Session 4 PM_Final-1
advertisement

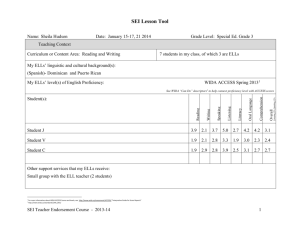
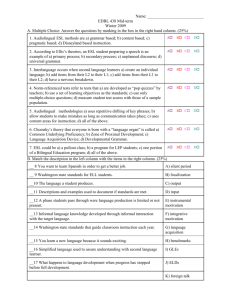
Massachusetts Sheltered English Instruction Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4: Second Language Acquisition in the SEI Classroom Participant Manual Version 1.0 Contents Overview of the SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Sessions ....................................................... 3 Session Information ...................................................................................................................... 3 Session Overview .............................................................................................................. 3 Regulatory Requirements Addressed in Session 4 ............................................................ 4 Session 4 Objectives ......................................................................................................... 4 Agenda .............................................................................................................................. 5 Session 4 Participant Handouts .................................................................................................... 6 What do you know about language proficiency? ................................................................ 6 Summarizing Theories of Language Acquisition ................................................................ 7 Theories of Language Acquisition – Instructional Implications ........................................... 8 Theories of Language Acquisition – Implications for YOUR teaching practice ................... 9 We’re going to Vietnam! .................................................................................................. 10 Cummins’ Four Quadrant Model Sorting Activity ............................................................. 11 Stages of Second Language Acquisition ......................................................................... 12 WIDA Levels of Language Proficiency ............................................................................. 13 Analyzing Sociocultural Factors ....................................................................................... 15 Upcoming Assignments .............................................................................................................. 17 Assignments due by Session 5 ........................................................................................ 17 Preparing for Session 5 (online) ...................................................................................... 17 Session 4 Notes .......................................................................................................................... 18 Participant Manual for the SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Overview of the SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Sessions Current Session MODULE A: ELLs: Their World and Second Language Acquisition Process in the SEI Classroom (Sessions 1—4) 1: Examining Data & Policies Relevant to ELLs 2: Diversity within ELL Populations (ONLINE 3 HOURS) 3: Cultural & Social Aspects of Teaching in the SEI Classroom 4. Second Language Acquisition in the SEI Classroom MODULE B: Academic Language and Literacy Development in the SEI Classroom (Sessions 5—16) 5. Sheltering Content (ONLINE 3 HOURS) 6: Vocabulary for ELLs I 7: Vocabulary for ELLs II 8. Vocabulary for ELLs III (ONLINE 2 HOURS) 9: Reading for ELLs I 10: Reading for ELLs II 11: Reading for ELLs III (ONLINE 2 HOURS) 12: Writing for ELLs I 13: Writing for ELLs II 14. Writing for ELLs III (ONLINE 2 HOURS) 15: Large-Scale Assessments for ELLs and Lesson Planning Presentations 16. Capstone Lesson Presentations, Course Evaluations Session Information Session Overview Session four provides participants with further study about the stages of second language acquisition, theories of second language acquisition and factors that contribute to one learning a new language. Sociocultural influences, political and ideological dimensions as well as socio-economic factors are presented. Including the components of second language acquisition within all classroom settings will be addressed. Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 3 of 19 Regulatory Requirements Addressed in Session 4 (Bolden regulations covered in the Session) 603 CMR 7.14: Endorsements (1) SEI Teacher Endorsement (b) Subject Matter Knowledge: 1. The basic structure and functions of language. 2. Second language acquisition factors as they affect access to the Massachusetts standards. 3. Social-cultural, affective, political, and other salient factors in second language acquisition. 4. Sheltered English immersion (SEI) principles and typologies: i. General academic and domain-specific discourse practices relevant to the grade level (k-5 or secondary), English proficiency level, and content area (English language arts and history; science and mathematics; other content areas). 5. Implementation of strategies for coordinating SEI and English language development instruction for English language learners. 6. Federal and Massachusetts' laws and regulations pertaining to English language learners. 7. Understanding of diversity and background of English language learner populations, including family systems, and communities, and their impact on teaching and learning. 8. Theory, research, and practice of reading and writing for English language learners. i. Practices and approaches for developing reading and writing skills and comprehension in English for English language learners who are at different levels of English language proficiency. 