endanger it. Why? A. More conspicuous to predators or Social outcast or Toxic marker Q. The population of a predator did not decline following a big reduction in the population of its main prey. Why? A. Different prey Q. A relationship between two organisms in which both benefit is called … A. Mutualism or Symbiosis Page 14 of 62 1.5 Ecosystem Study FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. In ecology the term flora refers to … A. Plants Q. Name one human activity that causes pollution. A. Fertiliser run-off Q. How were you able to identify the different plants in the ecosystem that you investigated? A. Key(s) or illustrations or guide book Q. Name pieces of apparatus used to collect animals from an ecosystem. A. Pooter; Beating tray; Pitfall trap; Net; etc. Q. State one role of microorganisms in waste management. A. To consume waste Q. Explain the term conservation. A. Management of ecosystems Q. In ecology the term fauna refers to … A. Animals Q. Name two groups of micro-organisms in the soil which are responsible for decomposition. A. Bacteria and Fungi Q. In relation to a study of an ecosystem explain what a qualitative survey is. A. What is present Q. Give two possible sources of error that may have arisen in the course of your survey of plant species. A. Misidentification; Non-random quadrat distribution; Not enough times; Miscount Q. In relation to a study of an ecosystem explain what a quantitative survey is. A. How many present Q. What is a quadrat used for in your ecology studies? A. Quantitative surveys e.g. distribution, frequency, cover Q. What is meant by nitrogen fixation? A. The conversion of nitrogen into nitrates Q. Farmers add nitrate fertilizers to the soil but not if heavy rain is forecast. Why not? A. Eutrophication Q. Name an important group of biomolecules that plants make from nitrates. A. Proteins Q. Explain the term ectoparasite. A. Organism living on host causing damage Q. Organisms that return nutrients to the environment by decay are called … A. Decomposers Q. Name one animal from the ecosystem you have studied and describe one way in which it is adapted to its habitat. A. e.g. Grasshopper / Green colour Q. What is meant by nitrification? A. The process of converting ammonia into nitrites and/or nitrites to nitrates Q. What is the function of the nitrogen cycle? A. To make nitrogen available for use by organisms Q. What is meant by pollution? A. Any harmful addition to the ecosystem Q. List two ways of minimising waste. A. Reduce; Reuse; Recycle Q. Name a group of organisms involved in nitrogen fixation. A. Bacteria; Monera; Lichens; Clover; Legumes Q. State problems associated with waste disposal in Ireland. A. Finding land for landfill sites; Litter; Pollution Page 15 of 62 2.1 Cell Structure & Microscopy 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. State a use for iodine in the biology laboratory. A. Starch detection; Staining cells Q. A microscope has an eyepiece lens marked ×10 and an objective lens marked ×20. What is the total magnification of the image? A. 200 Q. Name a powerful type of microscope that is used to show cell ultrastructure. A. Electron microscope Q. True or False. If the eyepiece lens of a microscope is marked X10 and the objective lens is marked X3, the total magnification is X13. A. FALSE Q. If the magnification of the eyepiece of a microscope is X 10 and the magnification of the objective lens is X 30, what magnification results when a slide is viewed? A. 300 Q. For what purpose did you use a Cover slip in the course of your practical activities? A. To examine a specimen / to reduce evaporation / to hold specimen in place / to protect lens Q. True or False. The microscope lenses closest to the stage are the eyepiece lenses. A. FALSE Q. Where in a cell would you expect to find phospholipids? A. Membrane Q. What term is used to describe bacterial cells? A. Prokaryotic Q. State two features of plant cells visible under a light microscope that indicate that they are typical plant cells. A. Cell wall / chloroplasts / large vacuoles / starch granules / shape Q. What cellular organelle is the site of energy release? A. Mitochondrion Q. What cellular organelle is the site of water storage? A. Vacuole Q. Is the cell of Amoeba prokaryotic or eukaryotic? A. Eukaryotic Q. What component of a cell allows osmosis to occur? A. Cell membrane Q. What is a selectively permeable (semipermeable) membrane? A. Allows some molecules through Q. Name two features of a plant cell which are not normally associated with an animal cell. A. Cell wall / vacuole / chloroplast / definite shape Q. What is usually found in the vacuole? A. Sap or component e.g. water, glucose Q. State a function of a Ribosome. A. Protein synthesis Q. Name a carbohydrate found in the cell wall. A. Cellulose Q. State a function of the cell membrane. A. Selectively permeable Q. When preparing an animal cell for examination under a microscope, name the stain that you used. A. Methylene blue Q. Give two characteristic features of eukaryotic cells. A. Nucleus, Membrane-bound organelles Q. The liquid in which chemical reactions take place in the cell is … A. Water or cytoplasm Q. True or False. Plant cells have chloroplasts; animal cells do not have chloroplasts. A. TRUE Page 16 of 62 2.1 Cell Structure & Microscopy 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. True or False. Cell membranes let only some molecules pass through. A. TRUE Q. State one feature that would allow you to identify a eukaryotic cell. A. Nucleus, Membrane-bound organelles Q. What is an enzyme? A. A biological catalyst Q. What term is used to describe cells similar to bacterial cells? A. Prokaryotic Q. For what purpose did you use Methylene blue in the course of your practical activities? A. To stain animal cells Q. Where in a plant cell does photosynthesis take place? A. Chloroplast Q. True or False. Animal cells do not have membranes. A. FALSE Q. Are fungi prokaryotic or eukaryotic? A. Eukaryotic Q. True or False. Human chromosomes are found in the nucleus. A. TRUE Q. List two differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. A. Plant cells have a wall, large vacuole, chloroplast Q. State the precise location of the cell membrane in plant cells. A. Immediately inside the cell wall Q. True or False. If the eyepiece lens of a microscope is marked X10 and the objective lens is marked X3, the total magnification is X13. A. FALSE Q. Where in a cell would you expect to find phospholipids? A. Membrane Q. State a function a Ribosome. A. Protein synthesis Q. True or False. Chloroplasts contain DNA. A. TRUE Q. True or False. The microscope lenses closest to the stage are the eyepiece lenses. A. FALSE Q. With what type of cell do you associate membrane-bound organelles? A. Eukaryotic Q. Why is a cover slip placed on a slide? A. To prevent drying out or to protect lens or easier to view or keeps cells in place Q. Give two functions of the cell membrane. A. Holds cell together / selectively permeable / displays antigens Q. State a function of the cell membrane. A. Selectively permeable Q. Which organelle is known as “the powerhouse of the cell”? A. Mitochondrion Q. Why does the nucleus of a cell have many pores? A. To allow passage of materials Q. Is the cell of Amoeba prokaryotic or eukaryotic? A. Eukaryotic Q. The release of energy is associated with what cellular organelle? A. Mitochondrion Page 17 of 62 2.2.3 Enzymes FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is meant by the term metabolism? A. All the chemical reactions in living cells Q. Give the term for the substance that results from the action of an enzyme on its substrate. A. Product Q. For what is ATP an abbreviation? A. Adenosine Triphosphate Q. In relation to an enzyme, explain the term optimum activity. A. Working at maximum rate Q. To which group of molecules do enzymes belong? A. Proteins Q. In an experiment that you carried out to investigate the effect of pH on the rate of enzyme action, explain how you varied the pH. A. Used buffers Q. What is a bioreactor? A. A Vessel in which products are made by cells or organisms. Q. What is meant by an enzyme? A. Organic protein catalyst Q. Explain the term bioprocessing. A. Using micro-organisms or enzymes to make product(s) Q. Name the compound from which the immobilising beads are formed in the laboratory. A. Sodium alginate Q. In an experiment to investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of action of an enzyme, how did you vary the temperature? A. Water bath or ice or thermostat Q. What is meant by immobilisation? A. Enzyme trapped in beads or gel so that it will react with, but not mix with, its substrate Q. In an expt. to investigate the effect of temp on the rate of action of an enzyme, how did you measure the rate of the enzyme’s action? A. By the volume of suds produced Q. Name a factor that influences the activity of an enzyme. A. Temperature or pH Q. What name is given to the substance that an enzyme acts on? A. Substrate Q. State one advantage of using an immobilised enzyme in a bioreactor. A. Enzyme can be recovered Q. True or False. Immobilised enzymes can act as catalysts. A. TRUE Q. Name a substance that is used to immobilise enzymes. A. Sodium alginate Q. Comment on the shape of enzyme molecules. A. Fits substrate / active site / folded /can change shape Q. State a use for Buffer solution in the biology laboratory. A. To keep pH constant Q. The action of amylase on starch is a catabolic reaction. Explain the underlined term. A. Breakdown of large molecules into smaller ones Q. Apart from C, H and O, there is one other element always present in the building blocks of enzymes. Name that element. A. Nitrogen Q. Suggest one reason why enzymes are not found in body soap or shampoo. A. May damage skin Q. Distinguish between Enzymes and Hormones A. A catalyst and a chemical messenger Page 18 of 62 2.2.4 Photosynthesis 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is the final destination of excited electrons in Pathway 1 of the light-dependent stage? A. Chlorophyll Q. What is carried into the dark phase as raw material for glucose manufacture? A. Hydrogen Q. Name the structure that is controlled by guard cells. A. Stomata Q. This is a possible destination for oxygen released during the light phase. A. Mitochondria Q. What is the waste product of Pathway 2? A. Oxygen Q. What is the energy source used during the light-independent phase? A. ATP Q. The splitting of water using light energy is known as … A. Photolysis Q. This is one of the limiting factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis. A. Temperature Q. Name the carrier of electrons into the lightdependent phase. A. NADP Q. What is the energy source of the light phase? A. Sunlight Q. What element is necessary for chlorophyll formation? A. Magnesium Q. What is the addition of a phosphate to ADP forming ATP, using light energy called? A. Photophosphorylation Q. Name the disc-shaped membranes found in the chloroplasts covered with chlorophyll molecules. A. Grana Q. Name the site of photosynthesis A. Chloroplast Q. What term that describes photosynthetic and chemosynthetic organisms? A. Autotrophs Q. Name the ion necessary for the production of ATP? A. Phosphate Q. One molecule of... is produced for every six molecules of CO2. A. Glucose Q. Name the layer of leaf tissue with the highest density of chloroplasts. A. Palisade Q. Name the aquatic plant that is usually used in photosynthesis experiments? A. Elodea Q. What are the sources of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? A. Respiration; Combustion (burning) Q. How could you artificially increase the rate of photosynthesis? A. Increase lighting, carbon dioxide or heating Q. As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis ... A. Increases Q. As light intensity decreases, the rate of photosynthesis ... A. Decreases Q. How would you vary the light intensity in an experiment? A. Adjust lamp distance or bulb wattage Page 19 of 62 2.2.4 Photosynthesis 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. How would you measure the rate of photosynthesis? A. Count the number of bubbles per minute OR Use a data logger Q. What is the equation for photosynthesis? 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light + Chlorophyll C6H12O6 + 6O2 Q. Give the location of cells in the leaf which contain most chlorophyll A. Near upper surface Q. What term is used to describe the type of nutrition in plants? A. Autotrophic Q. What is the equation for aerobic respiration? C6H12O6 + 6O2 Energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O Q. Name the organelle where chlorophyll is found. A. Chloroplast Q. What is the fate of water molecules in photosynthesis? A. Photolysis or Split into Protons (H+), electrons and Oxygen Q. What is the fate of the protons (H+) that result from the splitting of water? A. Released into pool and combine with CO2 to form glucose Q. Name some sources of carbon dioxide in pond water. A. Respiration (plant, animal, bacterial); Decomposition; From air Q. What is the fate of the electrons that result from the splitting of water? A. Passed to chlorophyll Q. Where does carbon dioxide enter a leaf? A. Stoma Q. What is the primary role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis? A. To trap or use light Q. Name the part of the leaf where most photosynthesis occurs. A. Palisade layer Q. During photosynthesis oxygen is produced from ... A. Water Q. The following are needed for photosynthesis carbon dioxide and ... A. Water Q. During which stage of photosynthesis is oxygen produced? A. Light dependent stage Q. What is the fate of oxygen produced during photosynthesis? A. Respiration; Diffuses to atmosphere Q. Name the gas used (needed) for photosynthesis. A. Carbon dioxide Q. Name the part of the plant where most photosynthesis takes place. A. Leaf Q. Why is photosynthesis important? A. Supplies O2 and food for other organisms Q. Why do cells in the palisade layer contain most chloroplasts? A. Usually closer to the light Q. What gas is produced during photosynthesis? A. Oxygen Q. Name the energy source for photosynthesis. A. Sun or light Q. As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis ... A. Increases Page 20 of 62 2.2.5 Respiration FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Yeast cells produce ethanol in fermentation. Is this process affected by temperature? Explain your answer. A. Yes. Rate of enzyme action affected by temperature Q. Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. A. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen or anaerobic respiration does not Q. Write a balanced equation to summarise aerobic respiration. A. C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Q. Where in the cell does the first stage of respiration occur? A. Cytoplasm Q. To what is pyruvic acid converted under anaerobic conditions in yeast? A. Ethanol and CO2 Q. Under aerobic conditions pyruvic acid is converted to an acetyl group and in the process a small molecule is released. Name this molecule. A. Carbon dioxide Q. In respiration acetyl co-enzyme A enters a cycle of reactions. What name is given to this cycle? A. Kreb’s cycle Q. To what is pyruvic acid converted under anaerobic conditions in a human muscle cell? A. Lactic acid Q. Is oxygen required for the first stage of respiration? A. No Q. Give two industrial uses of the anaerobic respiration of yeast. A. Baking, brewing Q. To what might pyruvic acid be converted, in the absence of oxygen? A. Lactic acid or Ethanol + CO2 Q. What is the final product of the first stage of respiration under aerobic conditions? A. Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Q. Pyruvic acid is used for the second stage of respiration. Where does this second stage take place? A. Mitochondrion Q. If conditions in a human muscle cell become anaerobic pyruvic acid is converted to another substance. Name this other substance. A. Lactic acid Q. When lactic acid builds up in the blood, a person is in oxygen debt. This debt must eventually be paid. Suggest how the debt is paid. A. Increased breathing (deeper or faster) or oxidation of lactic acid Q. What is the first stage process of respiration called? A. Glycolysis Q. In the first stage of respiration there is a release of ATP as glucose is converted to another substance. Name this other substance. A. Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Q. Where in the cell does Kreb’s Cycle take place? A. Mitochondrion Q. What is the cytosol? A. Cytoplasm minus organelles or liquid part of cytoplasm Q. What is fermentation? A. Anaerobic respiration or respiration that produces lactic acid or ethanol CO2 Q. Is oxygen required for the second stage of aerobic respiration? A. Yes Q. Suggest a situation in which some cells in the human body may not be able to engage in the second stage of aerobic respiration. A. Lack of oxygen or strenuous exercise or restricted blood supply Q. What term is used to describe respiration in which only Stage 1 occurs? A. Anaerobic or Fermentation Q. Name an organism that is used in industrial fermentation. A. Yeast Page 21 of 62 2.2.6 Movement through Membranes FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Water enters the outermost cells of the root by osmosis. What does this tell you about the cell sap of these outermost cells? A. Lower water concentration or higher solute concentration A. Pressure of cell contents on cell wall Q. Osmosis has been described as a special case of diffusion. Explain why. A. Movement of water along a concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane Q. Name a substance found in a plant cell vacuole. A. Water or sugar or sap or salt(s) or protein Q. What is meant by a selectively permeable membrane? A. Allowing some substances to pass through Q. Give locations in a cell at which there is a selectively permeable membrane. A. Chloroplast, mitochondrion, nucleus, vacuole Q. What is diffusion? A. Movement of molecules from area of high concentration to area of lower concentration Q. Give an example of osmosis in plants. A. Water movement between cells or from soil to root Q. Give a feature of a plant cell that allows it to remain turgid for long periods. A. Vacuole or cell wall or cell sap Q. True or False. Plant cell walls are fully permeable. A. TRUE Q. Water for photosynthesis enters the roots of plants by what process? A. Osmosis Q. Suggest a way in which turgor is of value to plants. A. Support Q. Why is diffusion alternatively known as passive transport? A. No energy (ATP) required Q. Explain the biological basis for the use of high sugar or high salt concentrations in the preservation of food. A. Bacteria lose water by osmosis; this leads to inactivity or death Q. What did you use as the selectively permeable membrane in your investigation of osmosis? A. Visking tubing Q. Name the terms used in biology to describe the movement of substances through cell membranes. A. Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport Q. What process is responsible for the uptake of minerals in a plant? A. Active transport Q. What is meant by osmoregulation? A. Controlling the water/salt balance within an organism Q. What is active transport? A. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient using energy Q. Where precisely does water enter a plant? A. Root hairs Q. Name two substances that enter a human muscle cell by diffusion. A. Oxygen; glucose; water; amino acids; phosphate; iron Q. The drooping of the leaves of a plant resulting from loss of turgidity due to lack of water is known as … A. Wilting Q. Suggest an advantage to the cell of having a selectively permeable membrane. A. Substances can be kept in (or out) or substances can be let in (or out) Q. Explain the term turgor. Q. In which tissue does water ascend through the plant? A. Xylem Page 22 of 62 2.2.7 Enzymes FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is a denatured enzyme? A. Loss of enzyme function or activity Q. Give two features of a denatured enzyme. A. Changed structure, loss of function Q. What is meant by an enzyme? A. Organic protein catalyst Q. What term is used for the substance(s) that result(s) from the action of an enzyme on its substrate? A. Product Q. Suggest a temperature at which human enzymes work best. A. 37 °C Q. What is meant by immobilisation? A. Enzyme trapped in beads or gel so that it will react with, but not mix with, its substrate Q. What is a vessel containing organisms producing useful products called? A. A Bioreactor Q. Name the product produced as a result of the action of catalase on hydrogen peroxide. A. Oxygen Q. What term best describes the shape of an enzyme? A. Folded Q. Name a substance that is used to immobilise enzymes. A. Alginate Q. To which group of molecules to which enzymes belong? A. Proteins Q. What is meant by an enzyme’s optimum pH? A. pH at which enzyme works best Q. In relation to an enzyme, explain the term optimum activity. A. Working at maximum rate Q. Name a factor that influences the activity of an enzyme. A. Temperature or pH Q. True or False. Enzymes are not essential for metabolism. A. FALSE Q. What is meant by the specificity of an enzyme? A. Enzyme acts on only a particular substrate Q. Give an advantage of using immobilised cells in industrial fermentation. A. Can be re-used or Pure product produced Q. State a use for Buffer solution in the biology laboratory. A. To keep pH constant Q. The loss of enzyme function or activity is known as … A. Denaturation Q. State one way by which an enzyme may be denatured. A. High temperature or high or low pH or agitation or high salinity or alcohol Q. The substrate for the enzyme amylase is … A. Starch Q. The substrate of the enzyme catalase is … A. Hydrogen peroxide Q. Apart from C, H and O, what other element is always present in the building blocks of enzymes. A. Nitrogen Q. True or False. Immobilised enzymes can act as catalysts. A. TRUE Page 23 of 62 2.2.9 Photosynthesis FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Explain the part played by NADP- in photosynthesis. A. Trapping and transferring electrons and hydrogen ions Q. What happens to water molecules when they reach the sites of photosynthesis? A. Photolysis or split into Protons (H+), electrons & oxygen Q. Give a brief explanation of the division of photosynthesis into light and dark stages. A. Light stage – light essential; Dark stage – independent of light Q. State a precise role for carbon dioxide photosynthesis: A. Supplies the carbon for the formation of C6H12O6 Q. In which of the stages of photosynthesis does ATP form? A. Light stage Q. What is the fate of the NADPH produced in the light-dependent stage? A. To carry H into the dark stage for the reduction of CO2 Q. What is the role of ATP in cells? A. Stores or provides energy or described Q. Where in a plant cell does photosynthesis take place? A. Chloroplast Q. What is an energised electron? A. Electron which has picked up extra energy from the sun Q. In which stage of photosynthesis does carbon dioxide provide carbon for carbohydrate formation? A. Dark stage Q. ATP is an abbreviation. What does it stand for? A. Adenosine triphosphate Q. Explain briefly the role of ATP in the energy exchanges of a cell. A. P ~ P bond holds or stores energy and releases it when needed Q. What is the fate of the ATP produced in the light-dependent stage? A. To supply energy for the reduction of CO2 in dark stage Q. Why is the dark stage given the alternative name of the light-independent stage? A. Light not required Q. Suggest a role for NAD / NADP+ in cell activities. A. Capturing or transferring electrons or protons or hydrogen (ions) Q. During the first stage of photosynthesis where do the energised electrons come from? A. Chlorophyll Q. What is the fate of the oxygen produced in the light-dependent stage? A. Respired or released into atmosphere Q. During photosynthesis compounds of the general formula Cx(H2O)y are formed. What name is given to this group of compounds? A. Carbohydrates Q. From which simple compound does the plant obtain the H used to make C6H12O6? A. Water Q. Name the simple compound that supplies the necessary energy for the second stage reactions. A. ATP Q. Name a gas that is essential for the dark stage. A. Carbon dioxide Q. Give the name of the second stage of photosynthesis. A. Dark stage Q. To what group of biomolecules do the main products of the dark stage belong? A. Monosaccharides or polysaccharides or carbohydrates Q. Where in the cell is chlorophyll found? A. Chloroplast(s) Page 24 of 62 2.2.10 Respiration FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Explain the role of ADP in relation to the small amount of energy released during the first stage of respiration. A. First stage uses energy / combines with phosphate / to form ATP/ ATP stores energy in high energy bond Q. Give one product, other than electrons, of the reactions in Kreb’s cycle. A. CO2 or ATP or Hydrogen ions (protons) Q. What is the first stage process of respiration called? A. Glycolysis Q. The electrons released in Kreb's Cycle pass along a transport chain and release energy. To what use is this energy put? A. To form ATP Q. What is the final product of the first stage of respiration under aerobic conditions? A. Pyruvic acid (Pyruvate) Q. If conditions in a human muscle cell become anaerobic pyruvic acid is converted to another substance. Name this other substance. A. Lactic acid Q. To what is pyruvic acid (pyruvate) converted under anaerobic conditions in yeast? A. Ethanol & CO2 Q. Under aerobic conditions pyruvate is converted to an acetyl group and a small molecule is released. Name this small molecule. A. Carbon dioxide Q. In the first stage of respiration there is a release of ATP as glucose is converted to another substance. Name this other substance. A. Pyruvic acid or pyruvate Q. In aerobic respiration the acetyl group enters a cycle of reactions. What name is given to this cycle? A. Krebs cycle Q. Name a compound to which pyruvate (pyruvic acid) may be converted, in the absence of oxygen. A. Lactic acid or ethanol & CO2 Q. In what part of the cell does the second stage of respiration take place? A. Mitochondrion Q. In the mitochondrion pyruvate is broken down to CO2 and a two-carbon compound. Name this two-carbon compound. A. Acetyl Co-enzyme A Q. For what is ATP an abbreviation? A. Adenosine Triphosphate Q. To what are the electrons transferred at the end of the electron transport chain in aerobic respiration? A. Oxygen or H+ (protons) Q. Where in the cell does the first stage of respiration occur? A. Cytoplasm Q. In Stage 2 of respiration electrons pass along an electron transport chain, releasing energy. In what molecule is this energy stored? A. ATP Q. Name the group of protein molecules that control the rate of respiration. A. Enzymes Q. What is fermentation? A. Anaerobic respiration or respiration that produces either ethanol or lactic acid Q. Is oxygen required for the first stage of respiration? A. No Q. C6H12O6 + 6O2 ENERGY + 6CO2 + 6H2O Is this the equation for photosynthesis or respiration? A. Respiration Q. How did you know that fermentation had ceased? A. Bubbling stopped Q. Is oxygen required for the second stage of respiration? A. Yes Q. Where does Kreb’s cycle take place? A. Mitochondrion Page 25 of 62 2.3 Cell Continuity FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Genes are found on what structures in a cell nucleus? A. Chromosomes Q. In genetics, what is meant by the term haploid? A. Single set of chromosomes or half the diploid number Q. What is a chromosome? A. Group of genes joined together or large DNA molecule Q. Give one way in which mitosis differs from meiosis. A. Two identical daughter cells OR can occur in haploid cells Q. What is the function