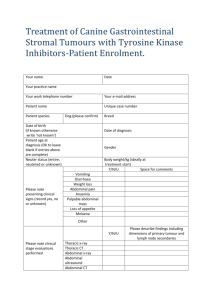
Supplementary Table 1. Active immunotherapies in phase II
advertisement

Supplementary Table 1. Active immunotherapies in phase II development Adjuvants/ immune modulators Study population PSA GM-CSF + costimulators Metastatic, castrationresistant prostate cancer 125 Viral vector (adenovirus) PSA Vector Recurrent/hormonerefractory prostate cancer 44 mRNA: CV9103/9104, CureVac® PSA + PSCA + PSMA + STEAP1 mRNA Metastatic, castrationresistant prostate cancer 38 HER2 GM-CSF High-risk breast cancer, in remission after standard treatment 182 HER2 GM-CSF High-risk breast cancer, in remission after standard treatment 172 EGFR Montanide ISA51 + CYC Stage IIIB/IV NSCLC, after chemotherapy 80 Telomerase GM-CSF Unresectable stage III NSCLC; after chemoradiotherapy 23 Type of immunotherapy Antigens Prostate cancer Viral vector (vaccinia/ fowlpox prime/boost): Prostvac®-VF Breast cancer Peptide: nelipepimut-S (E75), NeuVax™ Peptide: GP2 Lung cancer Peptide: CIMAvax EGF Peptide: GV1001 Patients(N) Efficacy results* Citation Clinical OS: 25.1 mo vs. 16.6 mo (HR 0.56; P=0.0061) PFS: 3.8 mo vs. 3.7 mo (HR 0.88; P=0.60) Immunologic No detectable antibody responses to PSA Clinical Increase in PSA doubling time in 64% of patients Immunologic T cell response: 100% (recurrent disease) and 67% (hormone-refractory disease) of patients Clinical Prolonged stabilization of PSA levels for individual patients Immunologic T cell response: 79% of patients, 58% with multiepitope responses Kantoff, P. W. et al. J. Clin. Oncol. 28, 1099-1105 (2010). NCT01322490 Clinical 2-yr DFS: Overall: 94.3% vs. 86.8% (P=0.08) Low HER2-expressing tumours: 94.0% vs. 79.4% (P=0.04) High HER2-expressing tumours: 90.3% vs. 83.3% (P=0.44) Clinical Recurrence rate: 4.3% vs. 11.6% (P=0.41) Immunologic DTH: 21.5 vs. 6.0 mm (P<0.01) Mittendorf, E. A. et al. Cancer. 118, 2594-2602 (2012). NCT01479244 Clinical OS: Overall (vaccine vs. control): 6.5 mo vs. 5.3 mo (P=0.098) Good vs. poor immune responders: 11.7 mo vs. 3.6 mo (P=0.002) Good immune responders vs. control: 11.7 mo vs. 5.3 mo (P=0.0024) Immunologic Good antibody response in 51% of patients Clinical OS: 28.8 mo PFS: Overall: 11.7 mo; Immune responders vs. non-responders: 12.2 mo vs. 6.0 mo (P=0.20) Immunologic T cell response: 16/23 patients (69.6%) Neninger Vinageras E. et al. J Clin Oncol. 26, 1452-1458 (2008). NCT01444118 Lubaroff, D. M. et al. Cancer Res. 72, Abstr 2692 (2012). Kübler, H. et al. J. Clin. Oncol. 29 suppl., Abstr 4535 (2011). Trappey, F. et al. J. Clin. Oncol. 31, Abstr 3005 (2013). Brunsvig, P. F. et al. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 6847-6857 (2011). NCT01579188 Viral vector (vaccinia): TG4010 MUC1 Adjuvants/ immune modulators Vector + IL-2 Allogeneic tumour cell: belagenpumatucel-L, Lucanix™ Allogeneic tumour cell: tergenpumatucel-L, HyperAcute® Lung Tumour cell Anti-idiotype: racotumomab Type of immunotherapy Antigens Study population Patients(N) Stage IV NSCLC, with chemotherapy 148 Anti-TGF-β Stage II–IV NSCLC; after front-line chemotherapy 75 Tumour cell αGT Stage IIIB/IV NSCLC; progressive or relapsed after chemotherapy 28 Idiotype Alum Stage IIIB/IV NSCLC; after primary treatment 176 survivin Montanide ISA51 + CYC Metastatic, treatmentrefractory stage IV melanoma 61 Peptide gp100 + MART-1 + tyrosinase GM-CSF + Montanide ISA51 Metastatic melanoma 22 Dendritic cell gp100 + MAGE-A1, A2, A3 + MART-1 + tyrosinase KLH Metastatic melanoma 24 Dendritic cell gp100 + tyrosinase (MHC-I/II) KLH Stage III/IV melanoma 33 Dendritic cell survivin + telomerase + p53 IL-2 + CYC +celecoxib Metastatic melanoma 28 Melanoma Peptide Efficacy results* Citation Clinical 6-mo PFS: 43.2% vs. 35.1% (P=0.307) OS: 10.7 mo vs. 10.3 mo (P=0.59) TTP: 5.9 mo vs. 5.2 mo (P=0.070) ORR: 41.9% vs. 28.4% (P=0.082) Outcomes worse than control in subset of patients with high levels of activated natural killer cells. Immunologic No significant differences between study arms in cellular responses to MUC1 Clinical OS: 14.4 mo; longer survival with higher (19.1 mo) vs. low (8.3 mo; P=0.0186) dose immunization Clinical OS: Overall: 11.3 mo IFN responders vs. non-responders: 21.9 mo vs. 5.5 mo (P<0.001) Immunologic Increased IFN responses in 61% of patients Clinical OS: 8.3 mo vs. 6.3 mo (P=0.02) Quoix, E. et al. Lancet Oncol. 