SPS7: Energy Transformations (SPS7eneergytranformations)
advertisement

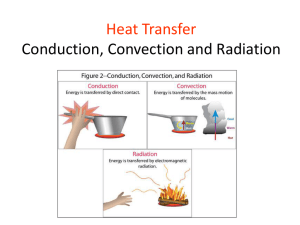
SPS7: Energy Transformations (SPS7eneergytranformations) Name:_____________________________________________ Date:________________________ 1. Tom is working on calorimetry experiments. What is Tom studying? A. light B. mass C. heat D. color 2. A softball is thrown and is hit high into the air. As it rises, the softball possesses A. only kinetic energy. C. both potential and kinetic energy. B. only potential energy. D. potential, kinetic, and electromagnetic energy. 3. A rock dropped from a cliff has greater kinetic energy just before it reaches the ground than it did at the top of the cliff. Which of the following explains this fact? A. The rock's mass decreases as it falls. B. Falling has increased the rock's total energy. C. The rock's potential gravitational energy has been converted into kinetic energy. D. Chemical analysis will reveal that the rock's chemical energy has been consumed. 4. The transfer of heat energy by heat traveling through a metal is known as A. conduction. B. convection. C. radiation. D. reflection. 5. Heat may be transferred through a vacuum by A. conduction. B. convection. C. radiation. D. reflection. 6. A toaster browns bread by converting A. electric energy to heat energy. C. mechanical energy to heat energy. B. heat energy to electric energy. D. chemical energy to electric energy. 7. Heat energy transferred by conduction will travel best through A. solids. B. liquids. C. gases. D. a vacuum. 8. Which is the best heat conductor? A. air B. iron C. wood D. glass 9. A person sitting in front of a fireplace feels what type of heat energy? A. convection energy B. conduction energy C. solar energy D. radiation energy 10. Thermal (heat) energy always flows from A. gas to a liquid. B. a liquid to a solid. C. a warmer region to a cooler region. D. a freezing material to a boiling material. 11. In an air-conditioned house, double glass windows and fiberglass insulation both have a similar ability to transmit heat. These substances serve to _____________ heat transfer, due to their ____________ thermal conductivity. A. prevent, high. B. prevent, low. C. allow, high . D. allow, low. 12. To prevent heat loss through house windows, which is the most environmentally efficient option? A. a double thickness of glass B. two panes of glass separated by air C. two panes of glass separated by a space to which extra air has been added D. two panes of glass separated by a space from which the air has been removed 13. In which of the following situations does a stone have the greatest kinetic energy? A. a stone at a cliff's edge C. a stone lying at the bottom of a cliff 14. B. a stone falling from a cliff D. a person carrying a stone up a mountain The sun's heat reaches Earth by what means? A. convection B. conduction C. collision D. radiation 15. Every person uses energy stored in the fat cells of his or her body. This stored energy is in the form of A. heat energy. 16. C. chemical energy. D. mechanical energy. A hang glider is able to sail through the air on warm winds which are heated by Earth's surface. This best illustrates one use of which principle of heat transfer? A. conduction 17. B. nuclear energy. B. convection C. radiation D. solar transfer If a particular substance is a good electrical insulator, then you can assume it probably A. has no isotopes. C. is a liquid at room temperature. B. does not lose electrons easily. D. is a compound, rather than an element. 18. In a laboratory, a sealed container with 100 g of steam is cooled until all the steam becomes a liquid. The container is then cooled further until all the water becomes a solid. Which of the following remains constant during both of these changes? A. the mass of the water C. the total energy of the water . B. the pressure in the container D. the position of the atoms in the container 19. The graph below compares three states of a substance. Which of the following choices is the best label for the y-axis? A. molecular density C. neutron density B. molecular motion D. neutron motion 20. In a copper wire, a temperature increase is the result of which of the following? A. an increase in the size of the copper particles B. a decrease in the mass of the copper particles C. an increase in the motion of the copper particles D. a decrease in the distance between the copper particles 21. The water contained in a geyser system gains energy from the underground material surrounding it. The water molecules gain kinetic energy and this results in an increase in the pressure of the water. Eventually the geyser erupts and expels water into the air above ground. Which of the following types of energy is the source for the initial energy gain of the water? A. electrical B. magnetic C. mechanical D. thermal . 