Mitosis and Meiosis Name: Levels of Biological organization Cells à
advertisement

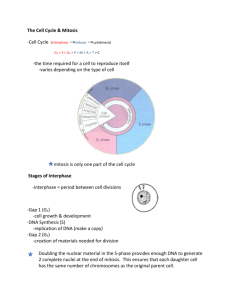
Mitosis and Meiosis • • Levels of Biological organization • Cells ___________________ • Tissues ___________________ • Organs ___________________ • Organ Systems ___________________ From zygote to Trillions of Cells • _____________________=Cell that forms when sperm and egg join • • • __________ gives you DNA from dad, ___________ gives you DNA from mom Shortly after sperm ________________________ egg, the zygote splits into a 2nd cell • • Name: ________________________ These 2 cells split into 4, then 8, then 16, etc. Each of these cells contains _______________________________ (Recall DNA replication) Why must cells divide • _____________ limits cell size • Cells get materials from surroundings through their _____________. This is also how they expel wastes • • If the cell gets too large, it would take a long time for these processes to occur DNA also limits cell size • ________________________________________________ • There is a limit on how fast this can happen. • If the cell is too large, it takes too long to make all of the structures from the proteins. • Surface area-to-volume • Cell Cycle • I-PMAT • The cell cycle can be divided into _______ stages • • • • Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis Interphase and Mitosis are further divided by certain events that happen • Interphase=G1, S, G2 • Mitosis=Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase NEITHER INTERPHASE NOR CYTOKINESIS ARE PARTS OF MITOSIS!!!!!! Interphase (G1, S, G2) • Think “_______________________________” • Most of the cell’s life is spent in __________________ • Period of ______________ and development • ____________ (Growth Phase 1) • • _____ Phase (Synthesis phase) • • Cell grows in size and synthesizes __________ and _____________________ DNA ______________________ ______ (Growth Phase 2) • Cell grows again, ________________ are duplicated, and ________________ are synthesized to prepare for cell division • Mitosis • Period of division • 4 parts (___________) • • • _________________ (“Prologue”) • _________________ (“Middle”) • _________________ (“Apart”) • _________________ (“Two”) Happens only in __________________________ (body) cells Prophase (“Prologue”) • First and ______________________ stage of mitosis • Prophase begins as strands of ______________ coil around proteins called _____________ and become a ____________________ (tightly wound strand of DNA and proteins) • • Each copy of DNA (from Interphase) coils and forms ____________________ strands • • Called __________________________________ These sister chromatids join together at the center (called a _________________) • Each chromosome has a “________________” (remember, you get one from your mom and one from your dad) • These are called homologous chromosomes • • The _____________________ disappears • ____________________ move to opposite ends of the cell • A structure called a _______________________ forms • • Made up of rod-like structures called ___________________________ Metaphase (“Middle”) • Spindle fibers attach to __________________ of chromosomes • Spindles extend from centriole on one side and attach to sister chromatid on that same side • Fibers help chromosomes __________________ in the middle • • Very important because it ensures that ½ of the chromosomes end up in each cell Anaphase (“Apart”) • Spindle fibers ___________________ and pull sister chromatids apart at the centromere • Each identical sister chromatid ________________ to one of the sides of the cell • • Telophase (“Two”) • Chromatids reach opposite ends • Chromatids begin to ____________________ into chromatin • __________________________ around chromatin • __________________ breaks down • Cells begin to __________________ • This ____________________________________ Cytokinesis • Division of _______________________ • Cell divides and ____________________ daughter cells are formed • Process differs in plants and animals • In plant cells, a structure called a _____________________ forms and separates the 2 daughter cells • • In animals cells, the cells “pinch in” until the cells are ____________________ Control of the Cell cycle • _____________________=uncontrolled cell division • Proteins (called _______) created during protein synthesis help to regulate the cell cycle • When these proteins are damaged by mutations of DNA, the cell’s normal cycle is disrupted and cells divide out of control • • Forms a __________________ Cancer cells take nutrients from healthy cells, and can occasionally move around in the body. • When cancer cells move around, it is called _______________________. • This forms new tumors throughout the body • Meiosis • Occurs only in _________________________ (males-sperm and female-egg cells) • The goal is to cut the original number of chromosomes in __________ • Offspring need to inherit from both parents • If the number was not cut in half, the offspring would have _________ the chromosomes as the parents • Terms • A ________________ cell is a cell that contains ____ of each chromosome (di=2) • • A _____________ cell is a cell that contains ___ of each chromosome (hap~half) • • These are typical body cells These have _____ the number of chromosomes as typical cells Phases of Meiosis • Very similar to mitosis • ___________________________________ • Starts with Interphase • • Only occurs __________ before meiosis begins Basically does mitosis _________________ • Meiosis ___ • • Meiosis ___ • • Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II Each ends with cytokinesis • • Meiosis-Interphase • _________________ the same as in Mitosis • Occurs only before Meiosis I, NOT Meiosis II Meiosis-Prophase I • Very similar to Prophase in Mitosis • One huge difference • Homologous chromosomes line up and form a structure called a ________________ • They tangle up and can actually break portions off and exchange DNA • Process is called ___________________________ • Increases genetic diversity by potentially allowing you to pass on traits from both grandparents to offspring • Meiosis-Metaphase I • Again, similar to Metaphase in Meiosis, but with a key difference • Spindle fibers _________________________, and line them up in the middle • This means that there are _____________________ next to one another in the center, instead of one as was the case in Mitosis • Meiosis-Anaphase I • Probably the most different from Mitosis • Whereas in Mitosis, sister chromatids separate at the centromere and move towards opposite ends of the cell, in Meiosis, tetrads are pulled apart and chromosomes (the pair of sister chromatids) move to each side of the cell • This ensures that there will be a ____________________ in the daughter cells • Meiosis-Telophase I • Occurs exactly as it did in Mitosis, except this time there is an _________________________ (pair of sister chromatids) in each of the _____________ cells • Another division is necessary to split the genetic material in half • Cytokinesis occurs, same as Mitosis • • Meiosis II • ____________________________ • This process occurs _________________________ AS MITOSIS • • ________________ cells are formed Only it is occurring in 2 cells at once Results of Mitosis and Meiosis • In Mitosis, 1 cell splits into 2 daughter cells • • The daughter cells are _____________________ In Meiosis I, a single cell splits into 2 daughter cells • Each of these cells contains the same amount of chromosomes as the parent cell • • Still diploid, and ________________________ In Meiosis II, the 2 daughter cells from Meiosis I undergo another cell division, and split into 2 more daughter cells • Each of these cells contains ½ of the original genetic material • Now ______________, and each ______________________