12, 1125-1133 (2011). NCT01383148 Clinical OS: Overall: 9.1 mo Immune responders vs. non-responders: 19.6 mo vs. 8.6 mo; P=0.0077) PFS: Overall: 2.8 mo Immunologic T cell responses in 13/41 (32%) patients Clinical OS: 13.4 mo PFS: 1.9 mo Immunologic T cell responses in 9/20 (45%) patients Clinical OS: Overall: 13.6 mo (vs. 7.3 mo matched controls) Immune responders vs. non-responders: 21.9 mo vs. 8.1 mo Immunologic T cell responses in 18/24 (75%) patients; multiepitope responses in 13/24 (54%) patients Clinical OS: 15.0 mo (vs. 8.3 mo with matched controls; P=0.089) PFS: 5.0 (vs. 2.8 mo with matched controls; P=0.0089) Immunologic T cell responses in 5/29 (17%) patients Clinical OS: 9.4 mo Immunologic Antigen-specific responses in 9/15 (60%) patients Becker, J. C. et al. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 61, 2091-2103 (2012). Nemunaitis, J. et al. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 4721-4730 (2006). NCT00676507 Morris, J. C. et al. J. Clin. Oncol. 30 suppl, Abstr 2571 (2012). NCT01774578 Macías, A. et al. Ann. Oncol. 23 suppl 9, Abstr 1238PD (2012). NCT014604722 Tarhini, A. A. et al. J. Immunother. 35, 359-366 (2012). Oshita, C. et al. Oncol. Rep. 28, 1131-1138 (2012). Aarntzen, E. H. et al. Cancer Res. 73, 19-29 (2013). Ellebaek, E. et al. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 61, 1791-1804 (2012). Type of immunotherapy Antigens Autologous tumour cell: MVax Haptenmodified tumour cells Allogeneic tumour cell Shed-antigens Allogeneic tumour cell Viral vector (vaccinia/ fowlpox prime/boost): Prostvac®-VF Pancreatic cancer Peptide Allogeneic tumour cell: algenputacel-L HyperAcute® Pancreas Colorectal cancer Viral vector (adenovirus) Dendritic cell Modified with CEA + MUC1-encoding poxvector (PANVAC) Renal cell carcinoma Peptide: IMA901 Adjuvants/ immune modulators BCG + IL2 + CYC Study population Patients(N) Efficacy results* Citation Clinical OS: With vs. without DTH to unmodified tumour cells: 16.5 vs 8.4 mo (P=0.023) Immunologic DTH to unmodified tumour cells in 42% of patients Clinical OS: 45.6 mo vs.32.4 mo (P=NS) Recurrence-free survival: 19.2 mo vs. 7.2 mo (P=0.03) – Berd, D. et al. Int. J. Cancer. 94, 531-539 (2001). NCT00477906 25 Clinical OS: Overall: 48 mo Immune responders vs. non responders: 82 mo vs. 15 mo (P=0.007) PFS: Overall: 9 mo Immune responders vs. non-responders: 9 mo vs. 7 mo (P=0.16) Immunologic CD8+ T cell responses in 22/25 (88%) patients Odunsi, K. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 109, 57975802 (2012). Clinical OS Immune responders vs. non-responders: 4.8 mo vs. 2.0 mo (P=0.0002) Immunologic T cell responses in 17/43 (40%) patients Clinical 1, 2 and 3-yr survival of 86%, 51% and 42%, respectively Gjertsen, M. K. et al. Int. J. Cancer. 92, 441-450 (2001). Clinical 1-yr survival of 48% Immunologic T cell responses in 15/32 (47%) patients Clinical 2-yr survival DC modified with PANVAC vs. PANVAC alone: 47% vs. 55%; P=0.48). Death 2/37 with DC-PANVAC vs. 5/37 with PANVAC alone Morse, M. A. et al. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 62, 1293-1301 (2013). Clinical OS: IMA901 + CYC vs. IMA alone: 23.5 mo vs. 14.8 mo (P=0.09) Improved survival in patients with multiepitope responses (P=0.023) Immunologic T cell responses in 20/27 (74%) patients; multiepitope responses in 8/27 (30%) patients Walter, S. et al. Nat. Med. 18, 1254-1261 (2012). NCT01265901 Metastatic melanoma 97 Alum Stage IIB/C or III melanoma; post-surgery 38 Tumour cell BCG + GM-CSF ≈108 NY-ESO-1 Vector Stage IIB/C or III melanoma; post-surgery Stage III/IV melanoma ras peptides GM-CSF Advanced/surgically resected pancreatic cancer 48 Tumour cell α-GT Surgically resected pancreatic cancer, with chemoradiotherapy 70 CEA Vector Metastatic colorectal cancer 32 CEA + MUC1/GMCSF PLIN2 + APOL1 + CCND1 + GUCY1A3 + PRUNE2 + MET + MUC1 + RGS5 + MMP7 + HBcAg Resected metastatic colorectal cancer; after resection (N=74) GM-CSF ± CYC Metastatic RCC 68 Bystryn, J. C. et al. Clin. Cancer Res. 7, 1882-1887 (2001). NCT01546571 NCT01729663 Hardacre, J. M. et al. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 17, 94-100 (2013). NCT01836432, NCT01072981 Morse, M. A. et al. Ann. Surg. 258, 879-886 (2013). Type of immunotherapy Antigens Dendritic cell: AGS-003 Tumour cell RNA Adjuvants/ immune modulators CD40L Study population Patients(N) Efficacy results* Citation Metastatic RCC 21 Clinical OS: 30.2 mo PFS: 11.2 mo Amin, A. et al. J. Clin. Oncol. 31 suppl, Abstr 357 (2013). NCT01582672 19 Clinical PFS: 1.6 mo (patients with AML and prior chemotherapy) Objective response in 10/17 patients with AML, and stable disease after initial progression in a further 4 patients Immunologic T cell responses in 8/18 (44%) patients – Keilholz, U. et al. Blood. 113, 6541-6548 (2009). 34 Clinical Reduction in slope of paraprotein concentration in 13/29 patients Immunologic T cell responses in 15/32 (47%) of patients Rossmann, E. et al. American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting. Abstr 2927 (2011). 10 Clinical Normalization of WT1 mRNA levels in 5/10 patients, including 2 patients converted from partial to full remission. Three long-term (≥3 yr) clinical responders. Clinical responses correlated with innate and adaptive immune responses Van Tendeloo, V. F. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 107, 13824-13829 (2010). Haematologic malignancies Peptide WT1 GM-CSF + KLH Acute myeloid leukaemia (N=17) or myelodysplastic syndrome (N=2) Peptide MAGE-A3 or NY-ESO-1 GM-CSF Peptide MUC1 Liposomal MPL +CYC Dendritic cell WT1 High-risk multiple myeloma, in combination with chemotherapy and ASCT Previously untreated asymptomatic stage I/II multiple myeloma or stage II/III disease in stable response/plateau phase Acute myeloid leukaemia, in remission following chemotherapy NCT00090493 Trials listed on clinicaltrials.gov; accessed September 19 2013. †Adjuvant components are shown in italics. * Phase III study results in shading, otherwise Phase II results; survival data are medians and comparisons are for active treatment vs. placebo/control, unless otherwise stated. ASCT: autologous stem cell transplantation; BCG: bacillus Calmette-Guérin; CYC: cyclophosphamide; DC: dendritic cells; DFS: disease-free survival; DTH = delayed type hypersensitivity; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; gp100: glycoprotein 100; GST: glutathione-S-transferase; GT: 1,3-galactosyltransferase; HER2: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2); HPV: human papillomavirus; ICAM-1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IMP-3: insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA binding protein 3; IFN-: interferon-; KLH: keyhole limpet hemocyanin; L-BLP25: BLP25 liposome vaccine; LFA-3: lymphocyte function-associated antigen-3; LY6K: lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus K; MAGE: melanoma antigen-encoding gene; mCRPC: metastatic, castrateresistant prostate cancer; MPL: monophosphoryl lipid A; MUC1: mucin-1; NHL: non-Hodgkin lymphoma; NS: not significant; NSLC: non-small cell lung cancer; OS: overall survival; PAP: prostatic acid phosphatase; PBMC: peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PSA: prostate specific antigen; PSCA: prostate stem cell antigen; PSMA: prostate specific membrane antigen; STEAP1: six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 1; TGF-β2: transforming growth factor β2; TTK: TTK protein kinase