of meiosis? A. Halving of chromosome numbers or to produce gametes Q. A what stage of mitosis are the chromosomes located at the equator of the cell before they begin to separate? A. Metaphase Q. What is the medical term for the group of disorders in which certain cells lose normal control of mitosis? A. Cancer Q. Towards the end of mitosis, in what type of cell does a cell plate form? A. Plant cell Q. Suggest a possible cause of cancer. A. e.g. Radiation, chemicals, smoking, viruses, etc. Q. To what are the chromosomes attached during metaphase of mitosis? A. Spindle Q. What name is applied to the period of the cell cycle in which division is not taking place? A. Interphase Q. What is a tissue? A. A group of cells with the same function Q. Give a cellular process that occurs during the period in the cell cycle in which the nucleus is not dividing. A. Replication or Growth or Protein synthesis or Respiration or Photosynthesis Q. Suggest a possible treatment for cancer. A. e.g. Chemotherapy / radiotherapy / surgery Q. What is the function of spindle fibres during cell division? A. For chromosomes to attach to & contract to separate chromosomes Q. Tissues grow by cell division. Name the type of cell division by which tissues grow. A. Mitosis Q. What is the role of mitosis in single-celled organisms? A. Reproduction Q. Name the two types of cell division. A. Mitosis & meiosis Q. Explain the term tissue culture. A. Cells grown on or in medium or cells grown outside organism Q. Give two examples of the use of tissue culture. A. Cancer research, Plant propagation Q. Name a gas that would be needed for the growth of tissue in the laboratory. A. Oxygen Q. Why are sterile conditions needed to grow a tissue culture in a laboratory? A. To avoid contamination Q. What type of cell division, mitosis or meiosis, is involved in tissue culture? A. Mitosis Q. Organs are found in both plants and animals. What is meant by the term organ? A. A group of tissues performing the same function Page 26 of 62 2.5.1 - 4 Genetics 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What term is used to describe differences within a population with respect to features such as height? A. Variation Q. Name the complementary base in RNA for Adenine. A. Uracil Q. Name a carbohydrate that is a component of nucleotides. A. Ribose or deoxyribose Q. Explain the term species. A. Interbreeding results in fertile offspring Q. Give one cause of genetic variation. A. Sexual reproduction; Gene or chromosome mutation; Genetic engineering Q. What does the ‘m’ stand for in mRNA? A. Messenger Q. Genetics is the study of ... A. Inheritance or heredity Q. True or False. Organisms of the same species can usually produce fertile offspring. A. TRUE Q. True or False. Chromosomes are made of DNA and lipid A. FALSE Q. Name the complementary base in RNA for Cytosine. A. Guanine Q. Explain briefly what is meant by a gene? A. Unit of heredity or code for protein or section of DNA Q. Name a component of a nucleotide that is neither a carbohydrate nor a nitrogenous base. A. Phosphate group Q. Give one example of an inherited human characteristic. A. e.g. Eye colour Q. What is a chromosome? A. Structure found in nucleus composed of DNA or genes or hereditary material Q. What is meant by genetic screening? A. Testing people for the presence of a specific gene Q. Give one example of a non-inherited human characteristic. A. e.g. Ability to roller skate Q. Give two applications of DNA profiling. A. Forensic science / paternity / medical Q. Explain what is meant by the term DNA profiling? A. Examining DNA for a pattern or band to compare Q. What is meant by non-coding DNA? A. Does not code for a protein Q. Give one structural difference between DNA and RNA. A. DNA contains thymine or RNA contains uracil Q. What are the two main events in the replication of DNA? A. DNA opens (unzips) & New strands made Q. True or False. RNA is not found in ribosomes. A. FALSE Q. Name the four bases that are found in DNA. A. Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine Q. The bases in DNA form a triplet code. What is meant by a triplet code? A. Three bases code for one amino acid Page 27 of 62 2.5.5 + 2.5.15 Genetics 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. The bases in DNA form a triplet code. What is meant by a triplet code? A. A sequence of three bases that code for one amino acid Q. Explain the term Replication in relation to DNA. A. Making a copy Q. In DNA profiling, what are used to cut DNA strands into fragments? A. Enzymes Q. To which structures in the cell does mRNA carry the code? A. Ribosome Q. Give the role of the enzyme RNA polymerase. A. Joins nucleotides together to make mRNA Q. The triplet code is transcribed into mRNA. What does this statement mean? A. Information (code) is copied to RNA molecule Q. Where in the cell would you expect to find most DNA? A. Nucleus or Chromosome or Gene Q. In which structures in the cell does translation occur? A. Ribosomes Q. DNA contains the instructions needed to make protein. These instructions are called the … code. A. Gene or Genetic Q. What does the letter ‘t’ stand for in tRNA? A. Transfer Q. During translation one end of a tRNA molecule attaches to an mRNA codon. What is attached to the other end of the tRNA molecule? A. An amino acid Q. What is meant by non-coding DNA? A. Does not code for a protein or for RNA Q. Explain the term Transcription in relation to DNA. A. Complimentary RNA production Q. What must happen to the newly formed protein before it can begin to work? A. It must fold into its functional shape Q. Give one structural difference between DNA and RNA. A. DNA contains thymine or RNA contains uracil Q. In DNA profiling DNA strands are cut into fragments. On what basis are these fragments then separated? A. Size or Use of gel electrophoresis Q. True or False. The base Uracil is found in DNA. A. FALSE Q. Each mRNA codon specifies one of three possible outcomes during protein synthesis. Name these three possible outcomes. A. Start; Adding an amino acid; Stop Q. Where in a cell are enzymes produced? A. Ribosomes Q. Give two applications (uses) of DNA profiling. A. Crime (forensic) or Medicine or Paternity or Archaeology or Evolution Q. What is meant by genetic screening? A. Checking for the presence of a specific gene Q. True or False. DNA is a double helical shape. A. TRUE Q. Where in a cell does transcription occur? A. Nucleus Q. Name the small biomolecules that are joined together to make a protein. A. Amino acids Page 28 of 62 2.5.6 - 2.5.8 Genetics 3 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What term is used to describe an individual’s genetic make-up? A. Genotype A. Neither allele masks the expression of the other Q. Name the sex chromosomes that are present in a human female cell. A. XX Q. Explain the term recessive. A. It is only expressed in the homozygous condition Q. A spontaneous change in the genetic material of an organism is called a ... A. Mutation Q. What is an allele? A. Alternative form of a gene Q. Explain homozygous A. Identical alleles or genes Q. A change in the structure of DNA is a … and may give rise to a … A. Mutation / Variation Q. What is meant by phenotype? A. Physical appearance or Expression of genotype or Result of genotype + environment Q. Explain the term dominant. A. An allele that is always expressed (masks its recessive partner) Q. Explain heterozygous. A. Different alleles or genes Q. Name a scientist responsible for the Theory of Natural Selection A. Darwin or Wallace Q. State two types of evidence used to support the theory of evolution. A. Fossils or Embryos or Anatomy or Genetics Q. How many possible gametes can a parent of genotype AaBb produce? A. Four Q. What is ‘junk’ DNA? A. Does not code for a protein Q. What is linkage? A. Genes on the same chromosome Q. Give two causes of mutation. A. Chemicals, Radiation, Viruses, Carcinogens, etc. Q. Human males and females differ in one of their twenty three pairs of chromosomes. What name is given to this pair of chromosomes? A. Heterosomes or sex chromosomes Q. What is meant by the term evolution? A. Inheritable change within a population in response to change in the environment by natural selection over time Q. What is sex-linkage? A. Genes located on sex (X or Y) chromosome Q. What is Natural Selection? A. Organisms best suited to environment have greater chance of breeding and survival Q. How many possible gametes can a parent of genotype Aa produce? A. Two Q. What is meant by genetic screening? A. Testing people for the presence of a specific gene Q. Name the sex chromosomes that are present in a human male cell. A. XY Q. What is incomplete dominance? Page 29 of 62 2.5.9 - 2.5.14 Genetics 4 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is the difference between a nucleus of an egg cell and that of a somatic (body) cell of an animal? A. Egg cell is haploid or Somatic cell is diploid Q. Explain the term isolation in the context of genetic engineering. A. Locating or Removal of a gene (or a piece of DNA or a plasmid) Q. Suggest an advantage of producing genetically identical animals. A. Same wool quality Q. In genetics, what is meant by sex linkage? A. Gene on sex (or X or Y) chromosome Q. What is meant by genetic engineering? A. Manipulation of genes Q. What term is used to describe alleles that lie on the same chromosome? A. Linked Q. State an application of genetic engineering involving a micro-organism. A. Production of hormone or enzymes or interferon Q. State an application of genetic engineering involving a plant. A. Slow ripening tomatoes or Herbicide resistant plants or freeze-resistant plants Q. Name three processes involved in genetic engineering. A. Isolation / cutting (or restriction) / transformation (or ligation) / introduction of base sequence (changes) / expression Q. Explain the term ligation in the context of genetic engineering. A. The joining of DNA (or plasmid or gene) Q. What is meant by Segregation? A. Separation of a pair of allelic genes during meiosis resulting in each gamete having only one of the pair of genes Q. Explain why linked genes do not assort independently. A. They are transmitted on the same chromosome Q. Name a condition in humans that is governed by a sex-linked allele. A. Haemophilia or Colour blindness Q. Which nitrogenous base can link only to thymine? A. Adenine Q. Explain the term expression in the context of genetic engineering. A. The activation of the inserted gene or production of product Q. Suggest a disadvantage of producing genetically identical animals. A. Lack of variation or Prone to disease Q. State the Law of Independent Assortment. A. During gamete formation each member of a pair of genes may combine randomly with either of another pair Q. Name the two types of nitrogenous base found in DNA. A. Purines and Pyrimidines Q. State an application of genetic engineering involving an animal. A. “antifreeze” in farmed fish or pharmaceuticals from transgenic animals Q. Which nitrogenous base can link only to cytosine? A. Guanine Q. Explain the term restriction (cutting) in the context of genetic engineering. A. Cutting the DNA (or plasmid) with a (restriction) enzyme Q. Explain the term transformation in the context of genetic engineering. A. The uptake of DNA (or plasmid or gene) Q. Name a cell organelle, apart from the nucleus, in which DNA is found. A. Mitochondrion or Chloroplast Q. Name the type of bonding which occurs between members of a base pair in the DNA molecule. A. Hydrogen Page 30 of 62 3.1.1 - 3.1.3 Monera Homework Solution Q. To which kingdom do bacteria belong? A. Monera or Prokaryotae A. Capsule or Mucilage; Protection Q. Other than being prokaryotic, state two ways in which a typical bacterial cell differs from a typical human cheek cell. A. Cell wall; size; capsule; flagellum; plasmid Q. What is meant when a bacterium is described as being pathogenic? A. Disease-causing Q. Describe how some bacteria respond in order to survive when environmental conditions become unfavourable. A. Produce (endo)spores Q. To which kingdom does the organism used in industrial fermentation belong? A. Fungi Q. What are antibiotics? A. Substances produced by micro-organisms that inhibit growth or reproduction of bacteria or fungi Q. What are photosynthetic bacteria? A. Using light to make food or obtain energy Q. Name two forms of heterotrophic nutrition found in bacteria. A. Parasitic and saprophytic Q. Why are antibiotics not prescribed for a person suffering from a viral infection? A. Antibiotics have no effect on viruses Q. What is autotrophic nutrition? A. Organism makes its own food Q. Suggest an advantage of classifying organisms. A. Identification Q. What is saprophytic nutrition? A. Organisms feed on dead matter Q. Give examples of two harmful bacteria. A. Tuberculosis; cholera; tetanus; sore throat Q. Name a structure, other than the capsule, which is not found in all bacteria. A. Flagellum or Plasmid Q. Name any two of the main bacterial types (shapes). A. Rod; Coccus; Spiral Q. What is the function of flagella? A. Movement Q. What is heterotrophic nutrition? A. Organism uses food already made by other organisms Q. Why are doctors reluctant to prescribe antibiotics to patients suffering from the common cold? A. Common cold is a viral disease; antibiotics do not affect viruses Q. Under what circumstances does a bacterial cell form an endospore? A. Harsh unfavourable conditions Q. Why are saprophytic bacteria important in nature? A. Decompose dead organisms or Recycle nutrients Q. What are chemosynthetic bacteria? A. Use a chemical reaction to make food or obtain energy (e.g. in soil) Q. What term is used for the organism from which a parasite obtains its food? A. Host Q. What term is used for the type of asexual reproduction used by bacteria? A. Binary fission Q. Some bacteria have a layer outside the cell wall. Name