Earth's Layers Study Guide: Earthquakes & Structure
advertisement

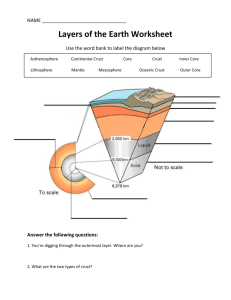
Answer Key Earth’s Layers Study Guide 1. Which layer of the Earth’s interior has the most volume? mantle 2. Describe the crust. The rigid, outermost layer of the Earth 3. What makes up the lithosphere? The crust and upper mantle 4. Which layer of the Earth do the tectonic plates move on top of? The asthenosphere (the middle mantle 5. Which two metals are the inner and outer core mostly made of? Iron and nickel 6. How is the outer core of Earth different from the inner core? the inner core is solid while the outer core is liquid 7. Scientists study different parts of earthquakes and how they are related. This illustration shows a cross section of the lithosphere when an earthquake is taking place. Where would the strongest effects of this earthquake be felt? What is the term for this location? What is happening at point “A”? Earthquake would be strongest at point B which is the epicenter. Point A is the focus. 8. How does energy travel through Earth’s crust after an earthquake? Through the crust as seismic waves 9. A tsunami is massive wave that can cause a tremendous amount of damage to land masses. What causes a tsunami? An earthquake on the ocean floor. 10.What causes an earthquake? The sudden release of accumulated strain at a plate boundary 11.Complete the table below comparing the oceanic and continental crust. Feature Location Main elements Density Thickness Oceanic crust Beneath the ocean and under continental crust oxygen, silicon, aluminum Higher density than continental crust Thinner than continental crust Continental crust Continental land masses oxygen, silicon, aluminum Lower density than oceanic crust Thicker than oceanic crust 12.What is the relationship between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere? The lithosphere floats on top of the asthenosphere and convection currents in the asthenosphere move the lithosphere across Earth’s surface. 13.Which of earth's spheres is best represented by the following diagram? geosphere 1 2 3 4 14.Think back to the lesson on the fundamental force of nature. What is one of the possible reasons that the core of the Earth is so hot? Weak nuclear force – radioactive decay occurring in the core 15.Describe the asthenosphere. Slow moving, hot, plastic like liquid rock located under the lithosphere 16.What do geologists believe is the source of the Earth’s magnetic field? The slow flowing of the iron and nickel in the Earth’s outer core 17.How do scientists know what Earth’s interior looks like? Studying seismic waves as they travel through the Earth 18.What is the difference between compression and rarefaction? Compression is the squeezing together of the wavelengths while rarefaction refers to it spreading out. Use the diagram of the wave below to answer questions 19 and 20. 19.What type of wave is diagrammed above? transverse 20.What do the labeled parts represent? S – crest T – amplitude W – wavelength X – trough