2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA assessment statements
advertisement

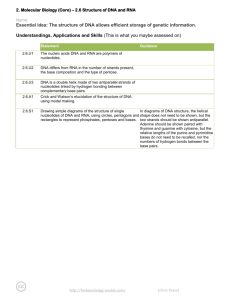
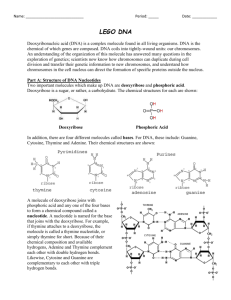
Potential command term assessment statements Topic 2: Molecular biology 2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA Essential Idea: The structure of DNA allows efficient storage of genetic information. Nature of science: Using models as representation of the real world—Crick and Watson used model making to discover the structure of DNA. State that the nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides. Distinguish between DNA and RNA by the: number of strands present the base composition the type of pentose. State the names of the four bases in DNA and the four bases in RNA. Draw simple diagrams of single nucleotide structure for DNA and RNA, using: circles to represent phosphates pentagons to represent pentose ribose and deoxyribose rectangles to represent bases. Explain how the structure of DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of covalently bonded nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. Draw a diagram of DNA structure showing: the two antiparallel strands adenine paired with thymine by hydrogen bonds guanine paired with cytosine by hydrogen bonds nucleotides covalently bonded through the deoxyribose – phosphate backbone Outline Watson and Crick’s elucidation of the structure of DNA using model making. Theory of Knowledge: The story of the elucidation of the structure of DNA illustrates that cooperation and collaboration among scientists exists alongside competition between research groups. To what extent is research in secret ‘anti-scientific’? What is the relationship between shared and personal knowledge in the natural sciences?