Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles: Scavenger Hunt
advertisement

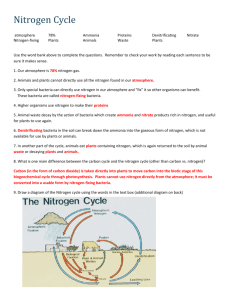
CARBON AND NITROGEN CYCLES: SCAVENGER HUNT is critically important to the formation of , which are monomers of proteins. The basic structure of the amino acid includes two . The one which contains nitrogen is known as the , and at the other end, a (which is a carbon linked with oxygen and hydrogen). There are known amino acids, which in turn form all of the proteins in your body, and all other organisms’ bodies for that matter. carry out almost all of the chemical reactions in your body, and are proteins too. The chief reservoir of nitrogen on Earth is the , which is about 78% nitrogen. This form of nitrogen is not assimilated by organisms besides one special group, which nitrogen in such a way as to make it useable by other life. Nitrogen can also be by the action of , which actually “burns” it out of the atmosphere, creating (NO3) which is nitrogen bound to three oxygen atoms. Nitrogen fixing bacteria called rhizobium are found in the roots of , and fix nitrogen either in the form of (NO3), or (NH3). Since NH3 is rather toxic, we are fortunate that there are bacteria in the soil and in the water which take up ammonia and convert it to , (NO2). Ammonia is also somewhat toxic, but bacteria, take it and convert it to nitrate, which can be taken up by plants to continue the cycle. is the process whereby plants absorb (NH3) , ions (NH4), and nitrate ions (NO3 ) through their roots. Most plants can take up and convert it to amino acids, which are, of course, the building blocks of proteins. acquire all of their amino acids when they eat plants (or other animals that consume plants). When organisms die and , or release the nitrogen is returned to the soil, usually in the form of . This NH3 or NH4 is a product of decomposing bacteria, and in this state, may be reused by plants. If this is indeed a cycle…how is N2 returned to the atmosphere? It turns out that there are bacteria (usually anaerobic) which take the nitrites and nitrates and combine the nitrogen back into gas, and nitrous oxide. This, of course, sends it back into the atmosphere to begin the cycle all over again. CARBON AND NITROGEN CYCLES: SCAVENGER HUNT is a molecule that has a huge capacity to absorb great amounts of thermal energy. It is this molecule that is most often attributed to global warming. The moves and stores carbon in the (living subsystem), lithosphere, (watery subsystem) and atmosphere. Carbon is stored in the biosphere as , and in the atmosphere as gas. In the lithosphere, which includes the solid part of Earth’s crust, both continental and oceanic…as well as soil organic matter, you will also find Earth’s fossil fuel deposits, and sedimentary rock deposits, which are generally composed of substances like or calcium carbonate (CaCO3). In the oceans, rivers and streams, carbon is stored as dissolved carbon dioxide gas and as calcium carbonate shells in marine organisms (although parts of the hydrosphere overlap with the atmosphere, because remember, can exist in three states on Earth, and when it is a gas, it is in the atmosphere). Humans have altered the through fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and land-use change. The net result of these processes is an increasing concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Remember, a carbon is an area that “stores” carbon. The largest storage place for carbon on Earth is the and marine .