Acids, Bases & Salts (C)
advertisement

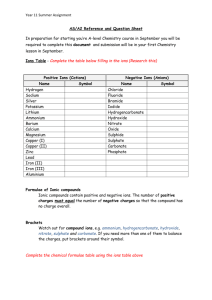
Page |1 Acids, Bases & Salts (C) Q.1. Write the balanced equations for the preparation of the following compounds (as the major product) starting from iron and using only one other substance: (i) Iron (II) chloride (ii) Iron (III) chloride (iii) Iron (II) sulphate (iv) Iron (II) sulphide. Ans : - (i) Fe + 2HCl (dil) → FeCl2 + H2 (ii) 2Fe (heated) + 3Cl2 (dry) → 2FeCl3 (iii) Fe + H2SO4 (dil) → FeSO4 + H2 Δ (iv) Fe + S → FeS Q.2. Copy and complete the following table – Column 3 has the names of the gases to be prepared using the substance you enter in Column 1 along with dilute or concentrated Sulphuric acid as indicated by you in Column 2. Column 1 Column 2 Column 3 Substance reacted Dilute or concentrated with acid Gas Sulphuric acid Hydrogen Ans : Column 1 Column 2 Column 3 Substance reacted Dilute or concentrated with acid Gas Any active metal (Mg, Zn) except Na, K, Ca and Pb dil. H2SO4 Hydrogen Na2CO3, NaHCO3 dil. H2SO4 Carbon dioxide Bleaching powder Sodium chloride and Manganese dioxide dil. H2SO4 conc. H2SO4 Chlorine Q.3. Write the equations for the laboratory preparation of : (i) Sodium sulphate using dilute Sulphuric acid. (ii) Lead sulphate using dilute Sulphuric acid. Ans : - (i) 2NaOH + H2SO4 (dil) → Na2SO4 + 2H2O (ii) Pb(NO3)2 + H2SO4 (dil) → PbSO4 + 2HNO3. Q.4. Write the equation for the laboratory preparation of the following salts using sulphuric acid: (i) Iron II sulphate from iron. (ii) Copper sulphate from copper. Page |2 (iii) Lead sulphate from lead nitrate. (iv) Sodium sulphate from sodium carbonate. Ans : - (i) Fe + H2SO4 (dil) → FeSO4 + H2 (ii) Cu + 2H2SO2 (conc.) → CuSO4 + H2O + SO2 (iii) Pb(NO3)2 + H2SO2 (dil.) → PbSO2 + 2HNO3 (iv) Na2CO3+ H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2. Q.5. Choosing the correct words given in brackets, complete the sentences given below: (i) An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water gives ________ (hydronium/hydroxide) ions as the only ________ (positive/negative) ions. (ii) An _________ (acid/basic) salt is one in which the hydrogen of an acid has been partially replaced by a _________ (metal/non-metal). Ans : - (i) hydronium, positive. (ii) acid, metal. Q.6. Which of the following methods, A, B, C, D, or E is generally used for preparing the chlorides listed below from (i) to (v). Answer by writing down the chloride and the letter pertaining to the corresponding method. Each letter is to be used only once. A. Action of an acid on a metal. B. Action of an acid on oxide or carbonate. C. Direct combination. D. Neutralization of an alkali by an acid. E. Precipitation (double decomposition). (i) Copper (II) chloride. (ii) Iron (II) chloride. (iii) Iron (III) chloride. (iv) Lead (II) chloride. (v) Sodium chloride. Ans : - (i) Copper (II) chloride – B. (ii) Iron (II) chloride – A. (iii) Iron (III) chloride – C. (iv) Lead (II) chloride – E. (v) Sodium chloride – D. Q. 7. Fill in the blanks with suitable words: An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water form Hydronium ions as the only (i) ___________ ions. A base is a compound which if soluble in water contains (ii) ____________ ions. A base reacts with an acid to form a (iii) _________ and water only. This type of reaction is known as (iv) _________ . Ans.: - (i) positive (ii) hydroxide (iii) salt (iv) neutralization. Q. 8. The preparation of Lead sulphate from Lead carbonate is a two-step process. (Laed sulphate cannot be prepared by adding dilute Sulphuric acid to Lead carbonate.) (i) What is the first step that is required to prepare Lead sulphate from Lead carbonate ? (ii) Write the equation for the reaction that will take place when this first step is carried out. (iii) Why is the direct addition of dilute sulphuric acid to Lead carbonate an impractical method of preparing Lead sulphate? Ans.: - (i) The first step is to convert insoluble lead carbonate into soluble lead nitrate by treating lead carbonate with dilute nitric acid. (ii) PbCO3 (s) + 2HNO3(dil) → Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 ↑ Page |3 (iii) When dilute sulphuric acid is added directly to lead carbonate, the lead sulphate thus formed will be deposited on solid lead carbonate disconnecting lead carbonate from sulphuric acid. Q. 9. (i) Which feature of the Ammonia molecule leads to the formation of the Ammonium ion when Ammonia dissolves in water? (ii) Name the other ion formed when Ammonia dissolves in water. (iii) Give one test that can be used to detect the presence of the ion produced in(ii). Ans.: - (i) Basic nature. (ii) Hydroxide ion. (iii) If an aqueous solution Fe2+ ions is added to a solution containing hydroxide ions, a dirty green precipitate is formed. Q. 10. Match the descriptions below with the appropriate term from the list A to F: A: Acidic oxide, B: Alkali, C: Amphoteric oxide, D: Basic oxide, E: Deliquescence, F: Efflorescence. (i) The property of spontaneously giving up water of crystallization to the atmosphere. (ii) A compound, soluble in water and the only negative ions in the solution are hydroxide ions. Ans : - (i) F (ii) B. Q.11. What is observed when, neutral litmus solution is added to sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. Ans.: - Colour of litmus solution is changed to blue. Q. 12. Acids dissolve in water to produce positively charged ions. Draw the structure of these ions. Ans.: H+ ! :O: H ! H Q. 13. Mention the colour changes observed when the following indicators are added to acids :(i) Alkaline phenolphthalein solution. (ii) Methyl orange solution. (iii) Neutral litmus solution. Ans : - (i) From pink to colourless. (ii) From pale yellow to pink. (iii) Neutral litmus solution changes to red colour. Q.14. Which of the following hydroxides is not an alkali :– (a) ammonium hydroxide (b) calcium hydroxide (c) copper hydroxide (d) sodium hydroxide. Ans : - (c) copper hydroxide. Page |4 Q.15. From the list given below, select the word(s) required to correctly complete blanks (i) to (v) in the following passage :ammonia, ammonium, carbonate, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, hydronium, hydroxide, precipitate, salt, water. A solution X turns blue litmus red, so it must contain (i) ---------- ions; another solution Y turns red litmus blue and therefore, must contain (ii) ------------- ions. When solution X and Y are mixed together, the products will be a (iii) ------------- and (iv) ------------- . If a piece of magnesium were put into solution X, (v) -------------- gas would be evolved. Ans.: - (i) hydronium (ii) hydroxide (iii) salt (iv) water (v) hydrogen. Q.16. Match the following :Column A Column B 1. Acid salt A. Sodium potassium carbonate 2. Mixed salt B. Alum 3. Complex salt C. Sodium carbonate 4. Double salt D. Sodium zincate 5. Normal salt E. Sodium hydrogen carbonate Ans :- 1. (E), 2. (A), 3. (D), 4. (B), 5. (C).