module specification template - Activating your university user account
advertisement

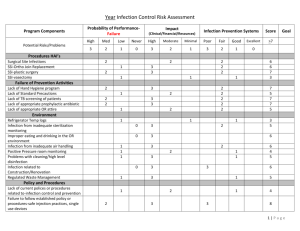
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module title Infection Prevention and Control Module code NA6163 Credit value 20 Level Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Mark the box to the right of the Level 0(for modules at foundation appropriate level with an ‘X’ level) × Level 7 Level 8 Entry criteria for registration on this module Pre-requisites Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Co-requisite modules Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Normal Course entry requirements apply. Module delivery Mode of delivery Taught Other × Distance Placement Pattern of delivery Weekly × Block Other Online When module is delivered Semester 1 × Semester 2 Throughout year Other Brief description of module This module will enable practitioners to develop existing infection content and/ or aims prevention and control practice in their clinical area, using research and Overview (max 80 words) evidence based theoretical knowledge. The module will demonstrate how micro- organisms, host factors, clinical interventions and the care setting interact with and contribute to patterns of infection. The implementation of infection prevention and public health systems in a variety of settings will be considered in relation to local, national and international infection control challenges. Module team/ author/ Michele Dryden (Module Leader), Shelia Loveridge, Martin Still, Karen coordinator(s) Butler, Tina Lloyd. School SNM Site/ campus where Falmer delivered Course(s) for which module is appropriate and status on that course Course BSc (Hons) Professional Practice BSc (Hons) Nurse Practitioner BSc (Hons) Community Specialist Practice Status (mandatory/ compulsory/ optional) Optional Optional Optional MODULE AIMS, ASSESSMENT AND SUPPORT Aims To be able to identify infection control risks within own area of practice. To critically analyse the theories relating to infection prevention and control in order to develop appropriate strategies for practice. Learning outcomes On successful completion of the module the student will be able to : 1. Demonstrate an in- depth understanding of how micro organisms are transmitted, multiply and cause harm. 2. Demonstrate wide ranging knowledge of physiological defence mechanisms, and their response to infection. 3. Critically analyse the wider public health agenda and its application to practice. 4. Critically explore and analyse behaviours or situations that contribute to infection prevention and control. 5. Demonstrate a change management approach to their own area of practice in relation to infection prevention and control. 6. Develop an in depth understanding of microbiology and patterns of infection within a wider public health context, taking into account national policies and the political agenda. Content Learning support Frameworks for change management. Epidemiology and surveillance. The role of Public Health England. Principles of microbiology. Mechanisms of bacterial and viral infection Immunity and consequences of infection. Emerging infections Legal and ethical issues in infection control Actions taken to break the chain of infection Audit and evidence based practice in infection control A good range of library resources, specialist websites and online learning resources support student learning. Up-to-date reading lists, suggested websites, journals and online learning resources will be provided on commencement of the module, using studentcentral. Indicative Reading Latest editions of the following texts: Burnett, E. 2011. Outcome Competences for Practitioners in Infection Prevention and Control. [online] Available from: http://bji.sagepub.com/content/early/2011/02/07/1757177410395797.ful l.pdf+html [05.04.2012] Hawker, J.et al. 2012. Communicable Disease Control Handbook, 3rd Ed. Blackwell Publishing. Infection Prevention Society. 2012.Quality Improvement Tools [online] available from: http://ips.uk.net/template1.aspx?PageID=84&cid=91&category=QualityImprovement-Tool- [accessed 15.01.2013] NICE. 2012.Infection Control. Prevention of healthcare-associated infection in primary and community care. DOH London. Available from: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG139 [10.02.2012] Skills for Health. 2011. Infection Prevention and Control. Staff Working Together. [online] Available from: http://www.skillsforcare.org.uk/nmsruntime/saveasdialog.aspx?lID=111 74&sID=2694 [10.02.2012]. World Health Organisation. 2013.Cleaner Care is Safer Care [online] available from: http://www.who.int/gpsc/en/ [accessed 15.01.2013 Key Websites: http://www.dh.gov.uk http://www.hpa.org.uk/ - Public Health England Key Journals: Journal of Infection Prevention Journal of Hospital Infection British Journal of Nursing (Infection Control supplement) Teaching and learning activities Details of teaching and learning activities Teaching and learning activities to include: Keynote lecturers Group discussion Case Scenarios linked to practice. E-learning resources on student central Tutorials Student Presentations Allocation of study hours (indicative) Where 10 credits = 100 learning hours SCHEDULED This is an indication of the number of hours students can expect to spend in scheduled teaching activities including lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshops/ studios, fieldwork, external visits, and work-based learning. Study hours GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY All students are expected to undertake guided independent study which includes wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, the completion of assessment tasks, and revisions. 140 PLACEMENT The placement is a specific type of learning away from the University that is not work-based learning or a year abroad. TOTAL STUDY HOURS 60 200 Assessment tasks Details of assessment for this module 1. A presentation (10 Minute) of an evidence based Risk assessment of a pertinent issue in infection control from the practitioner’s area of practice. Identifying the nature of the risk (common organisms and methods of transmission) and for whom (e.g. immunocompromised or critically ill patients). This will include an action plan of recommendations to your manager to reduce the risk in terms of physical interventions, equipment, education, and resources. This should include estimates of cost, time required and outcome measures as appropriate. (LOs: 1, 2, 6) 2. A 2,500 word reflective account (using a framework of student’s choice) which critically explores and analyses the issue presented formatively (LOs: 3, 4, 5). Must pass both elements to pass the module 1 Types of assessment task Indicative list of summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression. % weighting (or indicate if component is pass/fail) WRITTEN Written exam COURSEWORK Written assignment/ essay, report, dissertation, portfolio, project output, set exercise 50% PRACTICAL Oral assessment and presentation, practical skills assessment, set exercise 50% EXAMINATION INFORMATION Area examination board UGCPE Refer to Faculty Office for guidance in completing the following sections External examiners Name Position and institution Date appointed Carol Purcell University of Hull 01.09.2012 QUALITY ASSURANCE Date of first approval Only complete where this is not the first version Date of last revision Only complete where this is not the first version . August 2008 Date tenure ends 31.08.2016 Date of approval for this June 2013 version Version number 2 Modules replaced NA3121 Specify codes of modules for which this is a replacement Available as free-standing module? Yes × No