Digital_Certificate_..
advertisement

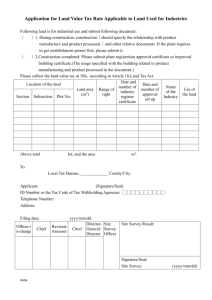
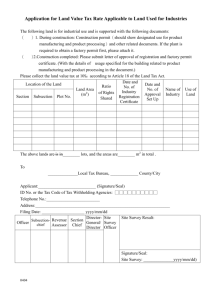
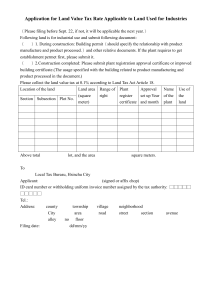
ICEGATE DIGITAL SIGNATURE CERTIFICATE PROCESS DOCUMENT Version – 1.0 OFFICE OF: THE ADDITIONAL DIRECTOR GENERAL, ICEGATE, C. R. BUILDING, I. P. ESTATE, NEW DELHI Version Control Version (x.yy) 1.0 Date of Revision 18-Mar-15 Description of Change First version Reason for Change Approved Version Affected Sections NA Approved By CBEC Table of Contents 1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 4 2. Digital Signature Certificate ....................................................................................................... 5 2.1 Contents of a Digital Certificate............................................................................................. 6 2.2 Defined Classes ......................................................................................................................7 2.3 PKI ..........................................................................................................................................7 3. Enabling PKI in ICEGATE .......................................................................................................... 8 3.1 Integration of PKI component ............................................................................................... 8 3.2 PKI Component functionalities............................................................................................. 8 4. Digital Signature implementation framework ..........................................................................10 4.1 Digital Signature implementation phases ............................................................................10 5. Benefits of Digital Signature implementation .......................................................................... 12 1. Introduction Indian Customs EDI Gateway (ICEGATE) is the gateway for the users of Indian Customs EDI system. All the Individuals (Importers/Exporters/CHAs/Airlines/Shipping Lines/Shipping Agents etc.), trade partners (Banks/Custodians/PQIS/FSSAI etc.) or Govt. Agencies (Ministry of Valuation/DGFT/CRIS/CONCOR/Ministry of Steel etc.) Commerce/DGCI&S/DG, connect ICEGATE for documents filing (BE/SB/IGM/EGM/CGM etc.), data sharing under Customs Business Process (several information shared through messages with the help of Server to Server SFTP communication system) or for administrative, statistical, analytical or policy making purpose through SFTP in automated environment. It provides Remote EDI Services (RES) to the trade and industry for filing documents, data exchange, e-payment, status enquiry, document tracking, query-reply etc. In recent past, ICEGATE has been observing challenges on account of impersonation of Identity of the registered user, tracing the identity of user, misuses of credibility of accredited clients etc. Further, Sec. 5 if the IT Act, 2000 envisages that the electronic documents, which are supposed to be signed by a person in case it is filed in a hard copy, must be singed digitally by the person authorized to sing it. Hence data exchange and acceptability of documents received through RES has imminent need to implement digital signature for the documents/ messages receiving / forwarding electronic to and fro the customs business partners, stakeholders and other Govt. Agencies. Further, demand from the trade and industry, several associations and other Ministries have been received for making Customs EDI business process paperless. To overcome the aforesaid challenges implementation of Digital Signature Certificate at ICEGATE is very important. It shall authenticate the identity, maintain users and data related integrity, support non-repudiation and prevent frauds. We may subsequently stop giving print to the importers/CHA/Exporter and provide digitally signed electronic copy only. This would inter-alia help in saving forests at a large level and increase trust in system. 2. Digital Signature Certificate In cryptography, a public key certificate (also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate) is an electronic document that uses a digital signature to bind a public key with an identity — information such as the name of a person or an organization, the address, and the email address. The certificate can be used to verify that a public key belongs to an individual. In a typical public-key infrastructure (PKI) scheme, the signature will be of a certificate authority (CA). In a web of trust scheme, the signature is of either the user (a self-signed certificate) or other users ("endorsements"). In either case, the signatures on a certificate are attestations by the certificate signer that the identity information and the public key belong together. A Digital signature will include a message/ document which is signed with the sender's private key, upon signing a hash value is generated which is transmitted with the message. On receiving the message is deciphered by user who has access to the sender's public key. The verification proves that the sender had access to the private key, and therefore is likely to be the person associated with the public key. This also ensures that the message has not been tampered with, as any manipulation of the message will result in changes to the encoded message , which otherwise remains unchanged between the sender and receiver. DSC FRAMEWORK Version User Name Signature Algorithm Signing by using CA’s Public Key User Certificate Users Public Key Serial Number CRL Cred CRL entia ls CA Name Validity User Name Public Key Verification & Integration Signature of issuer Extension 2.1 Contents of a Digital Certificate Serial Number: Used to uniquely identify the certificate. Subject: The person, or entity identified. Signature Algorithm: The algorithm used to create the signature. Signature: The actual signature to verify that it came from the issuer. Issuer: The entity that verified the information and issued the certificate. Valid-From: The date the certificate is first valid from. Valid-To: The expiration date. Key-Usage: Purpose of the public key (e.g. decipherment, signature, certificate signing...). Public Key: The public key. Thumbprint Algorithm: The algorithm used to hash the public key certificate. Thumbprint (also known as fingerprint): The hash itself, used as an abbreviated form of the public key certificate. 2.2 Defined Classes Class 1 for individuals, intended for email. Class 2 for organizations, for which proof of identity is required. Class 3 for servers and software signing, for which independent verification and checking of identity and authority is done by the issuing certificate authority. Class 4 for online business transactions between companies. Class 5 for private organizations or governmental security. 