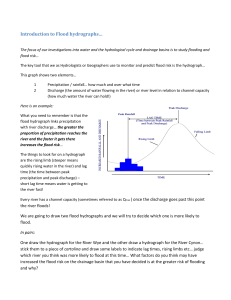
Y2 SemII Engineering Hydrology 2013
advertisement

KIGALI INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING & ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY END OF SEMESTER II EXAMINATIONS ACADEMIC YEAR: 2012-2013 YEAR OF STUDY: SEMESTER: 2 SUBJECT CODE & NAME: NO. OF STUDENTS: II Programme: Full Time Part Time √ WEE 3221 ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY DURATION: 2hrs 123 DATE OF SUBMISSION: MAX. MARKS: 60 20/03/2013 NAME OF INTERNAL EXAMINER: TEL: EXAMINATION PERIOD: APRIL 2013 MAJORO Felicien +250788484054 E-MAIL: f.majoro@kist.ac.rw SIGNATURE: Submitted (i) Syllabus √ (ii) Main Exam Qns. √ (iii) Marking scheme √ (iv) Supp exam Qns. √ (v) Marking scheme √ Head of Department: Date: KIGALI INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING AND ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY INTERNAL MODERATOR’S REPORT DETAILS OF MODERATOR Name of the Moderator: Ms UWIMPUHWE Charlotte Designation: Assistant Lecturer Area of Specialisation: Land and Water Sciences DETAILS OF MODERATING SUBJECT Module Code and Title: WEE 3221 Engineering Hydrology Year of Study: 2 Sem: II Academic Year: 2012-2013 DETAILS OF MODERATION Sl.No DESCRIPTION OF ASSESSMENT COMMENTS,if any 1. Coverage of Syllabus OK 2. Standard and Level of Question Paper OK 3. Allocation /Distribution of Marks OK 4. Allocation of Time OK 5. Qualitative Treatment (Theory) OK 6. Quantitative Treatment (Problem) OK 7. Correlation between Qualitative and Quantitative OK Have comments been incorporated in the question paper or marking scheme by the staff? Yes Signature of Moderator: Date: No INDICATIVE CONTENT WEE 3221 ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY UNIT I INTRODUCTION Definition and scope, Hydrological cycle, World water balance, Practical applications, Historical development. UNIT II PRECIPITATION Introduction, Formation of precipitation, Forms of precipitation, Types of precipitation, Weather systems for precipitation, Measurement of rainfall, Presentation of rainfall data, Mean precipitation over an area, Estimation of missing precipitation records, Double mass curve. UNIT III EVAPORATION Definitions, Mechanisms, Measurements, Equipment used, Empirical methods used to determine evaporation. UNIT IV INFILTRATION Infiltration process, infiltration capacity, measurement of infiltration, infiltration capacity values, infiltration indices. UNIT V STREAM FLOW MEASUREMENTS Introduction, Measurement of stage, Measurement of discharge: current meter, dilution methods, stage discharges, electromagnetic and ultrasonic methods, Indirect methods, Stage discharge relations, Extension of rating curve and its validity, Stream flow routing. UNIT VI RUNOFF Introduction, Components of runoff, Factor affecting runoff, Basin yield, Rainfall-runoff relationship, Peak runoff, Flow mass curve, Determination of runoff by mathematical models. UNIT VII FLOOD HYDROGRAPH Components of hydrograph, Factor affecting flood hydrograph, Base flow separation, Effective rainfall, Unit hydrograph, Instantaneous unit hydrograph, Unit hydrograph of different durations. UNIT VIII DESIGN FLOOD ESTIMATION Introduction, Definitions: Flood, Most Probable Flood, Design Flood. Various methods used for Design Flood Estimation. Rational method, Weibul method, Gumbel method and Log-Pearson type III Distribution. Risk in selecting a design flood and its return period. Flood Frequency analysis. UNIT IX FLOOD CONTROL METHODS Various Flood control methods: Structural measures & Non structural measures. Environmental issues of flood control projects: Positive impacts & Negative impacts. Econmics of Flood control projects: Benefit/cost analysis. UNIT IX HYDROLOGIC ROUTING Definition, reservoir routing, channel routing: prism storage, wedge storage; hydraulic method; numerical method. MAIN EXAM KIGALI INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Avenue de l'Armée, B.P. 3900 Kigali, Rwanda INSTITUTE EXAMINATIONS -SEM:II ACADEMIC YEAR 2012-2013 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: CIVIL ENGINEERING & ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY YEAR: 2 SEMESTER: II MODULE: DATE: GROUP: CE & WEE WEE 3221 ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY / 04 /2013 TIME: 2hours MAXIMUM MARKS = 60 INSTRUCTIONS 1. This paper contains FOUR (4) questions. 