this layer and state its function. Page 31 of 62 3.1.4 Fungi 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. To which kingdom do yeasts belong? A. Fungi Q. From what plant did you obtain the leaf yeast A. Ash Q. State one feature of Rhizopus that indicates that Rhizopus belongs to the kingdom Fungi. A. Stolon or rhizoids or mycelium or hyphae or sporangium or spores Q. What are parasitic fungi? A. They live in or on another living organism causing harm Q. Yeasts are eukaryotic organisms. What does this mean? A. Possesses membrane-bound nucleus or organelles Q. Name the nutrient medium on which you grew leaf yeast A. Malt agar Q. State a function of the zygospore in fungi. A. Survival; Dispersal Q. Give one way in which Rhizopus differs from yeast. A. Multicellular or Method of reproduction or Size or Structure Q. Give two examples of a harmful fungus. A. Ringworm or Athlete’s foot or Potato blight or Thrush or Dry rot or Death cap Q. What are saprophytic fungi? A. They live on dead organisms or matter Q. Give a role, other than anchorage, for rhizoids. A. Nutritional (Digestion or Absorption) Q. Give one example of a beneficial fungus. A. Yeast for brewing or baking or Agaricus campestris or Agaricus bisporus Q. Which term describes the mode of nutrition of Rhizopus? A. Saprophytic Q. State a function of the rhizoid in fungi. A. Anchors; Digestion; Absorption Q. What is a hypha? A. A filament Q. What is the role of parasitic fungi in nature? A. Keep populations under control or natural selection Q. What is the role of saprophytic fungi in nature? A. Recycling of nutrients and decay Q. Why is the reproduction associated with the sporangium of Rhizopus asexual? A. The spores all develop from one parent or no gametes involved Q. A mass of hyphae is called a … A. Mycelium Q. State a function of the sporangium in fungi. A. Produces spores; Stores spores; Asexual reproduction Q. Name a fungus, other than yeast, that you studied. A. Rhizopus Q. State a function of the gametangium in fungi. A. Produces gametes; Sexual reproduction Q. Name one structure in plant cells not found in fungi. A. Chloroplast Q. State one way in which yeast is beneficial to humans. A. Baking or brewing Page 32 of 62 3.1.4 Fungi 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Suggest an adverse condition that triggers sexual reproduction in Rhizopus. A. Dehydration Q. Name one economically harmful member of the Fungi kingdom. A. Rhizopus or mildew or rusts or smuts or blight or dry rot or athlete’s foot Q. Give two advantages to Rhizopus of zygospore formation. A. Can survive drought or named adverse condition; Dispersal Q. Give one beneficial use of fungi. A. Antibiotic production Q. What term is used to describe the process of asexual reproduction in yeast? A. Budding Q. Outline the importance of saprophytic nutrition in nature. A. It breaks down dead organisms or recycling of nutrients Q. How does asexual reproduction in Rhizopus differ from that in yeast? A. Rhizopus produces spores Q. TRUE or FALSE. Rhizopus is a member of the animal kingdom. A. FALSE Q. What takes place in the sporangium? A. Production of spores or reproduction Q. Having finished the experiment on leaf yeast, what did you do with the agar plates? A. Autoclave in disposal bag Q. Name a fungus, other than Rhizopus or yeast, and explain how it is of benefit to humans. A. Mushrooms; Edible Q. Name a fungus, other than Rhizopus or yeast, and explain how it is harmful to humans. A. Mushrooms; Poisonous Q. State a function of rhizoids. A. Anchorage or absorption or digestion or secretion of enzymes Q. State a function of the sporangiophore. A. Holds up/supports the sporangium Q. What term is used to describe the nutrition of Rhizopus? A. Heterotrophic Q. What is the purpose of using agar when growing fungi or bacteria in the laboratory? A. Source of nutrients Q. Which type of division, mitosis or meiosis, is involved in reproduction in yeast? A. Mitosis Q. Suggest one reason why leaf yeasts are more plentiful in July than in March. A. More leaves or more suitable temperature or more reproduction Q. What are anaerobic conditions? A. Lack of oxygen Q. Name the container in which you grew the leaf yeast A. Petri dish Q. What form of heterotrophic nutrition does Rhizopus have? A. Saprophytic Q. How did you recognise the leaf yeasts when they appeared on the agar? A. Pink colonies Q. In anaerobic conditions yeast produces ethanol and … A. Carbon dioxide Q. What is meant by sterile? A. Free from microorganisms or living things Page 33 of 62 3.1.4, 6, 10 Fungi, Protista, Growth Curves FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. To which kingdom does Amoeba belong? A. Protista or Protoctista A. Organisms are adapting to environment or low reproductive rate Q. What term is applied to the first part of a growth curve? A. Lag phase Q. Give one function of pseudopods (pseudopodia) in Amoeba. A. Feeding or Movement or Egestion or Homeostasis Q. What is continuous flow food processing? A. Nutrients constantly fed into bioreactor or Product removed constantly Q. What is batch food processing? A. Fixed amount of nutrients added at beginning or Bioreactor emptied at end of production Q. What is meant by saprophytic nutrition? A. Living on dead matter Q. Name one structure in plant cells not found in fungi. A. Chloroplast Q. Suggest one reason why the contractile vacuole is more active in freshwater amoebae than in marine amoebae. A. Freshwater more hypotonic or More H2O intake Q. Name the structure by which Amoeba gets rid of excess water that has entered by osmosis. A. Contractile vacuole Q. What is the role of the sporangium in the reproduction of Rhizopus? A. Production and release of spores Q. Name another form of nutrition (other than heterotrophic) employed by some fungi. A. Parasitic Q. What term is applied to the second part of a growth curve? A. Log or exponential phase Q. In fungi what is the function of the gametangium? A. Produces gametes or Sexual reproduction Q. State a function of rhizoids. A. Anchorage or absorption or digestion or secretion of enzymes Q. A single fungal filament is called a … A. Hypha Q. How does asexual reproduction in Rhizopus differ from that in yeast? A. Rhizopus produces spores Q. What term is used to describe the process of asexual reproduction in yeast? A. Budding Q. Give one difference between a plant cell and an Amoeba. A. Plant cell has cell wall Q. What is happening during the log or exponential growth phase? A. Organisms reproducing rapidly Q. State one function of the contractile vacuole of the Amoeba. A. Water balance or Osmoregulation Q. A mass of fungal filaments is called a … A. Mycelium Q. Name the substrate on which you grew leaf yeast. A. Malt agar Q. Yeasts are eukaryotic organisms. What does this mean? A. Possesses nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Q. What is happening during the lag growth phase? Page 34 of 62 3.2.1 Plant Structure 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Name two plant tissues that are not vascular tissues. A. Dermal; Ground; Meristematic Q. True or False. Lenticels serve the same function as stomata. A. TRUE A. Xylem Q. True or False. Parallel leaf veins are characteristic of monocotyledonous plants. A. TRUE Q. The walls of xylem vessels are reinforced with … A. Lignin Q. How is xylem adapted for its role in water transport? A. Tubular or continuous lumen; Reinforced lignified walls; Narrow bore Q. What is meant by the term monocotyledonous? A. One seed leaf or One embryonic leaf Q. In which of the vascular tissues are sugars mainly transported? A. Phloem Q. How does the vein arrangement in the leaves of dicot plants differ from that in monocots? A. Reticulate or Net or Branched Q. State a function of Dermal tissue. A. Protection Q. State three functions of a root. A. Anchorage; Absorption; Storage Q. When preparing a T.S. of a stem what did you use to cut the section? A. Blade or scalpel Q. State one way in which a transverse section through a monocotyledonous stem differs from a dicotyledonous one. A. Vascular bundles scattered Q. Where precisely is xylem tissue found in the stem of a young dicotyledonous plant? A. In the vascular bundle next to phloem Q. Give one location where mitosis occurs in flowering plants. A. Meristematic tissues or Ovule or Embryo sac or Pollen Q. Why is a dicotyledonous (dicot) plant so called? A. Two embryonic leaves or Two seed leaves Q. State another function of xylem other than water transport. A. Support Q. How are the veins arranged in the leaves of monocots? A. Parallel Q. Where would you find a meristem in a root? A. At the tip Q. What is meant by a vascular tissue? A. Transports substances Q. Where would you expect to find xylem and phloem in a leaf? A. Vein or Mid rib Q. Give an example of a monocotyledonous plant. A. e.g. Grass, maize, etc. Q. Name a dicotyledonous plant. A. Oak, Ash, Elm, Horse chestnut, etc. Q. Name the tissue in plant stems through which water rises to the leaves. Q. Name one substance found in the walls of xylem cells but not found in the walls of phloem cells. A. Lignin Page 35 of 62 3.2.1 Plant Structure 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Name one substance found in the walls of xylem cells but not found in the walls of phloem cells. A. Lignin Q. Name two vascular tissues and give one way in which they differ. A. Xylem; Phloem Q. State a function of ground tissue. A. Food storage; Photosynthesis; Strength; Support Q. Give a location of a meristem in a winter twig. A. Bud or Stem tip Q. Give two functions of a stem. A. Transport; Support; Displays flower or leaf or fruit; Gaseous exchange; Storage Q. Where in a young root would you find tissues xylem and phloem? A. Centre or Zone of differentiation or Vascular bundle Q. Give one main function of the leaf. A. Photosynthesis; Transpiration; Gas exchange; Storage of food; Release of waste products Q. Give a function of the guard cell. A. Controls stomatal size or Controls passage of gas or water vapour Q. Name two gases that enter or leave the leaf. A. Carbon dioxide; Oxygen; Nitrogen; Water vapour Q. Name the process by which the gases move in or out of the leaf. A. Diffusion or Passive transport Q. Name the tissue that transports water from the root to the leaves. A. Vascular tissue or Xylem Q. Flowers are the organs of which type of reproduction in the plant? A. Sexual Q. Which tissue transports food from the leaves? A. Phloem Q. Is xylem a living or dead tissue? A. Dead Q. Suggest a role of the lignin in xylem. A. Support Q. Name one process that causes water to move upwards through a plant. A. Root pressure; Cohesion; Adhesion; Transpiration stream Q. Name the structures in the leaves through which water exits the plant. A. Stomata Q. Vascular tissue is one type of plant tissue. Name two other plant tissues. A. Ground; Epidermal; Meristematic Q. True or False. Lenticels serve the same function as stomata. A. TRUE Q. State a function of Dermal tissue. A. Protection Q. True or False. Parallel leaf veins are characteristic of dicotyledonous plants. A. FALSE Q. In which direction does the transport of water take place? A. Upwards Q. State one way in which a transverse section through a monocotyledonous stem differs from a dicotyledonous one. A. Vascular bundles scattered Q. Give one location where mitosis occurs in flowering plants. A. Meristematic tissue or Buds or Ovule or Embryo sac or Pollen Page 36 of 62 3.2.2 Blood & Circulation 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Name two tissues that are present in the walls of arteries and veins. A. Collagen; Muscle; Endothelium Q. What is the function of the valves? A. Prevent backflow of blood Q. Which chamber of the heart has the greatest amount of muscle in its wall? A. Left ventricle Q. What is the function of collagen? A. Non-elastic fibres that prevent over expansion of blood vessels Q. Name the cavity of the body in which the heart and lungs are located. A. Thoracic Q. State one way in which heart muscle differs from other muscles in the body. A. Does not get tired Q. Describe the structure of the lymphatic system. A. Composed of lymph nodes and lymph vessels Q. State one factor that decreases heart rate. A. Sleep; Drugs (sedatives) Q. State the procedure that you followed to expose a semilunar valve. A. Cut aorta or Cut pulmonary artery Q. State the precise location of the liver in the human body A. Upper abdomen under the diaphragm to the right of the stomach Q. Where in your dissection did you find the origin of the coronary artery? A. Aorta or Near semilunar valve Q. To where does the pulmonary artery carry blood? A. The lungs Q. What is the function of the bicuspid valve? A. Prevent backflow of blood from left ventricle to left auricle (atrium) Q. State one factor that increases heart rate. A. Fear (fright); Exercise Q. What is the function of endothelium? A. Lining of blood vessels Q. Name the blood vessel that supplies the heart muscle with blood. A. Coronary artery Q. What is the function of a semilunar valve? A. Stops back flow of blood into ventricle or from artery Q. State a precise location in the human body at which red blood cells are made. A. Marrow of long bones Q. Name the blood vessel that returns blood to the heart from the lungs. A. Pulmonary vein Q. Name the two circuits of the human circulatory system. A. Pulmonary; Systemic Q. Name two substances that are dissolved in the liquid part of blood. A. Glucose; Urea; Insulin; Fibrinogen; etc. Q. Name the liquid part of blood. A. Plasma Q. State a function of red corpuscles. A. Transport oxygen Q. State a function of white cells. A. Protection against disease Page 37 of 62 3.2.2 Blood & Circulation 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Name two common blood-grouping systems. A. ABO and Rhesus Q. The hepatic portal vein carries blood from the alimentary canal to the … A. Liver