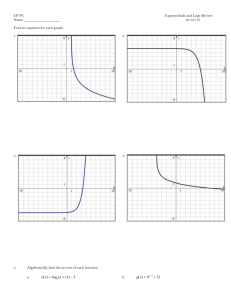
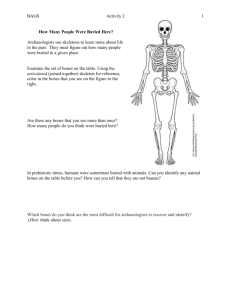
File - Oraib al
advertisement

CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 READ MARY LEAKEY ON PAGE 54 onwards. Key Terms: Anthropology: the study of how human beings behave and act together. Archaeologist: scientists who study human life a long time ago based on their artifacts and things left behind. Prehistory: Time before writing Fossil: hardened remains or imprints of living things. Geologist: Scientists who study the physical materials of Earth itself Artifact: objects made and used by humans Study of Early Humans: Prehistory: archaeologists look for the places where people may have lived. Depend on fossils. o Hardened remains or imprints of living things. (plants, feathers, bones, footprints.) o After a living thing dies it may be covered by sand or mud. Soft parts rot away Harder parts last longer Over years minerals from the soil slowly replace the onceliving material. Rocklike copy remains Bones tells us the size and the structure of an early humans’ body. Dating Ancient Remains: o Comparison: to compare objects found in similar layer of rocks or soil. Objects found in lower layers are generally older than those found in upper layers. o Radioactive dating: both living things and rocks contain radioactive elements that decay or break down over time. By measuring the amount of radioactive material left, scientists can tell when an object was formed. o DNA: genetic evidence has uncovered new information about how people changed and how they moved from place to place. STUDY THE DISCOVERIES OF MARY LEAKEY AND OTHER RESEARCHERS. READ THE TEXT CAREFULLY. SECTION 2: HUNTER-GATHERER SOCIETIES: Key Terms: Hunter-gatherer: Early humans lived by hunting small animals and gathering plants. Technology: Tools and skills that people use to meet their needs and wants. Culture: Includes many different elements that make up the way of life of a people. Nomads: People who move from place to place with the seasons. How Early Hunter-Gatherers Lived: Archaeologists knew little about hunter-gatherers but they knew their lives were harsh. o Many groups emerged o Most died out o They developed technology to survive. Simple tools: (PALEOLITHIC ERA) –STONE AGE Split Stones –cutting tools Chop down trees Cut/strip meat Scraping animal skin clean Skilled Tools: Thinner/sharper stone blades (Spears and arrows) Weapons from bones and antlers Hunt larger animals for food Discovery of Fire: Light in the dark Cook meat/plants Scare off danger Keep warm in the cold WANDERING BANDS: Culture was simple o Social and family organization, beliefs, values, technology, shelter, clothing, storytelling, art. o Small groups/bands: Ten/twelve adults and children Many were nomads Gather food from one area and move to the next. Caves (shelter) Men: hunted while Women: gathered fruits, grains, seeds and nuts. LATER STONE AGE PEOPLES: o 2 groups of humans emerged. o Had more developed culture than the homo habilis. o THE TABLE ON PAGE 66. VERY IMPORTANT SECTION 3: KEY TERMS ONLY.