9. The role of oral language development in literacy development for English language learners. 10. Formative and summative assessments for English language learners. 11. Literacy and academic language development. i. The role of vocabulary development in accessing academic language. Session 4 Objectives At the end of this session, participants will be able to identify and explain key theories of first language acquisition, in particular, Behaviorist, Innatist and Interactionist; (SEIT 1, 2) describe stages of second language development; (SEIT 2, 3) express familiarity with fundamental theories and understandings related to SLA, e.g., Cummins’ Common Underlying Proficiency, Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills (BICS) and Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency (CALP) distinction, Krashen’s Five Hypotheses, language transfer, and language competence vs. performance; (SEIT 2, 3) demonstrate an understanding of how long it takes for ELLs to become proficient in English and how effective SEI and ESL/ELD instruction can accelerate that process; (SEIT 2, 3) understand the significance of various key factors on second language acquisition, such as age, prior schooling in the L1, L1 literacy level, familiarity with school culture and academic discourses, metalinguistic/metacognitive awareness, motivation, and personality; (SEIT 2, 3, 8, 9, 11) explain when to emphasize fluency and communication and when to emphasize explicit error correction; (SEIT 2, 4) Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 4 of 19 distinguish between myths and facts related to Second Language Acquisition; (SLA). define “sociocultural,” “political,” and “ideological” in regard to second language acquisition; (SEIT 3) demonstrate knowledge of sociocultural, political, and ideological factors that can affect second language development (e.g., social distance, social and cultural capital, race/ethnicity, and identity); (SEIT 2, 3) create schools and classroom environments that reduce the environmental “affective filter.” (SEIT 2, 3) Agenda I. Introduction to Session 4 (10 min) II. Language Acquisition Theories (50 min) III. Roadmap and Agenda (7 minutes) Objectives (5 minutes) Introduction to Language Acquisition (14 min) Language Acquisition Theory Presentations (21 min) Instructional Implications for ELLs Modified True and False (10 min) Implications for Teaching Practice (5 min) Other Second Language Acquisition (SLA) Theories (20 min) We’re going to Vietnam! (10 min) Cummins’ SLA Theories (9 min) IV. Break (10 min) V. Other SLA Theories and Implications – continued (30 min) VI. Stages of SLA and Factors that Influence it (55 min) VII. Cummins’ SLA Theories – continued (20 min) Implications for Teaching (5 min) Learning about Stages of SLA (13 min) Factors that Influence SLA (32 min) Key Take Away and Reminders (10 min) Wrap-Up (5 min) Assignments (4 min) Assigned Readings (1 min) Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 5 of 19 Session 4 Participant Handouts What do you know about language proficiency? Complete each statement about language proficiency. 1. Being proficient in a language means that a person can _________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________. 2. People learn their first language by _______________________________________________. 3. There are many factors that can influence how well a person learns his or her first language: ______________________, ______________________________, and ________________ ____________________________, etc. 4. Becoming proficient in a second language means that people can _________________________________________________________________________ 5. Compared to learning a first language, learning a second language is _________________________________________________________________________. 6. There are many things that can help a person learn a second language: __________________________________________________________________________, ___________________________ and __________________________________________ 7. There are many factors that can influence how well a person learns his or her first language: ______________________, ______________________________ and ______________ ____________________________, etc. Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 6 of 19 Summarizing Theories of Language Acquisition Recreate the following graphic organizer in your chart paper to present a summary of your assigned theory of language acquisition. Make sure to use the appropriate graphic organizer! A. Graphic Organizer for First Language Acquisition Theories Motto or jingle explaining how children learn language according to this theory Picture representing the process of first language acquisition according to this theory One sentence summary of the theory Name of the theory and main contributor/s Strengths of this theory Weaknesses of this theory Application in the classroom – activities or methods associated with this theory B. Graphic Organizer for Second Language Acquisition Theories Key ideas associated with this theory Picture representing the process of second language acquisition according to this theory Strengths and weaknesses of this theory Name of the theory and main contributor/s Application in the classroom – what students would be doing in a classroom following this theory Why understanding this theory is useful for teachers of ELLs Application in the classroom – what a teacher would say or do if following this theory Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 7 of 19 Theories of Language Acquisition – Instructional Implications Read each