Q. Name the structure in the heart that controls the heartbeat. A. Pacemaker Q. State a possible effect of smoking on the pulse resting rate. A. Raises rate Q. Name the chamber of the heart that receives blood back from the lungs. A. Left atrium (auricle) Q. Is the blood in the Aorta oxygenated or deoxygenated? A. Oxygenated Q. Give one reason why the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the wall of the right ventricle. A. Pumps blood further Q. What is blood plasma? A. Blood without cells or Watery liquid part of blood Q. Name the major blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the lungs. A. Pulmonary arteries Q. The ABO blood group system has four blood groups. What are these four groups? A. A, B, AB, O Q. Valves are present in veins. What is their function? A. To prevent back flow of blood Q. Suggest a reason why it is important to know a person’s blood group. A. When getting a transfusion or To avoid reaction by mother to foetus Q. Name the major blood vessels that carry blood from the lungs to the heart. A. Pulmonary veins Q. Which has the bigger lumen (cavity), an artery or a vein? A. Vein Q. The wall of capillaries is only one cell thick. How is this related to their function? A. Substances can diffuse easily into and out of capillaries Q. Why are valves not needed in arteries? A. Blood is under pressure as it is pumped from heart Q. Give a role for blood plasma. A. Transports dissolved substances Q. What is the function of blood platelets? A. Blood clotting Q. What structure(s) protects the heart? A. Rib-cage Q. Name the upper chambers of the heart. A. Atria or Auricle Q. Name the valve between the upper and lower chambers on the left-hand side. A. Bicuspid (mitral) valve Q. How does a portal vein differ from other veins? A. Capillaries at both ends Q. Name the blood vessels that carry blood from the aorta to the kidneys. A. Renal arteries Q. Where in the body are white blood cells produced? A. Bone marrow Page 38 of 62 3.2.3 + 4 Blood Cells & Heartbeat FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. True or False. A nucleus is absent from human red blood cells. A. TRUE Q. State two ways in which red blood cells differ from typical body cells e.g. from the cheek lining. A. No nucleus; haemoglobin; shape; size; no mitochondria; carries O2 or CO2 Q. Name a group of white blood cells, other than lymphocytes. A. Phagocytic (white cells) or Monocytes Q. State a precise location in the human body at which red blood cells are made. A. Marrow of long bones Q. Cardiac muscle may be described as a contractile tissue. Explain the meaning of the underlined term. A. It can shorten A. Pacemaker Q. Some people may have the blood group B Positive (B+).What factor is present in their blood that makes it positive? A. Rhesus Q. Where in the body are white blood cells produced? A. Bone marrow Q. Blood is made up of plasma and blood cells. What is plasma? A. Liquid part of blood Q. Where is the pacemaker located in the heart? A. Right atrium Q. What is the function of white blood cells? A. Fight disease Q. Give the precise location of the SA node in the heart. A. In wall of right atrium Q. True or False. The sino-atrial node (pacemaker) is located on the right side of the heart. A. TRUE Q. What is the role of valves in the heart? A. To prevent backflow of blood Q. What is the role of the SA (sinoatrial) and AV (atrioventricular) nodes in the heart? A. Causes contraction of heart muscle or Pacemaker or Impulse generation Q. Give any two functions of the lymphatic system. A. Returns fluid to blood; Transport; Lymphocytes (Immunity) Q. Name the blood vessel that brings blood from the heart to the body. A. Aorta Q. Give two factors which cause an increase in heart rate. A. Exercise; Anxiety; Drugs; Infection Q. Mention two ways to maintain a healthy heart. A. Eat less fat; Exercise regularly; Avoid excess stress; Eat less salt; Don’t smoke Q. Name the blood vessels that supply the heart cells with blood. A. Coronary or Cardiac arteries Q. What causes the sound of a heartbeat? A. Valves closing Q. Give the precise location of the AV node in the heart. A. In (or near) septum or Near tricuspid valve or Between atrium and ventricle Q. What structure(s) protects the heart? A. Rib cage Q. Name the valve between the upper and lower chambers on the left-hand side. A. Bicuspid (mitral) valve Q. Name the structure in the heart that controls the heartbeat. Page 39 of 62 3.3.1 + 2 Nutrition & Storage in Plants FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Where precisely does water enter a plant? A. Root hairs Q. Name the process responsible for the uptake of minerals by roots? A. Active transport Q. Name an autotrophic organism. A. Grass, seaweed, fern, moss, etc. Q. Name a type of modified stem that functions in food storage. A. Rhizome or Corm or Tuber Q. In which tissue does water ascend through the plant? A. Xylem Q. Name the process responsible for the entry of water into a plant. A. Osmosis Q. What is the function of stomata? A. To allow exchange of gas or water vapour or Transpiration Q. State one way in which the tissue is adapted for transporting water and minerals. A. Has lignin for strength and support Q. Name the apertures in stems that are equivalent to stomata. A. Lenticels Q. Name a carbohydrate that you would expect to find stored in modified leaves. A. Starch or Sucrose or Glucose Q. Name the openings in the leaf which allow the entry of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. A. Stomata Q. TRUE or FALSE. A potato is a modified stem. A. TRUE Q. Name the plant tissue responsible for transporting food. A. Phloem Q. Describe how nitrates enter the root of a plant from the soil. A. Active transport Q. Name a gas that leaves the leaf at the stomata. A. Oxygen; Water vapour; Carbon dioxide; Nitrogen Q. Give one example of a root modified for food storage. A. Carrot; Turnip; Parsnip; etc. Q. Name a factor that influences the diameter of stomata. A. CO2 concentration or Light intensity or Potassium ions or Water Q. Name one process that causes water to move upwards in a plant. A. Root pressure or Cohesion or Adhesion or Capillarity or Transpiration Q. What will happen to the amount of water moving through a plant when it gets dark? A. Decreases Q. The walls of xylem vessels are reinforced with … A. Lignin Q. State a function of Dermal tissue. A. Protect from water loss or infection Q. Where precisely is xylem tissue found in the stem of a young dicotyledonous plant? A. Vascular bundle or Next to phloem Q. What is meant by the term dicotyledonous? A. Two seed leaves Q. Name a plant in which the leaves are modified for food storage. A. Onion or Tulip or Daffodil Page 40 of 62 3.3.3 + 4 Human Nutrition & Digestion 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is meant by the term omnivore? A. An animal that eats both animals and plants Q. What is meant by absorption? A. Movement across membrane into blood or lymph Q. What is a herbivore? A. An animal that feeds on plants only Q. What is a heterotrophic organism? A. One that uses food already made by other organisms Q. What is an autotrophic organism? A. One that makes its own food Q. What are the final products of the digestion of a protein? A. Amino acids Q. What is meant by the term digestion? A. Breaking down food Q. Name a carbohydrate-digesting enzyme in the human alimentary canal A. Amylase Q. What is peristalsis? A. Muscular activity or contractions to move food Q. What is the role of bile in fat digestion? A. Emulsification Q. Why is a low pH important in the stomach? A. Kills germs or Optimal pH for enzymes Q. The passage of the products of digestion from the intestine to the blood is called ... A. Absorption Q. Where in the alimentary canal does amylase act? A. Mouth and Small intestine Q. Describe two functions of bile in relation to digestion. A. Emulsification; Neutralisation or Raises pH or Makes alkaline Q. What is a carnivore? A. An animal that feeds on animals only Q. Why is fibre important? A. For peristalsis or Prevent constipation or bowel cancer Q. Where is lipase produced? A. Pancreas Q. Name an enzyme that is involved in the digestion of fat. A. Lipase Q. What are the products of fat digestion? A. Fatty acids and glycerol Q. State the product(s) of amylase digestion. A. Maltose Q. State a role of beneficial bacteria in the alimentary canal. A. Production of vitamins or Inhibition of pathogens Q. State two ways in which the villi are adapted for the absorption of soluble foods. A. Large surface area; Rich blood supply; Microvilli; Thin-walled; Lacteal Q. Name a structure in the human digestive system, other than teeth, which is involved in mechanical digestion. A. Tongue or Oesophagus or Stomach or Small intestine Q. What is a protease enzyme? A. Breaks down protein Page 41 of 62 3.3.4 Digestion 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Name a structure in the human digestive system, other than teeth, which is involved in mechanical digestion. A. Tongue or Oesophagus or Stomach or Small intestine Q. Describe two functions of bile in relation to digestion. A. Emulsification; Raises pH or makes alkaline Q. From which part of the alimentary canal does food arrive into the duodenum? A. Stomach Q. Name the part of the digestive system in which water is absorbed into the blood. A. Colon Q. Where does lipase act? A. Duodenum or Small intestine Q. Where is lipase secreted? A. Pancreas or Duodenum Q. What are symbiotic bacteria? A. Bacteria that live in or on another organism involving benefit Q. Give two activities of symbiotic bacteria in the human digestive system. A. Digestion; Production of vitamins; Benefit immune system; Compete with other microorganisms Q. Name the part of the digestive system in which the products of digestion absorbed into the blood. A. Ileum or villi Q. State one digestive function of the pancreas. A. Produces enzymes or neutralises chyme Q. What process results from the contraction of the muscles in the small intestine? A. Peristalsis Q. Explain how the ileum (small intestine) is adapted for the absorption of the products of digestion. A. Large surface area; Good blood and lymph supply; Lining one cell thick; Long; Villi Q. Indicate which of the following most accurately represents the pH of the contents of the small intestine. Acidic. Neutral. Alkaline. A. Alkaline Q. What is meant by the term digestion? A. The breakdown of food Q. Where in the human body is the liver located in relation to the stomach? A. Above and to the right Q. Name a process involved in the passage of the products of digestion into the blood. A. Diffusion or Passive transport Q. A person who has suffered from constipation may be advised to increase the amount of wholegrain cereal in her/his diet. Why? A. Adds fibre, fibre absorbs water, peristalsis encouraged, faster digestive transit Q. Why is digestion necessary? A. For solubility or For absorption or For transport Q. Name two glands that pass their secretions into the small intestine. A. Pancreas; Liver Q. What is the approximate pH of the site of action of lipase? A. 7 – 9 Q. Proteins are digested to simpler substances. What are these simpler substances called? A. Amino acids Q. In which organ is food churned into chyme? A. Stomach Q. Which teeth grind food into smaller pieces? A. Molars Q. From what organ does the bile duct leave? A. Gall bladder Page 42 of 62 3.3.4 Digestion 3 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Where is bile produced? A. Liver A. Gall bladder Q. What is the role of peristalsis in the digestive system? A. Push food along gut; Prevents constipation Q. The stomach secretes hydrochloric acid onto the ingested food. Give one function of this acid. A. Kill bacteria Q. State whether the contents the small intestine are acidic, neutral or alkaline. A. Alkaline Q. State whether the contents of the stomach are acidic, neutral or alkaline. A. Acidic Q. What is the substrate of the enzyme amylase? A. Starch Q. State two functions of symbiotic bacteria in the alimentary canal. A. Digest cellulose; Produce vitamins; Immunity Q. What is meant by egestion? A. Getting rid of undigested food waste Q. Where does bile act in the alimentary canal? A. Duodenum; Small intestine or Ileum Q. Give a role for incisor teeth. A. Cutting food Q. What is the product of the enzyme amylase? A. Maltose Q. Give one digestive function of the liver. A. Bile production Q. Give one non-digestive function of the pancreas. A. Produces insulin Q. Name an enzyme that is involved in the digestion of fat. A. Lipase Q. From which part of the digestive system does egestion occur? A. Rectum Q. Where does the partially digested food go when it leaves the stomach? A. Duodenum or small intestine Q. What is the role of bile in fat digestion? A. Emulsification Q. State one role of the pancreas in digestion. A. Makes enzymes or Makes NaHCO3 Q. What is a protease enzyme? A. Breaks down protein Q. From what part of the digestive system does the digested food enter the blood? A. Small intestine Q. Name a process involved in the passage of the products of digestion into the blood. A. Diffusion Q. Explain the term digestion? A. Breaking down of food Q. What are symbiotic bacteria? A. Bacteria that live in or on another organism involving benefit Q. Where is bile stored? Page 43 of 62 3.3.5 Blood Transport of Nutrients FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. True or False. Urea is formed in the kidneys. A. FALSE Q. TRUE or FALSE. The liver produces bile. A. TRUE Q. Name a process by which soluble foods are absorbed into the blood from the small intestine. A. Diffusion or Passive transport Q. Give one digestive function of the pancreas. A. Produces enzymes trypsin, amylase, lipase Q. What type of food is mainly absorbed into the lacteal of the villi? A. Fatty acids and glycerol Q. The stomach secretes hydrochloric acid onto the