American Cultures * 6
advertisement

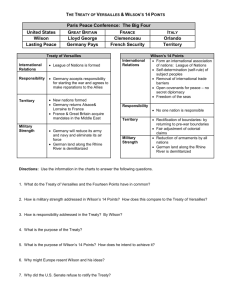
American Cultures – 6.0 Mr. Maurer World War I – Test Review THE GREAT WAR (p. 649 - 653) The Guns of August: 1. Explain how nationalism, imperialism, and the system of alliances in Europe all helped cause World War I. American Neutrality: 2. What was President Wilson’s official response when war broke out? 3. How did most American’s feel about the United States role in the war when war broke out in 1914? 4. What factor made it most difficult for America to maintain its neutrality during the war? 5. What was the single most important factor in the United States’ decision to join the war against Germany? Preparedness and Peace: 6. How did President Wilson respond to the sinking of the Lusitania and the Sussex? Safe for Democracy: 7. What was the single most important factor in the United States’ decision to join the war against Germany? 8. Why did Germany resume the use of unrestricted submarine warfare in 1917? 9. What reasons did President Wilson emphasize for going to war? 10. Identify and explain: the Zimmerman Note AMERICAN MOBILIZATION (p. 653 - 657) Selling the War: 11. Describe how the Committee for Public Information (CPI) sold the war to the American public. 12. What were the consequences of the CPI campaign? “You’re in the Army now”: 13. Identify and explain: Selective Service Act Racism in the Military: 14. Describe the circumstances under which African Americans served in the United States military during World War I Americans in Battle: 15. Explain the role that American troops actually played in fighting World War I. OVER HERE (p. 657- 663) Organizing the Economy: 16. Describe the relationship between government, business, and labor during the war. 17. Describe how the U.S. government raised the money necessary to fight the war. The Business of war: 18. Describe the effects World War I had on the American economy. 19. Describe the economic effects of World War I on big business, women, moderate labor unions (e.g. the AFL), and radical labor unions (e.g. the IWW). Labor and the War: 20. What happened to the more radical elements of the labor movement and specifically to the IWW? Women at Work: 21. What types of jobs did women take in support of the war effort? 22. What effect did war production have on women workers? 23. What happened to jobs for women at the war’s end? Prohibition 24. Identify and explain: Prohibition 25. How did American involvement in World War I help the Prohibitionist cause? 26. Explain how the passage of the income tax in 1913 helped make Prohibition possible. (from video) 27. Explain why prohibition advocates were anxious to get it passed before 1920. (from video) Muzzling Dissent: The Espionage and Sedition Act 28. Identify: The Espionage and Sedition Acts… Explain how these acts were used to control dissent for the war effort. 29. Identify: Schenk v. U.S., Debs v. U.S., and Abrams v. U.S. What was the common element in all these cases? 30. Summarize the main points Eugene Debs’ speech in Canton, Ohio. The Great Migration and Racial Tensions: 31. What was the Great Migration and how did it increase racial tensions? 32. What did many African American leaders feel would happen as a result of supporting the war effort? What happened instead? Labor Strife: 33. Why did the labor peace established during the war come to an abrupt end by 1919? 34. How did most Americans view the strikes? AN UNEASY PEACE (p. 666-671) The Fourteen Points: 35. Identify: The Fourteen Points… Explain the main ideas associated with the Fourteen Points. 36. What was the most controversial of Wilson’s 14 Points? Wilson in Paris: 37. How successful was Wilson in establishing his Fourteen Points as the basis of Treaty of Versailles? Explain. The Treaty Fight: 38. What was the end result over the battle over ratification of the Treaty of Versailles? 39. What did Wilson argue was the most important element of the Treaty of Versailles? 40. Who were Wilson’s strongest opponents in the fight over ratification? 41. How did Wilson attempt to raise public support for the treaty? What was the result? 42. What reason did Republicans in the Senate give for opposing U.S. membership in the League of Nations? The Russian Revolution and America’s Response: 43. What happened in Russia during the war? 44. Who took control of Russian and what actions did they take related to the war? 45. What was Wilson’s response to the developments in Russia? The Red Scare: 46. What was the Red Scare and what caused it? 47. Who was targeted by the government during the Red Scare?