UNIT 7 -- READING AND LEARNING GUIDE TOPICS TO KNOW
advertisement

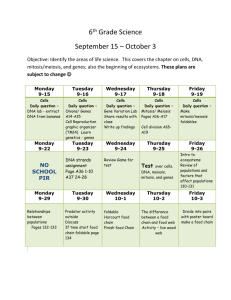
UNIT 7 -- READING AND LEARNING GUIDE TOPICS TO KNOW: Describe the various experiments and technological advances that lead to the identification of DNA as the genetic material. (Including: Griffith's experiment, Avery's experiment, Hershey and Chase experiment, Chargaff's rule) Explain the contributions of various scientists to the discovery of the structure of DNA. (Watson, Crick, Wilkins and Franklin) Explain what it means that DNA replication is semi-conservative. Use the Messelson-Stahl experiment as evidence. Describe the process of DNA replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Describe how proofreading and repair protect organisms from mutations Identify the major phases of eukaryotic cell cycle and describe the major events that occur during each phase. Explain how binary fission occurs in prokaryotes Explain the outcome and steps of mitosis, identify the stages of mitosis on graphic representations. Describe the molecular system that regulates progression through the cell cycle Describe how cell cycle control mechanisms respond to internal and external signals. Explain how cancers result from breakdowns in cell cycle control. Explain the adaptive value of programmed cell death Describe the life cycles of sexually reproducing organisms. Distinguish between haploid and diploid cells Explain how fertilization produces diploid offspring from haploid gametes. Describe how karyotypes are made and how they can be used to determine the gender of a person and various chromosomal disorders. Describe the purpose, steps and outcome of meiosis Distinguish between the processes of meiosis I and meiosis II Relate how meiosis and fertilization influence genetic variability. Explain the structure of chromosomes. Explain the types of mutations Describe the causes and consequences of mutations. Explain how genetic disorders may result from changes in chromosome structure or number. Distinguish between genes and alleles Explain the relationship between a genotype and a phenotype. Summarize Mendel's principles Explain how independent assortment leads to different genetic combinations in offspring. Analyze and solve monohybrid and dihybrid problems. Analyze and solve a test cross problem. Determine probabilities and outcome in various genetic problems. Apply the Chi-square test to determine the potential mode of inheritance Give examples of non-Mendelian inheritance Explain how dominance can follow complex patterns Understand that most genes have multiple phenotypic effects Relate environmental effects to phenotypes. Describe inheritance patterns in humans Explain the chromosomal theory of inheritance Explain how Morgan's experiments contributed to the understanding of heredity. Describe the cellular process of how genetic information passes from generation to generation. Describe the inheritance patterns of sex-linked genes Explain how linked genes deviate from Mendelian inheritance patterns Relate the use of heredity data for linked genes to the construction of genetic linkage maps. TEXT BOOK SECTIONS: Modules 33 - 48 MATH: Gene linkage calculations with map distances Probability calculations Chi-square calculations Genetic problems LABS: Laboratory Investigation 7 – Cell Division, Mitosis and Meiosis (with lab report) ON-LINE RESOURCES: Haploid vs. Diploid: http://www.bozemanscience.com/diploid-vs-haploid Meiosis: http://www.bozemanscience.com/meiosis Mitosis: http://www.bozemanscience.com/mitosis Lots of genetics videos on : http://www.bozemanscience.com/biology-main-page/ Comparing mitosis and meiosis: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__comparison_of_meiosis_and_ mitosis__quiz_1_.html The Advantage of Sex(ual reproduction): http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/sex/advantage/ Click and Learn on The p53 Gene and Cancer: http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/p53-geneand-cancer