ingested food. Give one function of this acid. A. Provides medium for pepsin Q. State a role that the liver plays in the digestive process. A. Produces bile; Emulsification; Produces NaHCO3; Neutralizes acid Q. The colon contains many symbiotic bacteria – mostly ‘good’ bacteria. State two benefits we get from these bacteria. A. Synthesise vitamins; Out-compete pathogens; Complement immune system; Break down fibre Q. Name a substance transported to the liver by the blood in the hepatic portal vein. A. Glucose, amino acids, minerals, vitamins, etc. Q. Where does the partially digested food go when it leaves the stomach? A. Duodenum Q. Name the blood vessel that brings oxygenated blood to the liver. A. Hepatic artery Q. What is the pH of the stomach contents? A. 1 – 2 Q. Where is bile stored after it has been made in the liver? A. Gall bladder Q. What is meant by egestion? A. Getting rid of undigested food waste Q. Give one role that the bile salts play in the digestive process. A. Emulsify fats or Neutralise acidic chyme Q. Give two functions of the liver, other than the manufacture of bile. A. Storage of minerals & vitamins; Deamination; Heat generation; Detoxification Q. The hepatic portal vein carries blood from the alimentary canal to the … A. Liver Q. Where in the digestive system are the products of digestion absorbed? A. Small intestine Q. What is meant by peristalsis? A. Muscular contractions in the walls of the alimentary canal to move food Q. Proteins are digested to simpler substances. What are these simpler substances called? A. Amino acids Q. Where in the human alimentary canal is most water absorbed? A. Colon or Large intestine Q. What is meant by a ‘balanced’ diet? A. One which contains all the food types in the correct proportions Q. State one digestive function of the pancreas. A. Produces enzymes or Neutralises chyme Q. Name the blood vessel that joins the small intestine) to the liver. A. Hepatic portal vein Page 44 of 62 3.4.1 - 3.4.4 Homeostasis, Plant Exchange, Breathing System FMQuiz HW Solution Q. What is homeostasis? A. Maintaining a constant internal environment Q. Note one reason why homeostasis is important in the human body. A. Allows normal metabolic activities or Keeps temperature suitable for enzyme reactions Q. What is the function of the stomata of the leaf? A. To allow exchange of gases; Transpiration Q. How does the liver contribute to homeostasis? A. Absorption or release of glucose; Heat generation Q. Name the apertures in stems that are equivalent to stomata. A. Lenticels Q. Name the process by which the gases move in or out of the leaf. A. Diffusion Q. Name the structures in plant cells in which photosynthesis occurs. A. Chloroplasts Q. What is the function of cilia in the trachea? A. Their motion carries trapped dirt particles and bacteria upwards to the glottis Q. Name a gas that leaves the leaf at the stoma(ta). A. Oxygen; Water vapour; Carbon dioxide; Nitrogen Q. In the spongy mesophyll, gases can diffuse throughout the leaf. Name one such gas. A. Air; Water vapour; O; CO2; N2 Q. How do the nephrons of the kidneys contribute to homeostasis? A. Excretion or reabsorption of water; Excretion of salts; Reabsorption of salts Q. Name a factor that influences the diameter of the stoma(ta). A. CO2; Light intensity; Potassium ions; Water Q. Give a function of the guard cell. A. Controls stomatal size; Controls passage of gases Q. Where do cilia occur in the breathing system? A. Trachea Q. State precisely the events that take place in the alveoli. A. Exchange of gases – CO2 out, O2 in by diffusion Q. State the function of the epiglottis. A. To close off trachea Q. Name the process involved in the passage of gas between the alveolus and the blood. A. Diffusion Q. Tiny holes called ... allow gases to enter and leave the leaf. A. Stomata Q. How do the lungs contribute to homeostasis? A. Excretion of water or CO2; Release of heat Q. How are alveoli adapted for their purpose? A. Capillary network; Moist surface; Thin walled; Elastic wall; Large surface area; One cell thick Q. Name the main gas transported in the pulmonary vein. A. Oxygen Q. How is oxygen transported in the blood? A. By oxyhaemoglobin Q. State the function of the larynx. A. To make sound Q. Describe the role of the diaphragm in inhalation. A. Contracts, lowers and increases volume of thorax Page 45 of 62 3.4.4 + 3.4.7 Breathing System FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is the average breathing rate at rest? A. 16 bpm Q. What is the function of the larynx? A. To produce sound Q. Name the process involved in the passage of gas between the alveolus and the blood. A. Diffusion Q. What is the function of the epiglottis? A. Prevent food going down 'the wrong way' Q. Name the blood vessel that returns blood rich in oxygen to the heart. A. Pulmonary vein Q. State a possible effect of smoking on the breathing resting rate. A. Raises rate Q. How did you measure the breathing resting rate? A. Observe; Count; Repeat; Average; Record Q. True or False. Humans receive nitrogen from the air they inhale for protein manufacture. A. FALSE Q. Where is the epiglottis? A. At the back of the throat; Top of oesophagus Q. The trachea contains rings of cartilage. Suggest a function of this cartilage. A. To keep trachea open; Protection of trachea Q. Name the muscles that are used in breathing. A. Diaphragm and intercostal Q. True or False. Humans receive oxygen from the air they inhale. A. TRUE Q. When the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract the volume of the thorax … and the pressure … A. Increases; Decreases Q. Breathing rate in humans is controlled by the concentration of what gas dissolved in the blood? A. Carbon dioxide Q. What is the role of alveoli in the lungs? A. Exchange gases Q. State the location in the human body of the intercostal muscles. A. Between ribs Q. Give one way in which water is lost from the body. A. Sweating; Breathing out water vapour; Urination Q. Give one feature of the alveoli that allows efficient exchange of gases. A. Thin walls; Moist surfaces; Surrounded by capillaries; Large surface area; Expandable Q. What is the function of cilia in the breathing system? A. To trap dirt and bacteria and sweep them upwards to the glottis Q. Outline the steps involved in inhalation. A. Impulse from brain; Diaphragm & intercostal muscles contract; Thorax volume increases; Pressure decreases; Air inhaled Q. What is respiration? A. Controlled release of energy from food, within the cells of an organism Q. When the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax the volume of the thorax … and the pressure … A. Decreases; Increases Q. Where do cilia occur in the breathing system? A. Trachea Q. Name the main gas transported in the pulmonary artery. A. Carbon dioxide Page 46 of 62 3.4.6 Excretory System 1 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is meant by the term excretion? A. Elimination of waste products of metabolism Q. Name the tube/structure that delivers urine outside the body. A. Urethra Q. State the role of the kidneys in homeostasis. A. Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Q. Explain the term glomerular filtrate. A. Plasma that has entered Bowman’s capsule Q. What tube/structure connects the kidney to the bladder? A. Ureter Q. Carbon dioxide is an excretory product. Name a substance from which it is derived. A. Carbohydrate or Fat or Fatty acids Q. Explain the term plasma. A. Liquid part of the blood Q. What is the source of the heat that keeps the body at a fairly constant temperature? A. Respiration Q. Explain why red blood cells are normally absent from glomerular filtrate. A. Too big to pass into Bowman’s capsule Q. From which blood vessel does the renal artery arise? A. Aorta Q. Urea is an excretory product. Name a substance from which it is derived. A. Protein or Amino acid Q. The concentration of glucose is the same in plasma and glomerular filtrate. Why is this? A. Glucose is small or passes through Q. Where in the human kidney does reabsorption take place? A. Proximal convoluted tubule Q. Name the blood vessel that supplies blood to a kidney. A. Renal artery Q. In which cavity of the body are the kidneys located? A. Abdominal or Abdomen Q. Name one substance, other than water, excreted in the urine. A. Urea or Salt or Uric acid Q. Why is glucose normally absent from urine? A. Usually reabsorbed Q. Give a feature of the kidney which indicates that it is an exocrine gland. A. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Q. Mention one method of excretion in flowering plants. A. Diffusion; Leaf fall; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata Q. State two responses that result when body temperature begins to drop. A. Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Q. State two ways in which the body is insulated against loss of heat. A. Fat (adipose tissue); Trapped air or Hair Q. Describe the ways in which the body responds when its internal temperature rises above the normal level. A. Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat less air trapped Q. Explain briefly how sweating assists in the shedding of excess heat A. Sweating places a film of water on the body surface, which is heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Q. What is an endotherm? A. An animal that produces its own body heat or Body temperature independent of temperature of environment Page 47 of 62 3.4.6, 8 Excretory System 2 FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What word is used to describe animals which are not endotherms? A. Ectotherms Q. Suggest an advantage of being an endotherm. A. Temperature always suitable for optimum enzyme activity; Activity independent of environmental temperature Q. What is the main source of a dog’s body heat? A. Respiration Q. Describe the role of the skin in helping to raise body temperature. A. Constriction of blood vessels; Hair stands up; Insulation by subcutaneous fat Q. Name an excretory substance present in urine. A. Urea; Water; Salt Q. Describe the role of the skin in helping to lower body temperature. A. Sweating; Dilation of blood vessels; Hair flat Q. Give a precise target area for the hormone ADH. A. Distal tubule; Collecting duct Q. What is the main source of a lizard’s body heat? A. Environment or The sun or Metabolism Q. To what structure does the ureter link the kidney? A. Bladder Q. Where does filtration occur in the kidney? A. Cortex; Bowman’s capsule Q. What happens to the small arteries (arterioles) in the skin when the external temperature drops? A. Constrict Q. Explain why red blood cells are normally absent from glomerular filtrate. A. Too big to pass into Bowman’s capsule Q. What is meant by osmoregulation? A. Balancing salt or water concentration Q. To which main blood vessel does the renal artery link the kidney? A. Aorta Q. Name the fluid present in the ureter. A. Urine Q. Filtration ensures that cells and valuable substances are not lost from the body when urine is being formed. Name two of these substances or cells. A. Blood cells; Proteins; Glucose Q. List two functions of the skin other than excretion. A. Protection; Melanin production Q. Suggest a treatment that may be used for a person whose kidneys are not carrying out their normal functions. A. Dialysis Q. Name an organ in the human body, other than the kidney, in which excretion takes place. A. Skin; Lungs; Liver Q. Reabsorption of useful substances takes place in the kidney. In what part does this occur? A. Cortex; Medulla; Nephron; Convoluted tubule; Loop of Henle Q. Children typically have higher body temperatures than adults. Suggest a reason for this. A. Higher metabolism; Growing (i.e. more cell division); More active; More infections Q. Why is glucose normally absent from urine? A. Usually reabsorbed Q. From which blood vessel is the afferent arteriole derived? A. Renal artery/arteriole Q. When the water content of the blood drops a hormone is released. Name this hormone and the endocrine gland from which it is secreted. A. ADH (vasopressin); Pituitary Page 48 of 62 3.5.2 Plant Responses FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. State a location in a flowering plant where a growth regulator is secreted. A. Apical meristems of shoots Q. Name the group of substances in plants which control responses to external stimuli. A. Plant growth regulators or auxins Q. Give an example of the use of a synthetic growth regulator. A. Rooting powder; Weed killer; Ripening of fruit; Seedless fruits Q. Suggest a benefit to the plant of phototropism. A. Photosynthesis Q. Give locations for two meristems in plants. A. Root tip; Shoot tip; Bud; Embryo; Seed Q. What is an auxin? A. A growth regulator in plants Q. What growth regulator did you use when investigating plant growth? A. IAA Q. Define tropism. A. Growth response of plant to a stimulus Q. List three types of tropism. A. Thigmotropism; Phototropism; Geotropism; Hydrotropism; Chemotropism Q. State two ways in which growth regulators in plants are similar to hormones in animals. A. Chemical in nature; Made at one site & function at another; Transport slow / in vascular tissue Q. List three methods used by plants to protect themselves from adverse external environments. A. Thorns; Stinging cells; Leaf fall; Perennation; Dormancy Q. Give the term used for the growth response by a plant shoot to unidirectional light. A. Phototropism Q. TRUE or FALSE. The growth response of a plant to touch is called thigmotropism. A. TRUE Q. Define thigmotropism. A. Growth response of a plant to touch Q. Give an example of a growth regulator that promotes growth. A. Auxin; IAA; NAA; Ethene Q. Give an example of a growth regulator that inhibits growth. A. Auxin; IAA; NAA; Abscisic acid; Ethene Q. Name the plant used when you investigated the effect of a growth regulator on plant tissue. A. Cress Q. Name the growth response of roots growing