IME 341 Intro to Manufacturing Processes
advertisement
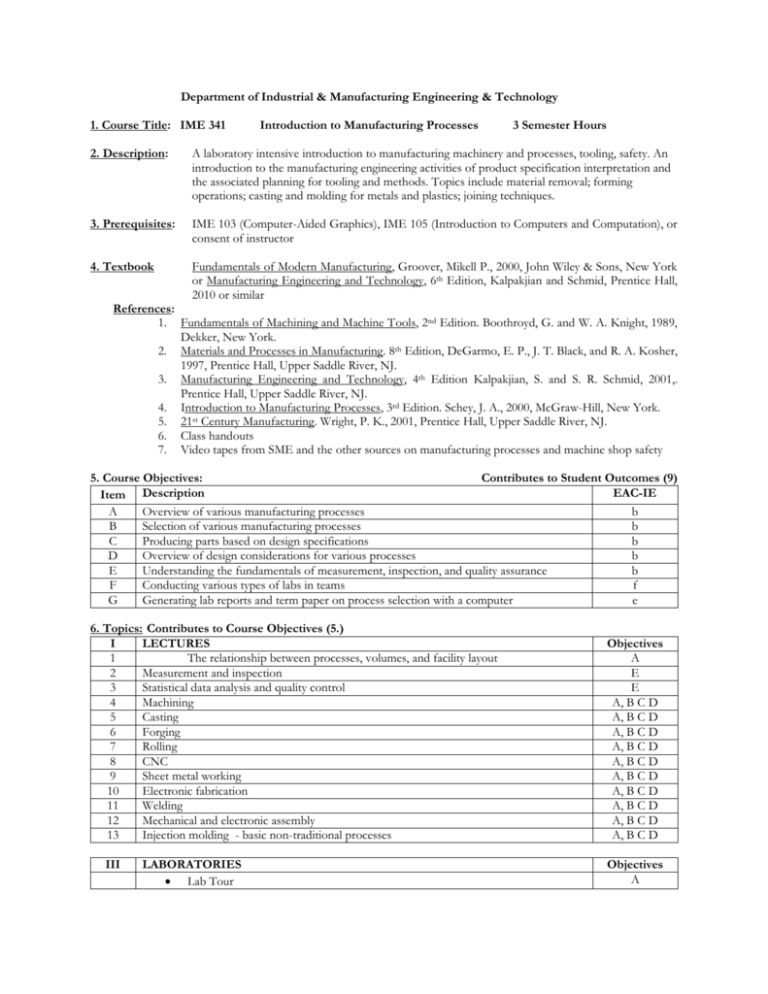
Department of Industrial & Manufacturing Engineering & Technology 1. Course Title: IME 341 Introduction to Manufacturing Processes 3 Semester Hours 2. Description: A laboratory intensive introduction to manufacturing machinery and processes, tooling, safety. An introduction to the manufacturing engineering activities of product specification interpretation and the associated planning for tooling and methods. Topics include material removal; forming operations; casting and molding for metals and plastics; joining techniques. 3. Prerequisites: IME 103 (Computer-Aided Graphics), IME 105 (Introduction to Computers and Computation), or consent of instructor 4. Textbook Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing, Groover, Mikell P., 2000, John Wiley & Sons, New York or Manufacturing Engineering and Technology, 6th Edition, Kalpakjian and Schmid, Prentice Hall, 2010 or similar References: 1. Fundamentals of Machining and Machine Tools, 2nd Edition. Boothroyd, G. and W. A. Knight, 1989, Dekker, New York. 2. Materials and Processes in Manufacturing. 8th Edition, DeGarmo, E. P., J. T. Black, and R. A. Kosher, 1997, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. 3. Manufacturing Engineering and Technology, 4th Edition Kalpakjian, S. and S. R. Schmid, 2001,. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. 4. Introduction to Manufacturing Processes, 3rd Edition. Schey, J. A., 2000, McGraw-Hill, New York. 5. 21st Century Manufacturing. Wright, P. K., 2001, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. 6. Class handouts 7. Video tapes from SME and the other sources on manufacturing processes and machine shop safety 5. Course Objectives: Contributes to Student Outcomes (9) EAC-IE Item Description A Overview of various manufacturing processes b B Selection of various manufacturing processes b C Producing parts based on design specifications b D Overview of design considerations for various processes b E Understanding the fundamentals of measurement, inspection, and quality assurance b F Conducting various types of labs in teams f G Generating lab reports and term paper on process selection with a computer e 6. Topics: Contributes to Course Objectives (5.) I LECTURES 1 The relationship between processes, volumes, and facility layout 2 Measurement and inspection 3 Statistical data analysis and quality control 4 Machining 5 Casting 6 Forging 7 Rolling 8 CNC 9 Sheet metal working 10 Electronic fabrication 11 Welding 12 Mechanical and electronic assembly 13 Injection molding - basic non-traditional processes III LABORATORIES Lab Tour Objectives A E E A, B C D A, B C D A, B C D A, B C D A, B C D A, B C D A, B C D A, B C D A, B C D A, B C D Objectives A III 1 Manual measurement and inspection Statistical process control charting Demonstration and work shop safety Lathe project (including band sawing, turning, & boring; three weeks) Mill project (including band sawing, milling, & drilling; three weeks) Welding project Casting project Bending/stamping project CNC programming CNC machining Injection molding lab PROJECTS/PAPERS Team-based term paper on any topic related to the course. The paper must include problem definition, method identification, data collection, data analysis, and technical inferences E E, F, G F A, B, C, F, G A, B, C, F, G A, B, C, F, G A, B, C, F, G A, B, C, F, G A, B, C, F, G A, B, C, F, G A, B, C, F, G Objectives F, G 7. Class Schedule: Two sessions of 50 minutes and two hour lab per week 8. Contribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component: EAC Mathematics and Basic Science Engineering Topics, Engineering Sciences, Engineering Design General Education 9.Relationship of Course to IE Student Outcomes: (Note: Contribution ranks from 0.5 to 5.0) Code Student Outcomes, A Graduate from the Program Will Have: Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics a and science to system modeling and to problems related to production processes or services. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to design and conduct experiments, b and to analyze and interpret data. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to design, select, implement, and c control a manufacturing or service system and its components or processes to meet desired needs. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams d and the ability to apply a concurrent approach and project management to process and product development. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to identify, formulate, and determine e optimal solutions to system problems, while considering physical and economic constraints as well as safety and ergonomic issues. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an understanding of the professional and ethical f responsibilities of an industrial engineer. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to effectively communicate technical g and social concepts through appropriate methods. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an understanding of the impact of industrial h engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context. Industrial Engineering graduates will have the recognition of the need for, and an ability to i engage in lifelong learning. Industrial Engineering graduates will have knowledge of contemporary issues facing j engineers. 0 hrs 3 hrs 0 hrs Contribution 1.00 1.17 0.75 k Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to use the proper techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for industrial engineering practice utilizing supporting technologies. 10. Prepared by: Ye Li, 02/2013 New student outcomes updated on 12-28-2012 Reviewed by: Curriculum Committee