2. Answer THREE (3) Questions only: Question ONE (1) from Section “A” is Compulsory and Answer any TWO (2) from Section “B” 3. All questions carry equal marks. 4. No written materials allowed. 5. Do not forget to write your Registration Number. 6. Write all your answers in the booklet provided 7. Do not write any answers on this questions paper. 8. Start each question in a NEW page Section A: Q1 is compulsory QUESTION 1.(20 marks i.e 4 marks for each sub question) With a neat sketch, (i) What do you understand by hydrological budget? (ii) Write and express the hydrologic budget of surface water system; (iii) Write and express the hydrologic budget of groundwater system? (iv) Deduce the system hydrologic budget of a basin; (v) The water budget terms for a lake included precipitation (P) of 48.26mm/year, evaporation (E) of 38.1mm/year, surface water inflow (Qin)of 0 mm/year, surface out flow( Qout) of 441.96mm/year, and the change in lake volume (∆𝑠) of 0 mm/year. Determine the net groundwater flow. Section B: Attempt any 2 Questions from the following Q2, Q3 & Q4 Question2 (20marks) (i) Draw a labeled neat sketch of Symon’s non-recording raingauge (2marks). Describe its working principle (2marks). (ii) Rain-gauge station D was inoperative for part of a month during which a storm occurred. The storm rainfall recorded in the three surrounding stations A, B and C were 8.5, 6.7and 9.0 cm, respectively. If the average annual rainfall for the stations are 75, 84, 70 and 90 cm, respectively, estimate the storm rainfall at station D. (2marks) (iii) The followings are the rain gauge observations during a storm. Prepare a table (2marks) and draw the mass curve (2marks) and the rainfall hyetograph (2marks). Time since the commencement of the storm (min) 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 Accumulated rainfall (cm) 0.1 0.2 0.8 1.5 1.8 2.0 2.5 2.7 2.9 3.1 (iv) Compute the daily evaporation from a Class A pan (2marks) if the amounts of water added to bring the water level to the fixed point are as follows: Day Rainfall (mm) Water (mm) added (+) or removed(-) 1 14 2 6 3 12 4 8 5 0 6 5 7 6 –5 3 0 0 7 4 3 What is the evaporation loss of water in this week from a lake (2marks) of surface area of 640 ha, assuming a pan coefficient of 0.75? (v) The total observed runoff volume during a storm of 6-hr duration with a uniform intensity of 15 mm/hr is 21.6 x 106 m3 . If the area of the basin is 300 km2, find the average infiltration rate (2marks) and the runoff coefficient for the basin (2marks). Question3. (20pts i.e. 4 marks each sub-question) (i) A culvert is proposed across a stream draining an area of 185 ha. The catchment has a slope of 0.004 and the length of travel for water is 1150 m. Estimate the 25 years flood if rainfall is given by: 𝑖= 1000 𝑇𝑟 0.2 (𝑡 + 20)0.7 where i(mm/hr); Tr(years) and t(min). Assume a runoff coefficient of 0.35. (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) The analysis of a 30 year flood data at a point on a river yielded xavg = 1200 m3/s and Sx = 650 m3/s. For what discharge would you design a hydraulic structure at that point to provide 95% assurance that this structure will not fail in the next 50 years? List and discuss briefly at least 8 flood control methods. List and discuss briefly various (at least 4) environmental issues of flood control projects; What do you understand by “Sustainability of a WRDP”? Question 4. (20pts i.e 5 marks each sub-question) The inflow hydrograph readings for a stream reach are given below. The Muskinghum coefficients are K = 36hr and x = 0.15. Route the flood through the reach and determine the outflow hydrograph. Determine also the reduction in peak and the time of peak of outflow. NOTE: The outflow at the beginning of the flood may be taken as the same as the inflow. Time (hours) Inflow (cumecs) Time (hours) Inflow (cumecs) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96 108 120 24 45 88 272 342 288 240 198 162 133 110 132 144 156 168 180 192 204 216 228 240 - 90 79 68 61 56 54 51 48 45 42 - 1 Taking the routing period as 12 hr = 2 day, compute the coefficients c0, c1 and c2 of the routing equation. Fill the stream flow routing table by Muskingum method. Provide the routing curves by plotting the inflow and the outflow hydrographs on the same graph. Determine the peak travel time (i.e the time lag) and the reduction in peak discharge.