22. A student in a laboratory transfers a beaker containing a hot solution from the lab table to a cool water bath. Which of the following parts of the system experiences an increase in heat energy? A. beaker B. lab table C. solution D. water bath T 23. Which is an example of energy from chemical bonds being formed or broken transformed into energy of motion? A. lighting a match B. turning on a battery-operated toy car C. pushing a button on the TV remote control D. the wind turning the blades of a windmill 24. In a coal burning power plant, coal is burned to heat steam to turn a turbine. The turbine generates power that is sent to homes and businesses. Order the energy transformations of the power plant. A. chemical, mechanical, electrical C. mechanical, chemical, electrical B. electrical, chemical, mechanical D. mechanical, electrical, chemical 25. What do all of the processes listed here have in common? sawing a piece of wood lighting a match turning on a light bulb A. All transform into a form of energy from chemical energy. B. All transform into a form of energy from electrical energy. C. All transform a form of energy into light energy. D. All transform a form of energy into heat energy. 26. The image is a double-paned window. These types of windows are used in all new homes and consist of two sealed panes of glass with a vacuum between the glass. The particles on the outside of the window are moving faster than those on the inside. The double-paned window does a good job of insulating the inside of the house from these faster, hotter particles. Double-paned windows do an excellent job of PREVENTING heat transfer by means of A. conduction. B. convection. C. radiation. D. transformation. 27. In this type of heat transfer, no molecular motion is necessary. Heat can be transferred across large distances without any particles being present. A. conduction B. convection C. radiation D. transformation 28. Many restaurants and kitchens use iron skillets to cook bacon, eggs, and biscuits for breakfast. A standard skillet has a mass of 850 g. When cooking bacon for breakfast the skillet starts at a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius. At the end of cooking, the temperature of the skillet reaches 120 degrees Celsius. The specific heat of iron is 0.45 J/(g°C). Determine the heat energy gained by the iron skillet. A. 4.03 J B. 382.5 J C. 36,337.5 J D. 179,444.4 J 29. A pot with 2400 g of water at a temperature of 25 °C is heated on a stove until the water boils (100°C). The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/(g°C). Determine the heat energy needed to heat the water in the pot to boiling A. 133.76 J B. 43,062.2 J C. 752,400 J D. 1,003,200 J (Q = mc T) 30. Points A, B and C lie along a line of equal pressure, 760 mm of mercury, atmospheric pressure. The energy required to move from A to B to C A. increases at all points. B. decreases at all points. C. increases, decreases at B, then increases again. D. decreases, increases at B, then decreases again. 31. Which of these processes occurs along the BC line in the diagram? A. boiling B. condensing C. melting D. vaporizing 32. Solid magnesium has a specific heat of 1.01 J/g°C. How much heat is given off by a 20.0 gram sample of magnesium when it cools from 70.0°C to 50.0°C? A. 202 J B. 404 J C. 808 J D. 1010 J 1. C) heat 2. C) both potential and kinetic energy. 3. C) The rock's potential gravitational energy has been converted into kinetic energy. 4. A) conduction. 5. C) radiation. 6. A) electric energy to heat energy. 7. A) solids. 8. B) iron 9. D) radiation energy 10. C) a warmer region to a cooler region. 11. B) prevent heat transfer due to their low thermal conductivity. 12. D) two panes of glass separated by a space from which the air has been removed 13. B) a stone falling from a cliff 14. D) radiation 15. C) chemical energy. 16. B) convection 17. B) does not lose electrons easily. 18. A) the mass of the water 19. B) molecular motion 20. C) an increase in the motion of the copper particles 21. D) thermal 22. D) water bath 23. B) turning on a battery-operated toy car 24. A) chemical, mechanical, electrical 25. D) All transform a form of energy into heat energy. 26. A) conduction. 27. C) radiation 28. C) 36,337.5 J 29. C) 752,400 J 30. A) increases at all points. 31. C) melting 32. B) 404 J