(1.7) Angles and their Measures
advertisement

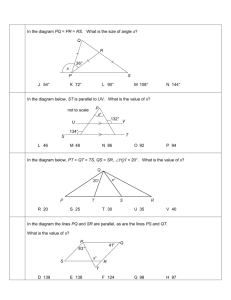
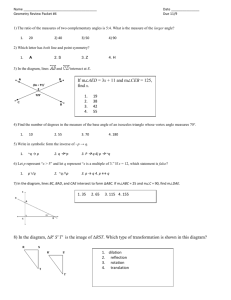
Expectation Identify the parts of and appropriately label angles. Find the measure of and identify the type of angles. Find unknown angle measurements using the Angle Addition Postulate. Meets Expectation Almost Meets Expectation Does Not Meet Expectation Teacher Comment MEASURING AND CLASSIFYING ANGLES Find the measure of the angle. Then classify the angle. Create an angle based on the given measurement. (1) m∠ABC = 76° (2) m∠JKL = 103° (3) m∠RST = 90° (4) m∠VWX = 175° (1) In the coordinate plane, plot the points and sketch ∠ABC. List the coordinates of a point that lies in the exterior of the angle and list the coordinates of a point that lies in the interior of the angle. A: (–5, –4) B: (–3, 0) C: (1, –4) (2) A: (–5, 0) B: (–1, –4) C: (4, 2) Exterior Point: Exterior Point: Interior Point: Interior Point: Use the Angle Addition Postulate to find the missing angle measurement. (1) m∠CDF = __________ (2) m∠PQR = __________ (3) (4) (5) Find the value of x and the unknown measurements. (6) Q is in the interior of ∠ROS . S is in the interior of ∠QOP . P is in the interior of ∠SOT . m∠ROT = 127°, m∠SOT = 71°, and m∠ROQ = m∠QOS = m∠POT . Make a sketch and find all missing angle measurements. m∠QOP = __________ m∠QOT = __________ m∠ROQ = __________ m∠SOP = __________ Using a protractor, accurately plot five points, A, B, C, D, and E, so that all three statements are true. (7) ∠DBE is a straight angle. ∠DBA is a right angle. ∠ABC is a straight angle. (8) C is in the interior of ∠ADE. m∠ADC + m∠CDE = 120°. ∠CDB is a straight angle. Use a compass and straightedge to find the angle bisector. Use a compass and straightedge to find the angle bisector. (1) (2) (3) In the diagram, BT is the angle bisector of ∠ABC. Find the value of x. Then find the measurements of all three angles.