statement, answer T (if true) or F (if false) given the theories studied. If the answer is false, write the correct answer on the line. 1. When teachers teach ELLs, they should use the same English they do when teaching Native English speakers. ____ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Teachers should expose ELLs to language that is right at their level of second language development. _____ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. Some strategies that help native speakers develop their first language (L1) can help ELLs develop their second language (L2). ____ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. The best language teaching for ELLs focuses on teaching how the English language works in structured interactions where ELLs use the exact grammar and vocabulary they have been taught. ____ ________________________________________________________________________ 5. Because it’s important to keep a low anxiety environment, teachers should not force students who are on their “silent period” to speak in English. ____ ________________________________________________________________________ 6. ELLs need opportunities to interact with Native English speaking peers even if they are not completely fluent in English. ____ ________________________________________________________________________ 7. Teachers of ELLs should always correct language errors and mistakes explicitly because ELLs use this feedback to learn the language. ____ ________________________________________________________________________ Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 8 of 19 Theories of Language Acquisition – Implications for YOUR teaching practice Think about the theories of language acquisition discussed. Write down: 3 3 practices that you already use that align well with theory 2 2 practices you should try in your classroom Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 1 1 current practice you should consider changing page 9 of 19 We’re going to Vietnam! Imagine you are taking a trip to Vietnam tomorrow. Rate each communicative/language task by the level of difficulty you would experience if you had to do it all in Vietnamese. Rating Scale 1 = Piece of cake! 2 = Doable – with a little help from my Vietnamese friends (or if they know a little English!) 3 = Tough, but possible 4 = Impossible! Language Situation or Task 1 2 3 1. Calling a Vietnamese airline to make reservations 2. Responding to an airline staff member who wants to check your passport and boarding pass at the airport 3. Checking in at a Vietnamese hotel 4. Hailing a cab and giving directions to a common tourist attraction 5. Writing a note complaining about poor service in your hotel 6. Reading the airplane magazine 7. Reading the airplane’s safety brochure 8. Participating in a guest panel discussing the current economic situation in the US at a Vietnamese university 9. Ordering food at a restaurant 10. Listening to the Hanoi evening news Discussion Questions a) Which language tasks would be easier (ratings 1-2)? Why? b) How could you make these language tasks easier? c) Which language tasks would be harder (ratings 3-4)? Why? d) Do you see any patterns between language tasks that are easier and those that are harder? Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 10 of 19 4 Cummins’ Four Quadrant Model Sorting Activity Sort each communicative task into the appropriate Quadrant with a partner. Write the letter of each language task in the right quadrant. Make sure you can explain why you’ve placed a task into a Quadrant to another pair. Cognitively Undemanding (Simple, easy concepts) I III ContextEmbedded ContextReduced (Many clues) (Few clues) II IV Cognitively Demanding (Hard, complex concepts) Source: Adapted from Echavarria & Graves, 2011 OR Cummins, 1981b Communicative Tasks – for teachers of older students a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) Reading a science textbook in order to understand how to calculate speed Acting out a historical event Pointing to items in the classroom Writing a short paragraph explaining what the student did last summer Writing a short paragraph explaining what the slope of a graph means Watching a move about Lewis and Clark’s exploration Participating in a flag football game during recess Listening to a lecture on atoms and molecules Communicative Tasks – - for teachers of younger students a) Talking to a friend at recess b) Describing a weekend trip to the zoo c) Participating in a phonics lesson about the silent e d) Telling a sibling about what happened at school today e) Performing in a class play f) Reading aloud from a new story g) Listening to the teacher read a favorite story Communicative Tasks for teachers of younger students adapted from Trumbull, E. and Pacheco, Maria (2005). The teacher’s Guide to Diversity: Building a Knowledge Base, Volume II: Language, The Education Alliance at Brown University, Pp. 75-76. Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 11 of 19 Stages of Second Language Acquisition Krashen’s Stages of Second Language Acquisition Stage Characteristics Approximate Time Frame Preproduction The student 0-6 months Early Production Has minimal comprehension Does not make verbal utterances Can nod “yes” or “no” in response to simple questions Draws and points The student Speech Emergence Intermediate Fluency Advanced Fluency 6 months – 1 year Has limited comprehension Produces one or two word oral responses Can use key words and familiar phrases to communicate Uses present-tense verbs The student 1-3 years Has good comprehension Can produce simple sentences orally and in writing Makes grammar and pronunciation errors Frequently misunderstands jokes The student 3-5 years Has excellent comprehension Makes few grammatical errors The student has a language level similar to that of native speakers of the same age. 5-7 years Krashen, S.D., & Terrell, T. (1983) The natural approach: Language acquisition in the classroom. Oxford: Pergamon. Hill, J., & Flynn, K. (2006) Classroom instruction that works with English Language Learners. Alexandria: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development. Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 12 of 19 WIDA Levels of Language Proficiency © 2010 Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System, on behalf of the WIDA Consortium Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 13 of 19 Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 4 Version 1.0 page 14 of 19 Analyzing Sociocultural Factors Analyze how sociocultural factors may affect second language acquisition in each given scenario. Guiding Questions: What role could family/school/cultural norms and conventions, identity and, other sociocultural factors play in each student’s language development? What advice would you give their teachers? Scenario #1: Khumar Khumar lives with this mother and grandmother. Khumar’s Grandmother, Sofia, speaks no English, but is very interested in Khumar’s education. She always asks him whether he has finished his homework and even checks his worksheets to make sure Khumar completed them. Khumar’s mother, Patricia, is also very involved in Khumar’s education. When she gets home from work around 7 she always asks Khumar about what he learned about in school. Patricia is a housekeeper at a local hotel, so she is not usually available to visit school during parent teacher conferences. Although Khumar is only in 3 rd grade, Patricia says she would like Khumar to go to college some day. She says that she regrets not having the chance to finish high school, but that she will do anything it takes to make sure Khumar is successful in school. In contrast, Khumar’s teacher complains that Khumar’s family seems uninterested in his education. Mr. Browne has left numerous messages for Patricia’s voicemail but has never heard back. He is worried that Khumar is not developing language fast enough to keep up with school work. Scenario #2: Adiel Adiel is a teenage student who came to the US as a refugee. Adiel grew up in a village, helping out his father with the family farm. In Adiel’s culture, men and women do not usually interact unless they are closely related. Farmers are not given an opportunity to participate in politics or go to school, so Adiel never learned to read or write in his native language. However, Adiel learned to speak several languages while selling produce at the town’s market. Adiel goes to a suburban school, where most of his classmates and teachers are white, middle class US citizens. Adiel’s teacher, Mrs. O’Donnell, has tried very hard to befriend Adiel. Mrs. O’Donnell is worried that Adiel is isolated and has not integrated into school life although he has been in the US for almost two years. Mrs. O’Donnell does not understand why Adiel won’t talk to her about school assignments, or join the after school club she sponsors although she has invited him repeatedly. Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 1 February 2013 Page 15 of 19 Scenario #3: Cynthia Cynthia moved to the US against her wishes. Cynthia’s mother fled her home country because her husband was on the run from the police for selling drugs. Although Cynthia was a very outgoing and successful learner in her home country, she is shy and apathetic in her new school. After a whole year in the US, Cynthia still refuses to speak English, even when she knows it will affect her grade. Her math teacher, Mrs. Caruthers, says Cynthia is also very disrespectful. Recently, Cynthia was suspended for threatening a teacher. During an altercation, Cynthia got really close to Mrs. Caruthers, pointed a finger at her, and yelled at her in Spanish. Cynthia said Mrs. Caruthers was treating her unfairly. Mrs. Caruthers’ assistant, who is also Hispanic, told the principal she did not think Cynthia intended to hurt Mrs. Caruthers. Nevertheless, Mrs. Caruthers thinks Cynthia deserved to be suspended in order to learn to respect her elders and other people’s personal space. Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 1 February 2013 Page 16 of 19 Upcoming Assignments Assignments due by Session 5 Journal Entry due by the beginning of Session 5 Describe several different ways in which you help to keep your English learners’ affective filters low. This might include any aspects of your classroom environment, teaching practice, or interpersonal interactions with students and families. Include some additional ideas you are considering as a result of course readings or discussions. Preparing for Session 5 (online) Review the online materials and read the required readings for Session 5: Coleman, R. & Goldenberg, C. (2010). What does research say about effective practices for ELLs? Kappa Delta Pi Record, 46(2), (60-65). Echevarria, J. & Graves, A. (2011). Sheltered instruction in the content areas. In Sheltered content instruction: Teaching English learners with diverse abilities (4th ed.). (44-54). Boston, MA: Pearson. Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 1 February 2013 Page 17 of 19 Session 4 Notes ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 1 February 2013 Page 18 of 19 ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Participant Manual for SEI Teacher Endorsement Course Session 1 February 2013 Page 19 of 19