PLE #2 Rubric - UCEA || University Council for Educational
advertisement
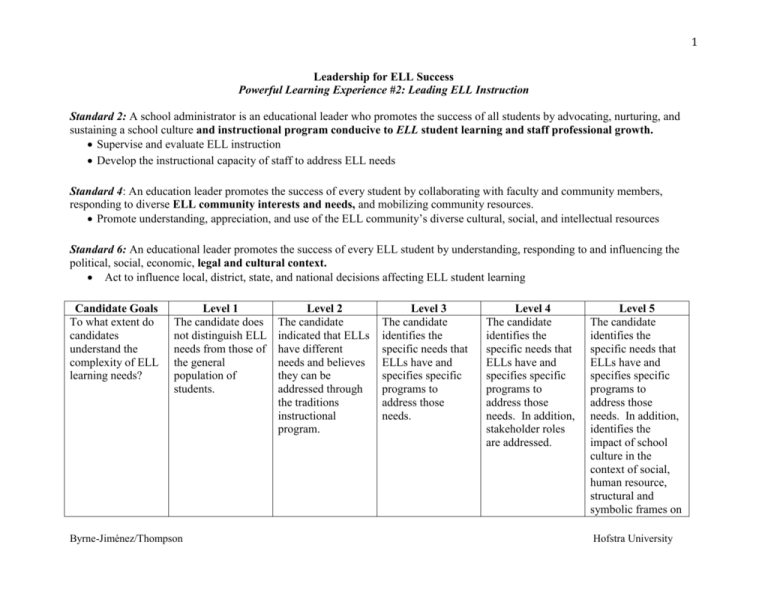
1 Leadership for ELL Success Powerful Learning Experience #2: Leading ELL Instruction Standard 2: A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by advocating, nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to ELL student learning and staff professional growth. Supervise and evaluate ELL instruction Develop the instructional capacity of staff to address ELL needs Standard 4: An education leader promotes the success of every student by collaborating with faculty and community members, responding to diverse ELL community interests and needs, and mobilizing community resources. Promote understanding, appreciation, and use of the ELL community’s diverse cultural, social, and intellectual resources Standard 6: An educational leader promotes the success of every ELL student by understanding, responding to and influencing the political, social, economic, legal and cultural context. Act to influence local, district, state, and national decisions affecting ELL student learning Candidate Goals To what extent do candidates understand the complexity of ELL learning needs? Level 1 The candidate does not distinguish ELL needs from those of the general population of students. Byrne-Jiménez/Thompson Level 2 The candidate indicated that ELLs have different needs and believes they can be addressed through the traditions instructional program. Level 3 The candidate identifies the specific needs that ELLs have and specifies specific programs to address those needs. Level 4 The candidate identifies the specific needs that ELLs have and specifies specific programs to address those needs. In addition, stakeholder roles are addressed. Level 5 The candidate identifies the specific needs that ELLs have and specifies specific programs to address those needs. In addition, identifies the impact of school culture in the context of social, human resource, structural and symbolic frames on Hofstra University 2 At what levels of understanding do candidates identify and the scope and depth of strategies to maximize ELL instructional outcomes? The candidate does not identify strategies for ELLs. Identified strategies reflect general characteristic of students. ELL strategies are identified that draw on readings and the specific characteristics of ELLs. ELL supports are identified that support a positive literacy environment and draw on students’ prior learning and experience, social/emotional development and interests. Supports are research based. What is the level of understanding candidates have of the challenges faced by teachers as they address ELL learning needs? Candidates’ assessment of teachers is focused on students and is limited to what ELLs cannot do. Candidates’ assessment of teachers is exclusively data driven. Candidates assess teachers based on their ability to address student academic language development including their justification for the use of specific strategies for ELLs. What processes do candidates use to make instruction Candidate does Candidate makes distinguish between decisions based ELL and the exclusively on Candidates recognize the need for teachers to understand the language demands of ELLs that are central to their learning and supports them through professional development Candidates make decision using disaggregated ELL learning. ELL supports are identified that support a positive literacy environment and draw on students’ prior learning and experience, social/emotional development and interests. Strategies are research-based. and school resources are modified to implement ELL strategies. Candidates assess teachers based on their ability to address student academic language at various level of their development through the needs and strengths of ELLs. Candidates makes decision using disaggregated Candidates uses a strategic planning approach to Byrne-Jiménez/Thompson Hofstra University 3 program decisions that support ELL learning needs? general student population in making decisions about the instructional program. Byrne-Jiménez/Thompson summative data and student data, legal mandates. teacher characteristics and legal mandates. student data ,teacher characteristics, and legal mandates, In addition, school climate is considered in the decision making process. decision making that embraces all stakeholders in the internal and the external community. Hofstra University