2.3 PKI PKI (Public key Infrastructure) is an arrangement in cryptography that facilitates third party examination of, and vouching for, user identities.PKI allows the binding of public keys to users. These public keys are most frequently stored in cartificates. This binding of public keys to users is usually carried out by software in a central location, in coordination with other associated software components installed in distributed locations. 3. Enabling PKI in ICEGATE 3.1 Integration of PKI component PKI Component should be added in the application to make application PKI enabled. As PKI component executes at client side, it should be added in the application such a way that it makes component downloadable at client side. PKI component can be embedded in the web pages using its tags. When component is embedded to the web page, it will expose few component specific JavaScript functions to the web page. Web pages can communicate with the embedded component by calling JavaScript functions.PKI Component provides following functionalities 3.2 PKI Component functionalities Certificate Selection: PKI component retrieves the list of all installed certificate at client side, display it in a pop up box and allow user to select a certificate from list. Certificate Verification: After Selection of certificate, component will perform validation on selected certificate such as: Date verification Certificate Chain Verification ROOT CA verification CRL verification Is Private Key Exists Data OR File Signing: The user shall utilize any class – III PKI DSC for signing documents. He will use web-based Common Singer Component while signing documents. This component shall verify CRL also at the time of signing. It will share credentials of user, CA, validation and Public Key in encrypted form along with Hash Value. Data OR File Verification: Application will provide Original data, hash & public key of Signer certificate to component, using all above information component will verify signature on data. If original data/file or signature is tempered verification will be failed. Encryption: Application provides component a public key with which data needs to be encrypted. Component will process Public Key & Original data (Or user entered Data) & generate encrypted representation of original data. Decryption: Application provides component an encrypted data, component will pop up a certificate dialog, which allows user to select certificate private key. After selection component will verify the certificate & retrieve private key. Using private key & encrypted data component can reproduce original data. 4. Digital Signature implementation framework ICEGATE receives inbound documents from various individual users like importers, Exporters, CHA etc. and send outbound messages to various agencies like DGFT, DGCI&S, PQIS, FSSAI etc. The framework of Digital Signature in automated environment of ICEGATE is different from other normal framework, so keeping in view workflow and specific functionalities of ICEGATE it was required to create specific architecture of Digital Certificate implementation. It was also required to have a DSC which could be operated in automated environment without any interference of human being. The normal Digital Signature issued on the name of an individual was not function for outbound messages which are send by ICEGATE system. Considering the unique requirement of ICEGATE system Controller of Certifying Authority(CCA) introduced a new type of Digital Certificate with name “ Organization Document Signer Certificate” in September,2014. The implementation of DSC was planned in phased manner. 4.1 Digital Signature implementation phases The implementation of Digital Signature is ICEGATE has been envisaged in following two phases: i. Phase 1 - Implementation of certificates for individual users: All Importers, Exporter, Customs Brokers, Shipping Lines, Airlines or their agents who are authorized to file any document through Remote EDI System at ICEGATE will have to use the Class 3 Digital Signature Certificates for digitally signing the Customs Documents (Bills of Entry, Shipping Bills, IGM, EGM, CGM) before submitting them to ICEGATE for processing. Keeping in view the different platforms of RES utilities deployed by users and to avoid delay in submission of documents at ICEGATE level, web-based Common Signer Component has been provided to the users through ICEGATE website for signing all the Customs Documents. The Web-based Common Signer available free of cost to all the users through ICEGATE portal supported by M/s (n)Code. It is platform neutral and verifies validity, CRL etc. at the time of signing. This component may be used with any Class – III DSC valid issued by any CA. The user authorized for signing documents shall use DSC in his name and execute signing process and send the Digitally signed documents to ICEGATE. On receiving the digitally signed documents the ICEGATE server side verifier shall verify the user’s credentials, validity of certificate, CAs credentials, Public Key and CRL status and Hash Value of certificate and integrated the data with ICES database. Validation of credentials of the person who sings document, sends document and the CHA who files the documents would be completed in the process. Records of digitally signed documents shall be preserved for legal purpose if any. ii. Phase 2 - Implementation of Certificates for server to server communication: In the phase DSC will be implemented for all the agencies with which server to server communication is done by the Department for all inbound and outbound messages. ICEGATE will digitally sign all outbound messages with Organizational Document Signer DSC, which was introduced by CCA keeping into view the specific requirement of ICEGATE system. 5. Benefits of Digital Signature implementation The following are the key benefits of implementing digital signature for ICEGATE inbound messages: i. Authentication -. Digital signatures are used to authenticate the source of messages. The ownership of a digital signature key is bound to a specific user and thus a valid signature shows that the message was sent by that user. ii. Integrity – With Digital certificates it can ascertained that the message has not been altered during transmission. Digital Signatures provide this feature by using cryptographic message digest functions iii. Non Repudiation – Digital signatures ensure that the sender who has signed the information cannot at a later time deny having signed it . In case of legal issues user can be held liable for documents received from him. iv. Tracking: A digitally signed document can easily be tracked and located in a short amount of time. v. Environment friendless: By implementing Digital signature lot of paper can be saved, which in turn may reduce the number of trees which are cut for making the paper.