Name: __KEY___10 points_____________________________

Name: __KEY___10 points_____________________________ Period: ______
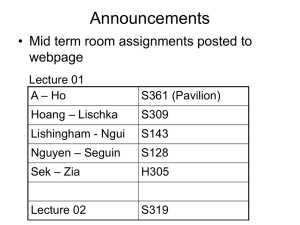
Synaptic Events Worksheet
Use your textbook to complete this activity…
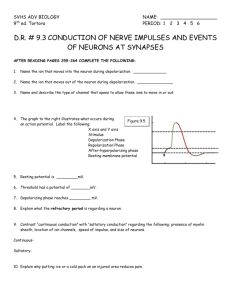
Label the following parts on the diagram below:
Presynaptic neuron
Nerve impulse
Synaptic end bulb
Synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitter receptors
Voltage-gated channel
Postsynaptic neuron
Closed ion channel
Open ion channel
Synaptic vesicle
Summarize how a typical synapse operates below according to your textbook: 5 blanks @ ½ point each
(1) _ nerve impulse arrives at synaptic end bulb of presynaptic axon __________________________
(2) _ depolarizing phase of nerve impulse opens voltage-gated Ca 2+ channels, which are present in membrane of synaptic end bulbs; Ca ions more concentrated in intestinal fluid, Ca 2+ flows into synaptic end bulb through opened channels __________________________________________
(3) _ increase in Ca 2+ concentration inside synaptic end bulb triggers exocytosis of some of the synaptic vesicles; which releases thousands of neurotransmitter molecules into synaptic cleft _
(4) _ neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across synaptic cleft bind to neurotransmitter receptors in postsynaptic neuron’s plasma membrane; binding opens ion channels; certain ions allowed to flow across membrane ___________________________________________________________
(5) _ as ions flow through opened channels, the voltage across the membrane changes; depending on which ions the channels admit, the voltage change may de depolarization or hyperpolarization; if depolarization in postsynaptic neuron reaches threshold, then it triggers one or more nerve impulses _______________________________________________________
Why can information only move in one direction across a synapse?
_ neurotransmitters only in presynaptic neuron ____ 1 point ____________________________________
Why is this probably a good thing?
_ ”crossed signals” ____ 1 point __________________________________________________________
Over>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Neurotransmitters
Use your textbook to fill in information about the chemicals listed below… 11 chemicals @ ½ point each
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Acetylcholine (ACh) released by many PNS neurons and some CNS neurons; excitatory neurotransmitter at some synapse, i.e. neuromuscular junction; inhibitory at other synapses, i.e. parasympathetic neurons slow heart rate by releasing ACh at inhibitory synapses
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Glutamate amino acid neurotransmitter in CNS; powerful excitatory
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Aspartate amino acid neurotransmitter in CNS; powerful excitatory
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) amino acid neurotransmitter in CNS; important inhibitory neurotransmitter; it is enhanced by antianxiety drugs like: diazepam (Valium)
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Glycine amino acid neurotransmitter in CNS; important inhibitory neurotransmitter
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Norepinephrine (NE) modified amino acid neurotransmitter; plays role in arousal (awakening from deep sleep), dreaming, and regulating mood
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Dopamine (DA) modified amino acid neurotransmitter; active during emotional responses, addictive behaviors, and pleasurable experiences; also help regulate skeletal muscle tone and some aspects of movement due to contraction of skeletal muscles---one type of schizophrenia due to accumulation of excess dopamine
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Serotonin modified amino acid neurotransmitter; thought to be involved in sensory perception, temperature regulation, control of mood, appetite, and the onset of sleep
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Neuropeptides neurotransmitter consisting of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Endorphins neuropeptides that are the body’s natural painkillers; linked to improved memory and learning and to feelings of pleasure and euphoria…acupuncture may produce analgesia (loss of pain sensation) by increasing release of endorphins
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Nitric acid (NO) simple gas neurotransmitter; different from other neurotransmitters because not synthesized in advance and packaged into synaptic vesicles, rather formed on demand, diffuses out of cells that produce it into neighboring cells, and acts immediately; research suggests plays a role in learning and memory
_____________________________________________________________________________________