File lesson plans 12-1-5-14 accel
advertisement

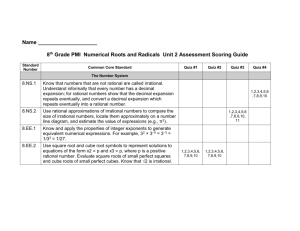
GlynnMiddle School LFS Weekly Lesson Plan Teacher: Irvin Subject Acc. Math Dates: Dec. 1-5, 2014 Unit Topic: Exponents and Equations Standard(s): GPS/CCGPS Work with radicals and integer exponents. MCC8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. MCC8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational. MCC8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. MCC8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. Analyze and solve linear equations and pairs of simultaneous linear equations. MCC8.EE.7 Solve linear equations in one variable. equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form 𝑥=𝑎, 𝑎=𝑎, or 𝑎=𝑏 results (where 𝑎 and 𝑏 are different numbers). MCC8.EE.7b Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms. Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. MCC8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. MCC8.NS.2 Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π2). Prior to teaching: Perfect Squares 1-25, Cubes 1-12, How do you write rational numbers as decimals? EQ tied to the standard: How do we evaluate and estimate squares and square roots? GlynnMiddle School LFS Weekly Lesson Plan How do we evaluate cube roots? Activating Strategy Vocabulary List provided, Terms reviewed daily, choral response with illustrations Teaching Strategies: hands-on activities Summarizing Strategy: Choral Response and written summaries Standards for Mathematical Practice 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4 Model with mathematics. 5 Use appropriate tools strategically. 6 Attend to precision. 7 Look for and make use of structure. 8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Monday Essential Question How do I evaluate square roots and cube roots? Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday How do we solve cubed problems? How do I write number in scientific notation? How do I know that a number is rational or irrational? How do I evaluate squares and cubes, and classify real numbers? How do I solve equations with rational numbers? Activating/Acceleration: (Some ideas: KWL, Pre-reading, Think Pair Share, Thinking Maps, Vocabulary Overview, Word Splash, Survey, Big Four) Drill Perfect squares Review square roots and cube roots with a Two roots and partner by checking Principal Square Roots homework. Growing perfect List examples of rational squares numbers classification Rational and Irrational Quiz GlynnMiddle School LFS Weekly Lesson Plan Can perfect squares be negative? Students will work in interactive notebooks after their homework has been checked with a partner. Explain ½ is rational, model long division =.5 Convert other fractions/ratios to decimals with your neighbor Think pair share Classify numbers as counting(natural), whole, integer, rational, and irrational Students will use Learn Zillion and Graphic organizer to Quiz knowledge background Brain pop for classify numbers of square roots to help introducing scientific in solving cubed roots. notation TIMS method will be TIMS method and Solve equations with used to help students graphic organizer will Rational numbers understand cubed be used to help in roots and factoring. solving problems. Students will complete Student task cards task cards and color will be utilized for activity on cubed roots practice Simplify expressions and update interactive with square roots and books. cube roots Summarizing Strategies: (Some ideas: Ticket Out the Door, 3-2-1, The Important Thing, One Word, Learning Logs) Can you arrange 12 Student will discuss How do you know? What makes pi an Quiz squares to make a with a partner the In your own words irrational number? larger square? difference between a explain how to What is the relationship between tiles in the form of a square and the length of the sides? Can area be negative? GlynnMiddle School LFS Weekly Lesson Plan Can you arrange 20 square root and a cube convert .12 to a cubes to make a larger root. fraction cube? Extending/Refining Activity: This is for all students. After they acquire, then take them up a notch with thinking skills/writing prompts. (Some ideas: Cause/Effect, Compare/Contrast, Write, Classify, Analyze, Evaluate, Inductive, Deductive) Find the area of a cube? What is the relationship between the area and the side lengths? Repeating decimals Identify other words that Solve equations with vs terminating begin with prefix- ir. partners decimals How does the meaning Convert two digit of those words relate to repeating decimals irrational? by solving 100x-x= They all mean “not” 99x to Assignment and/or Assessment: A variety of informal, performance, constructed response, selected response WB 87-90 WB 81-84 WB 99-102 Quiz WB 105-108 Differentiation: Notes Notes Hands-On Activities Hands-On Activities Manipulatives Manipulatives Smart Board Smart Board White Boards White Boards Peer Partners Peer Partners Accommodations: (Sped, 504, SST) Notes Hands-On Activities Manipulatives Smart Board White Boards Peer Partners Notes Hands-On Activities Manipulatives Smart Board White Boards Peer Partners Notes Hands-On Activities Manipulatives Smart Board White Boards Peer Partners GlynnMiddle School LFS Weekly Lesson Plan Differentiated Instruction Remedial Instruction Differentiated Instruction Remedial Instruction Differentiated Instruction Remedial Instruction Differentiated Instruction Remedial Instruction Differentiated Instruction Remedial Instruction