INSTRUCTIONS TO AUTHORS FOR THE PREPARATION
advertisement

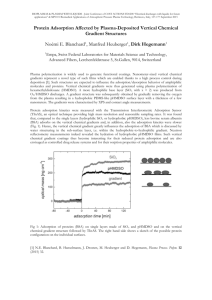
Anisotropic surface energies and adsorption behavior
of commonly exposed calcite surfaces
Zhiyong Gao *, Wei Sun, Yuehua Hu
School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, Hunan,
China
ABSTRACT
Surface energies of commonly exposed calcite surfaces, namely {018} and {104} surfaces,
were calculated based on density function theory (DFT) and evaluated by contact angle
measurements. The results obtained through two methods showed that {018} surface has a
greater surface energy than {104} surface, which could be explained by the difference in their
surface broken bonds density. The different adsorption behaviour of sodium oleate on the
two surfaces were also investigated by molecular dynamics simulation, contact angle
measurement and AFM observation. Our MD simulations indicated that oleate molecule
could form bridged configuration with adjacent two Ca sites on {018} surface through
chemisorption, while on (104) surface a monodentate form was favoured energetically. At a
given NaOl concentration in the range of 10-7-10-4 mol/L, the contact angle on the {018}
surface were found to be much larger than those on the {104} surface. AFM results also
demonstrated that at the concentration of 5×10-5 mol/L, where oleate adsorb as a monolayer
on calcite, the oleate species on {108} surface were arranged more compactly than those on
{104} surface. The different adsorption behaviours could be interpreted by the activity of
surface Ca sites possessing on these two surfaces. The link between surface energies as well
as adsorption behavior of the surfactant and localized surface chemistry was established for
calcite.
Key words: calcite; surface energy; oleate; adsorption; contact angle
*Corresponding author: Lecturer, School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central
South University, No. 932, Lushan South Road, Changsha, Hunan, China.
Phone: +86-731-88879299, Email: zhiyong.gao@csu.edu.cn
(b)
(a)
Fig. 1 The optimized adsorption models of oleate molecule on calcite {018} (a) and {104} (b) surfaces
after molecular dynamics (MD) simulation
(1. The adsorption energy of oleate molecule with {018} and {104} surfaces was calculated to be 362.43
and 318.4kcal/ mol, respectively; 2. The numbers such as 2.342 and 2.521 Å denote bond length between
O atom of oleate with surface Ca site)