Supplementary Information (docx 90K)
advertisement

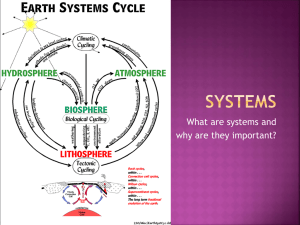
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. TGFβ1 promotes stemness properties of lung cancer cells. (a) A549 cells were treated with or without TGFβ1 for 3 d. Morphologic phenotypes and F-actin expression was detected by immunofluorescence staining. BF, bright field. (b) The expression of stemness-related proteins of A549 secondary spheres was analyzed by flow cytometry. The number indicates MFI. (c) Secondary spheres (5 103) were transfected with luciferase reporter constructs containing the promoter region of OCT-4, SOX-2, and NANOG. The luciferase activities were detected 2 d after transfection. ** indicates P < 0.01 compared with untreated control cells. (d) Secondary spheres (5 102) were seeded as single cell in soft agar and cultured for 4 weeks in the presence or absence of TGFβ1 (5 ng/mL). Colonies larger than 100 m were counted. ** indicates P < 0.01 compared with untreated control cells. (e) Secondary spheres (5 103) were seeded in 96-well plate and incubated with increasing concentrations of cisplatin (0, 5, 10, 20, and 40 μM) or etoposide (0, 10, 20, 40, 80, and 100 μM). Cell viability was analyzed 48 h after drug treatment by performing CellTiter-Glo Luminescent cell viability assay. Estimated IC50 values for each group are indicated. (f) The images represent TGF-β1 expression in human lung adenocarcinoma tissue analyzed by IHC. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Supplementary Figure 2. CXCR7 knockdown repressed TGFβ1-induced cell migration, invasion, and EMT. (a) shLuc-, shCXCR4-, shCXCR7- or shCXCR4/shCXCR7-infected A549 cells were seeded on the 24-well plates and incubated with medium in the presence or absence of TGFβ1 (5 ng/mL) for 48 h. Morphologic changes and immunoreactivity for CXCR7, CXCR4, and F-actin was determined by immunofluorescence. (b) Migratory (Left) and invasiveness (Right) ability of shLuc-, shCXCR7-infected cells were determined by transwell assay, respectively. **, P < 0.01 compared with untreated shLuc control cells; ##, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-treated shLuc cells. (c) shLuc-infected cells (2 105) were pre-treated with AMD3100 for 1 h. Knockdown cells were then incubated with or without TGFβ1 for 72 h. Expression of EMT markers was analyzed by western blotting. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Supplementary Figure 3. CXCR7 participated in TGFβ1-induced sphere formation and stemness properties of EKVX cells. EKVX knockdown cells were cultured in defined serum-free DMEM/F12 medium in the presence or absence of TGFβ1 (10 ng/mL) for 30 d. Spheres were then serially passaged to form secondary spheres and the number of spheres was counted. (a) Top, representative bright-field light microscopy images of spheres (magnification, 40). Bottom, quantification of primary and secondary sphere numbers. **, P < 0.01 compared with primary TGFβ1-induced shLuc cells; ##, P < 0.01 compared with secondary TGFβ1-induced shLuc cells. (b-c) Expression of NANOG, SOX-2, OCT-4, and CD44 of secondary spheres were determined by qRT-PCR (b) and flow cytometry (c). The number represents the MFI. **, P < 0.01; ##, P < 0.01; ++, P < 0.01; ΔΔ, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-induced shLuc cells. (d) Secondary spheres (5 103) were transfected with OCT-4, SOX-2, or NANOG reporter constructs. Luciferase reporter activities were detected after 48 h of transfection. **, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-induced shLuc cells. (e) Secondary spheres induced by TGFβ1 treatment (5 102) were seeded in 96-well plates and treated with increasing concentrations of cisplatin or etoposide for 48 h. Cell viability was analyzed by CellTiter-Glo Luminescent cell viability assay. Estimated IC50 values for each group are indicated. Supplementary Figure 4. Determine the effects of CXCR4 and CXCR7 knockdown by using different shRNA targeting sequences. CXCR7 and CXCR4 were silenced by lentivirus infection using different shRNA targeting sequences compared to the originally used shRNAs. (a) A549 knockdown cells were treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/mL) for 2 d and the morphologic phenotypes were examined by microscopy. B, A549 cells were grown to confluence and scratched. Cells were treated with or without TGFβ1 (5 ng/mL) for 18 h and their migratory ability was determined. (c-d) Migration and invasion ability were examined by a transwell assay in the presence or absence of TGFβ1, respectively. (e) Knockdown cells (2 105) were incubated with TGFβ1 for 3 d. E-cadherin and N-cadherin expression was examined by western blotting. (f) Knockdown cells (2 102) were seeded and cultured in defined serum-free DMEM/F12 tumor sphere medium in the presence or absence of TGFβ1 (10 ng/mL) for 30 d. The number of spheres was counted. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-untreated shLuc control; ##, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-treated shLuc. (g-h) Expression of stemness genes of primary spheres was analyzed by qRT-PCR (g) and flow cytometry (h). The number represents the MFI. **, P < 0.01; ##, P < 0.01; ++, P < 0.01; ΔΔ, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-treated shLuc group. Supplementary Figure 5. CXCL12 involves in the maintenance of sphere formation of lung cancer cells. (a) A549 knockdown cells were stimulated with CXCL12 (100 ng/mL) for 2 d and the morphologic phenotypes were examined by microscopy. (b) A549 knockdown cells (2 104) were seeded on the upper chamber of transwell inserts and incubated for 24 h with or without CXCL12 (100 ng/mL) in the lower chamber. Migratory and invasiveness abilities were determined. **, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-untreated shLuc; ##, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-treated shLuc. (c) Knockdown cells (2 105) were incubated with CXCL12 (100 ng/mL) for 3 d. The expression of EMT markers was analyzed by western blotting. (d) Knockdown cells (2 105) were treated with CXCL12 (100 ng/mL) for 24 h. The expression of EMT-associated transcriptional factors was analyzed by qRT-PCR. **, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-treated shLuc; ##, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-untreated shLuc. (e) Knockdown cells (2 102) were grown in defined serum-free DMEM/F12 tumor sphere medium in the presence or absence of CXCL12 (100 ng/mL) for 30 d. Top, Representative bright-field light microscopy images of spheres. Bottom, Quantification of primary sphere numbers. (f) OCT-4, SOX-2, NANOG, and CD44 expression was determined by qRT-PCR. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-untreated shLuc control; ##, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-treated shLuc; +, P < 0.05 compared with TGFβ1-untreated shLuc. (g) A549 cells were infected with shCXCL12 lentiviruses to inhibit CXCL12 expression. Luciferase shRNA (shLuc) was used as a control. Left top, Knockdown cells (2 102) were cultured in sphere medium in the presence or absence of TGFβ1 (10 ng/mL) for 30 d. The spheres larger than 100 mm were counted in each well. The expression of stemness genes was examined by qRT-PCR. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-untreated shLuc control; ##, P < 0.01 compared with TGFβ1-treated shLuc.