towards water. A. Hydrotropism Q. What do you understand by the term adverse external environment? A. Surroundings that are harmful to organism(s) Q. Define Chemotropism A. Growth response of a plant to chemicals Q. Through which part of a stem are growth promoters transported? A. Vascular bundles / tissue Q. For what purpose did you use IAA in the course of your practical activities? A. To examine the effect of growth regulators on plants Q. Shoots grow away from gravity. This is an example of … A. Negative geotropism Q. How would you make up solutions of different concentrations from a stock solution of IAA? A. Serial dilution Page 49 of 62 3.5.3 + 7 Defence System FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is meant by the term immunity? A. The ability of the body to resist infection Q. How does the skin help to defend the body against pathogenic micro‑organisms? A. Contains the enzyme lysozyme – a bactericidal agent; Continuous unbroken covering Q. What is the purpose of vaccination? A. To induce immunity Q. True or False. Immunity that results from vaccination is effectively the same as the immunity that develops following an infection. A. TRUE Q. What is meant by the term active immunity? A. Long-term immunity resulting from the production of antibodies; Q. Give a role of memory T-cells. A. Recognise and destroy infected or damaged cells; Memory activation; Suppress immune system Q. Give an example of a beneficial application of a virus. A. Bacteriophage; Used in genetic engineering; Vaccine production; Vector in disease treatment Q. Give a role of helper T-cells. A. Stimulate B cells; Stimulate killer T cells; Recognise antigens Q. Name a virus whose activity poses a major threat to human health. A. HIV Q. What is meant by the term passive immunity? A. Recipient receives antiserum, containing antibodies, from an already immunised individual Q. What is meant by the term antigen? A. Substance on cell membrane; Surface of virus or bacteria; Foreign substance that causes antibody production Q. What is meant by the term antibody? A. Substance produced in response to presence of antigen Q. What is the role of antibodies in the body? A. To inactivate antigens Q. Give a role of Killer T-cells. A. Destroy infected or damaged cells Q. What is meant by the term vaccination? A. ‘Safe dose’ of a pathogen, causing antibody production or an immune response Q. Give a role of suppressor T-cells. A. Switch off immune system Q. To which group of blood cells do lymphocytes belong? A. White blood cells Q. How is HIV transmitted? A. Sexual contact Q. Give a role of T-cells. A. Act in one of four processes as helper Tcells, killer T-cells, suppressor T-cells or memory T-cells Q. Give a role of B-cells. A. Produce antibodies Q. Name the two main chemical components of a virus. A. DNA or RNA; Protein Q. Comment on the difficulty of describing a virus as a living organism. A. Non-cellular; One nucleic acid; Obligate parasite; No metabolism; Do not possess organelles Q. Give one example of the use of hormone supplements. A. Treatment of diabetes; Contraception Q. Name two diseases of humans caused by viruses. A. Smallpox; Chicken pox; Measles; Polio; ‘Flu; Common cold; Leaf mosaic; AIDS or HIV; Mumps; Rubella; Rabies Page 50 of 62 3.5.3 Endocrine & Musculoskeletal System FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is an exocrine gland? A. A ducted gland Q. Name one disorder of the musculoskeletal system. A. Arthritis; Osteoporosis Q. Name a product of the endocrine portion of the pancreas. A. Insulin; Glucagon Q. State two ways in which hormone action differs from nerve action. A. Chemical transmission; Slower action; Longer lasting effect; Many target organs Q. What is an endocrine gland? A. A ductless or hormone producing gland Q. Explain what is meant by the axial skeleton? A. Vertebral column and skull & rib cage Q. Give a function of red marrow. A. Formation of blood cells Q. Give a deficiency symptom of insulin. A. Diabetes mellitus Q. What is a hormone? A. A chemical messenger; Product of endocrine gland Q. State two ways in which hormones are similar to plant growth regulators. A. Produced in one location; Acts in different location; Prolonged effect Q. Give two examples of the use of hormone supplements. A. Treatment of diabetes; Contraception Q. What is meant by an antagonistic muscle pair? A. Pair of muscles that have opposite effects Q. Give a function of cartilage. A. Protection; Absorbs shock; Reduces friction Q. Where are the discs in the human backbone? A. Between the vertebrae Q. Give a function of a tendon. A. Joins muscle to bone Q. Hormones are secreted by … glands. A. Endocrine Q. What is the function of the discs in the human backbone? A. Shock absorption; Friction-free movement; Prevention of wear and tear Q. State one way in which hormone action differs from nerve action. A. Slower to act; More sustained; Chemical in nature Q. What is the role of Yellow bone marrow? A. Fat storage Q. What is meant by feedback in relation to hormone action? A. When the level of a hormone in the blood controls the production of another or itself Q. Give two functions of the human skeleton. A. Strength; Support; Shape; Mobility; Protection; Muscle attachment; Blood cell production Q. Name a long bone in the human body. A. Femur; Tibia; Fibula; Humerus; Radius; Ulna Q. What is the role of Red bone marrow? A. Blood cell formation Q. State a function of spongy bone. A. Strength; Rigidity; Makes marrow Page 51 of 62 3.5.3 Eye & Ear FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is the function of the semi-circular canals? A. Balance Q. Suggest a reason why two eyes are better than one. A. Increased visual field; To judge distance (depth); 3D vision Q. What is the function of the cochlea? A. Hearing Q. What is connected to the middle ear by the Eustachian tube? A. Throat Q. What surrounds the bones in the middle ear? A. Air Q. Name two sense organs, other than the ear and the eye, in the human body. A. Skin; Tongue; Nose Q. What is the function of the lens of the eye? A. To focus light onto the retina Q. What is the function of the retina of the eye? A. To convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Q. Outline the role of the suspensory ligaments in vision. A. Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Q. In which part of the ear are nerve impulses generated? A. Cochlea or semi-circular canals Q. In which part of the eye are nerve impulses generated? A. Retina Q. Suggest one way by which the ear may be protected. A. Skull / bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Q. The hammer (malleus) is a very small bone located in the ... A. Ear Q. Which is present in the middle ear, gas or liquid? A. Gas Q. In which part of the eye would you find rods and cones? A. Retina Q. Outline the role of the cones in vision. A. Detect colour Q. What is the function of the Eustachian tube? A. To equalise pressure on the eardrum Q. Outline the role of the optic nerve in vision. A. Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Q. TRUE or FALSE. The semi-circular canals in the ear are involved in balance. A. TRUE Q. Outline the role of the brain in vision. A. Interprets information received from retina Q. Name the coloured part of the eye. A. Iris Q. Explain how the iris works. A. Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Q. What is the function of the pupil in the eye? A. To allow light in Q. Name the type of chemical that carries messages between two neurons. A. Neurotransmitter Page 52 of 62 3.5.3 Musculoskeletal System FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Give two functions of the human skeleton. A. Strength; Support; Shape; Mobility; Protection; Muscle attachment; Blood cell production Q. Name one disorder of the musculoskeletal system. A. Arthritis; Osteoporosis Q. Explain what is meant by the axial skeleton? A. Vertebral column and skull & rib cage A. Fat storage; Can convert to red marrow Q. Name a long bone in the human body. A. Femur; Tibia; Fibula; Humerus; Radius; Ulna Q. State a function of spongy bone. A. Strength; Rigidity; Makes marrow Q. State a function of medullary cavity. A. Makes (yellow) marrow; Stores fat; Makes blood cells Q. Bones are joined to other bones by ... A. Ligaments Q. Give a function of Red marrow. A. Formation of blood cells Q. A pair of muscles that have opposite effects are called … A. Antagonistic muscle pair Q. Give a function of Cartilage. A. Protection (absorbs shock); Reduces friction; Allows bone elongation Q. Name the vertebrae found in the neck. A. Cervical Q. Name the part of the central nervous system that runs through the vertebrae. A. Spinal cord Q. A tendon joins ......... to bone. A. Muscle Q. Where are the discs in the human backbone? A. Between the vertebrae Q. Give a function of synovial fluid. A. Lubrication; Shock absorption; Protection Q. Where are thoracic vertebrae found? A. Back of chest Q. Name the vertebrae found in the small of the back. A. Lumbar Q. Muscles are joined to bones by... A. Tendons Q. Which upper arm muscle contracts to raise the lower arm? A. Biceps Q. Where are caudal vertebrae found? A. Tail end of spinal column Q. What is the function of the discs in the human backbone? A. Shock absorption; Friction-free movement; Prevention of wear and tear Q. Name the type of joint at the elbow. A. Hinge; Synovial Q. Suggest one reason why the bones of birds are almost hollow. A. To be light; To allow flight Q. Give a role of Yellow bone marrow. Page 53 of 62 3.5.3 Nervous System FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. True or False. Motor neurons conduct impulses towards the central nervous system. A. FALSE A. Language; Reason; Consciousness; Senses; Memory; Intelligence; Emotions Q. What is a neuron? A. Nerve cell Q. What is grey matter? A. Cell bodies of neurons; Few axons; Little myelin Q. Briefly explain the role of neurotransmitter substances. A. Carries impulse across synaptic cleft and triggers impulse in next neuron Q. What are interneurons or association neurons? A. Nerves that link two neurons Q. State a function for the Myelin sheath. A. Insulation; Protection; Speeds impulse Q. State one function of the hypothalamus of the brain. A. Homeostasis; Endocrine function Q. Give a function of dendrites. A. Receives and carries impulses to the cell body Q. What is white matter? A. Many axons; Much myelin; Few cell bodies Q. What is a sensory neuron? A. Nerve that carries impulse from receptor towards CNS Q. State one function of the cerebellum of the brain. A. Movement; Balance; Coordination Q. State a function for Schwann cells. A. Produces myelin sheath Q. What term is used for glands that secrete hormones? A. Endocrine Q. What is the central nervous system? A. Brain and spinal cord Q. State one function of the medulla oblongata of the brain. A. Involuntary muscle control Q. TRUE or FALSE. A motor neuron carries impulses to the brain. A. FALSE Q. Name the small gaps between neurons. A. Synaptic cleft; Synapse Q. What is peripheral nervous system? A. Nerves leading to and from CNS; Nerves not in CNS Q. What is a motor neuron? A. Nerve that carries impulse away from CNS to effector Q. Give one way in which a nervous response differs from a hormonal response. A. Faster; Shorter-lived; Electrical in nature Q. State one function of the cerebrum of the brain. Q. Neurons produce neurotransmitter substances. What is their function? A. To carry impulse across synapse Q. Give an example of a reflex action in humans. A. Knee-jerk Q. Why are reflex actions important in humans? A. Fast response; Defence against injury Page 54 of 62 3.6.1 Asexual, Flower Structure, Gamete Formation FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What is meant by vegetative propagation? A. Reproduction that does not involve the production of seed Q. Give examples of natural vegetative propagation that involve different parts of a plant. A. Rhizomes; Corms; Root & stem tubers; Bulbs Q. List techniques of artificial vegetative propagation that are used for flowering plants. A. Cuttings; Layering; Grafting; Budding; Tissue culturing A. One fuses with “egg” nucleus other fuses with primary endosperm nucleus or polar nuclei Q. Are the products of vegetative propagation clones? A. Yes Q. Two male gametes are derived from the generative nucleus. Do these gametes form as a result of mitosis or meiosis? A. Mitosis Q. State a role of the sepal. A. Protection; Photosynthesis Q. What is the function of the petal? A. Attraction of insects Q. What is the role of the stigma? A. Traps (catch) pollen; Where pollen lands Q. Suggest one advantage of artificial propagation. A. Fast; Preserves desirable features; Cheap; More reliable Q. Name a part of a flower from which a fruit develops. A. Carpel; Ovary Q. Give two differences between vegetative propagation and propagation involving seeds. A. No gametes (one parent); Identical plants; Rapid production; No outside agent Q. What term is used for the type of asexual reproduction that produces a daughter plant by runners? A. Vegetative propagation Q. Would you expect a daughter plant produced by a runner to be haploid or diploid? A. Diploid Q. Name the two main types of reproduction. A. Sexual & Asexual Q. What is the role of the stigma? A. Receives pollen Q. Give two ways in which the petals may be adapted for their function. A. Colour; Scent; Size; Shape Q. Describe the development of pollen grains from microspore mother cells. A. Meiosis, 4 haploid microspores, divides by mitosis, tube and generative nucleus, pollen grain matures Q. What happens to the two polar nuclei? A. Fuse with male gamete nucleus to form triploid endosperm nucleus Q. State what happens to the ovule after fertilisation. A. Becomes the seed Q. Suggest one disadvantage of artificial propagation. A. Lack of variation; Diseases inherited Q. State a role of the ovary. A. Produces (contains) ovule or embryo sac or female gametes; Becomes fruit; Site of fertilisation Q. Describe the fate of the two male gamete nuclei. Q. State a role of the anther. A. Pollen production, storage and release Q. True or False. Endosperm is a food reserve in some seeds. A. TRUE Page 55 of 62 3.6.1 Dormancy & Germination FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. State a difference between the seeds of monocots and dicots other than the number of seed leaves. A. Food store as endosperm; No endosperm A. Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen Q. For what purpose is oxygen needed in germination? A. Aerobic respiration Q. True or False. Light is essential for the germination of seeds. A. FALSE Q. Seeds may remain inactive for a period before germination. What term is used to describe this period of inactivity? A. Dormancy Q. What is dormancy? A. Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Q. What term is given to the growth of an embryo into a plant? A. Germination Q. What is meant by germination? A. Growth of seed or embryo Q. Why is digestion necessary in a germinating seed? A. To make food soluble and transportable Q. What is an agar plate? A. Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Q. Suggest one way in which knowledge of dormancy is useful to farmers and gardeners. A. Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Q. Suggest two advantages of dormancy. A. Germination at suitable time; Survival of plant during unfavourable conditions Q. Why is it necessary for plants to disperse their seeds? A. Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Q. After fertilisation, what part of the flower becomes the fruit? A. Ovary Q. Name the stage in the plant’s life cycle that follows dormancy. A. Germination; Growth Q. For what purpose is water needed in germination? A. Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Q. For what purpose is a suitable temperature needed in germination? A. Optimum enzyme activity Q. State a use for a water bath in biological investigations. A. Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Denaturing enzyme; Heating Q. From what does a seed develop? A. Ovule Q. What type of agar plates did you use when investigating the digestive activity of seeds? A. Milk or Starch Q. How did you demonstrate the requirement for oxygen when investigating the factors necessary for seed germination? A. Anaerobic jar Q. State one method that is used to produce seedless fruits. A. Growth regulator; Selective propagation Q. State two locations in the seed where food may be stored. A. Cotyledon; Endosperm Q. What is the role of the fruit? A. Reproduction; Seed dispersal Q. State three environmental factors that are necessary for germination. Page 56 of 62 3.6.1 Fruit Formation & Dispersal FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. From what does a seed develop? A. Ovule Q. What is a non-endospermic seed? A. Main food store is in cotyledons Q. What is an endospermic seed? A. Main food store is in the endosperm Q. What is the next step after pollination in the lifecycle of the plant? A. Fertilisation Q. State one method that is used to produce seedless fruits. A. Growth regulator; Selective propagation Q. From what structure in the carpel does the seed develop? A. Ovule Q. State two locations in the seed where food may be stored. A. Cotyledon; Endosperm Q. The radicle of the embryo will develop into the … A. Root Q. Give two methods of fruit and seed dispersal. A. Wind; Animal; Self; Water Q. Name a carbohydrate that you would expect to be present in the food store of a seed. A. Starch Q. The plumule of the embryo will develop into the … A. Shoot Q. Give two advantages of fruit and seed dispersal to a plant. A. Colonisation; Reduces competition Q. What is meant by fertilisation? A. Fusion of gametes; Formation of zygote Q. What is a cotyledon? A. A ‘seed leaf’, i.e. the first leaf that develops in the embryo. It is a food store Q. Name a monocotyledon. A. Grass, Maize, etc. Q. To which part of a flower is pollen carried? A. Stigma of the carpel Q. Some flowers have nectaries. How are these flowers pollinated? A. Insects Q. Name a dicotyledon. A. Broad bean, Peanut, Pea, etc. Q. Give an example of a plant that uses wind as a method of seed dispersal. A. Dandelion; Sycamore Q. What is the role of the fruit? A. Reproduction; Seed dispersal Q. Name a part of a flower that may develop into a fruit. A. Ovary Q. Give an example of a plant that uses animals as a method of seed dispersal. A. Blackberry; Burdock Q. Suggest why cross-pollination is preferable to self-pollination. A. Increases variation; Reduces chance of genetic problems Q. What is an embryo? A. Part of seed that becomes the new plant Page 57 of 62 3.6.1 Pollination & Fertilisation FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. What happens to the two polar nuclei? A. Fuse with male gamete nucleus to form triploid endosperm nucleus Q. To which part of a flower is pollen carried? A. Stigma of the carpel Q. What happens to the ovary after fertilisation? A. Becomes the fruit Q. What happens to the ovule after fertilisation? A. Becomes the seed Q. True or False. Endosperm is a food reserve in some seeds. A. TRUE Q. Give one location in a seed in which food is stored. A. Endosperm; Cotyledon; Nucellus Q. What is fertilisation? A. Fusion of gametes; Formation of zygote Q. What is pollination? A. Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma Q. From which structure in the seed did the root develop? A. Radicle Q. Name a carbohydrate that you would expect to be present in the food store of a seed. A. Starch Q. How are wind-pollinated flowers adapted? A. No colours; No scent; No nectar; Small or no petals; Long stamens; Long feathery stigmas Q. Give two ways in which pollen may be transported to another flower. A. Wind; Insect; Artificial Q. Name a structure through which the pollen tube grows in order to reach the embryo sac. A. Stigma; Style; Ovary; Micropyle Q. What forms in the ovary of a flower after pollination and fertilization? A. Seed; Zygote; Embryo; Food reserve Q. In which part of a flower does a seed form? A. Carpel; Ovary Q. What process follows pollination in the life cycle of a flowering plant? A. Fertilisation Q. Some flowers have nectaries. How are these flowers pollinated? A. Insects Q. What is the difference between selfpollination and cross-pollination? A. Occurs on same plant or flower; Occurs between plants of same species Q. Name the part of the flower where fertilisation occurs. A. Embryo sac; Ovule; Ovary Q. Suggest a substance that flowers produce that may cause hay fever in some people. A. Pollen Q. Name two ways in which cross-pollination happens. A. Wind; Insect Q. Suggest why cross-pollination is preferable to self-pollination. A. Increases variation; Reduces chance of genetic problems Q. What is the function of the sepals? A. Protection; Photosynthesis Q. In which part of the flower is pollen produced? A. Anther; Stamen Page 58 of 62 3.6.2 Birth, Breastfeeding, Infertility & Birth Control FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Name two female hormones that have a role in the menstrual cycle. A. Oestrogen; Progesterone; FSH; LH Q. Outline how birth occurs. A. Change in hormone levels; Contractions; Waters break; Cervix dilates; Delivery; Cord cut; Afterbirth Q. What happens to the menstrual cycle when a woman reaches the menopause? A. It stops Q. Explain the term implantation. A. Embedding of embryo in endometrium Q. When may it be considered that the process of fertilisation is complete? A. When the male and female nuclei have fused Q. Give one change experienced by the mother that indicates to her that the birth process is starting. A. Contractions; Waters break Q. Where does fertilisation normally occur in the reproductive system of the human female? A. Half way along Fallopian tube Q. State one cause of infertility in the female. A. Hormonal; Blockage; Failure to ovulate Q. What is meant by in vitro fertilisation? A. Fertilisation outside the body Q. What is fertilisation? A. Fusion of gametes Q. What is meant by contraception? A. Prevention of fertilisation or implantation or pregnancy Q. Name a hormone associated with the maintenance of the placenta. A. Progesterone Q. Where does implantation occur in the human female reproductive system? A. Uterus Q. For how long will sperm survive in the female reproductive tract? A. Up to seven days Q. For how long do ova remain viable? A. Up to two days Q. From what is the placenta formed? A. Embryonic and uterine tissues Q. Give two biological advantages of breastfeeding. A. Transfer of antibodies; Balanced diet; Bonding; Contraception; Correct temperature; Milk sterile Q. Give an account of the importance of the placenta during human development in the womb. A. Transport in/out; Barrier (plasma proteins, etc.); Produces progesterone Q. Where does meiosis occur in the human female reproductive system? A. Ovary Q. State one cause of infertility in the male. A. Low sperm count; Hormonal Q. Give an example of a surgical method of male contraception. A. Vasectomy Q. What is done with the products of in vitro fertilisation? A. Implanted in a womb; Stored for future use; Destroyed Q. List three methods of contraception other than surgical. A. Condom; Pill; IUD; Diaphragm; Spermicide; Implants Q. Where is FSH produced? A. Pituitary Page 59 of 62 3.6.2 Structures & Hormones FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Where is testosterone secreted in the body of the human male? A. Testis Q. Where in the human female reproductive system does meiosis occur? A. Ovary Q. Give a brief account of the role of testosterone. A. Development of secondary sexual characteristics; Development of sex organs; Sperm production Q. What is the menstrual cycle? A. Monthly cycle in female; Lining of uterus (endometrium) shed; Blood discharged Q. Where are sperm produced? A. Testis Q. Name a gland that secretes seminal fluid. A. Cowper’s gland; Seminal vesicles; Prostate gland Q. Where does meiosis occur in the human male reproductive system? A. Testis Q. State a function of seminal fluid. A. Allows sperm to swim; Provides nutrients; Lubricant; Protects sperm Q. Where in the human female reproductive system does zygote formation occur? A. Fallopian tube Q. Where are sperm stored in the human male reproductive system? A. Epididymis Q. What is semen? A. Sperm cells and seminal fluid Q. State two secondary sexual characteristics of the human male. A. Broken voice; Body hair; More muscle; Enlargement of testes; Enlargement of penis Q. What maintains the secondary sexual characteristics in the adult human male? A. Testosterone Q. In which part of the human female reproductive system is the ovum (egg) formed? A. Ovary Q. Where in the human female reproductive system does implantation occur? A. Uterus Q. What happens in the womb during menstruation (days 1 – 5)? A. Loss of blood; Loss of endometrium Q. Explain the term ovulation. A. Release of egg from ovary Q. What is the function of the prostate gland? A. Seminal fluid production; Nutrition of sperm Q. What is the function of the sperm duct? A. To carry sperm Q. State two ways in which sperm differ from ova (eggs). A. Size; Shape; Motile; Chromosomal difference Q. What term is used for the time in a young person’s life when physical changes that distinguish the sexes take place? A. Puberty Q. What is the function of the midpiece of the sperm? A. Respiration; Produce energy Q. What is meant by the fertile period? A. Time when fertilisation is possible; When egg is in oviduct Q. Where does fertilisation occur in the female body? A. Oviducts Page 60 of 62 3.6.4 + 5 Embryo Development & Menstrual Cycle FMQuiz Homework Solution Q. Where is FSH produced? A. Pituitary Q. Give one function of FSH. A. Production of follicle (egg); Stimulate oestrogen production Q. What is the role of oestrogen in the menstrual cycle? A. Repairs endometrium; Inhibits FSH; Stimulates LH Q. What is the role of progesterone in the menstrual cycle? A. Maintenance of endometrium; Inhibits FSH; Inhibits LH Q. Explain what is meant by germ layers? A. Layer of cells in the blastula (embryo); Give rise to specific tissues or organs Q. Which part of the female reproductive system is influenced by both FSH and LH? A. Ovary; Follicle Q. By which type of cell division does the zygote divide? A. Mitosis Q. What is the next developmental stage after the morula? A. Blastocyst Q. What is the morula? A. Solid ball of cells Q. What is meant by the term infertility? A. Inability to produce offspring Q. Name a tissue that the ectoderm gives rise to. A. Skin; Nails; Hair; Nervous system Q. What is a placenta? A. Structure attached to inner surface of the womb of pregnant mammals, helps to nourish the foetus, and discharges its waste Q. Name a tissue that the mesoderm gives rise to. A. Muscles; Skeleton; Excretory system; Respiratory system; Circulatory system Q. Explain the term implantation. A. Embedding of embryo in endometrium Q. From what tissues does a placenta form? A. Uterine and embryonic tissue Q. What is meant by in-vitro fertilisation? A. Sperm and egg fuse outside the body Q. Describe the amnion. A. Sac; Membrane Q. What is the role of the amnion? A. Holds; Produces fluid; Protects embryo or foetus Q. What is the blastocyst? A. Fluid-filled or hollow ball of cells Q. What is meant by fertilization? A. Fusion of gametes; Formation of zygote Q. Name a tissue that the endoderm gives rise to. A. Inner lining of gut or named part of; Liver; Pancreas Q. In which part of the human female reproductive system does fertilization occur? A. Fallopian tube; Oviduct Q. Explain the importance of the amnion for the foetus. A. Contains amniotic fluid; Protects embryo Q. What is meant by the fertile period? A. Time when fertilisation is possible; When egg is in oviduct Page 61 of 62 Page 62 of 62