The Nature of Stress

Lecture 2 Stress in Simple Words
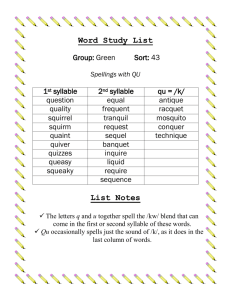
Word Stress
Complicated and complex matter
Incorrect stress placement may lead to major intelligibility problems
English stress cannot be decided in terms of a relation to the syllables of a word.
French: usually the last syllable is stressed
Polish: usually the penultimate syllable is stressed
Czech and Slovak: usually the 1 st syllable is stressed
The Nature of Stress
1st syllable stress: examples:
2nd syllable stress: examples:
Final syllable stress: examples:
Stress is marked by a __________________________________.
Prominence
From the perceptual POV, all stressed syllables share 1 common characteristic: _________________.
What makes a syllable prominent?
1.
______________
2.
______________
3.
______________
4.
______________
These 4 factors work together in combination. However, it seems that the strongest effect is produced by _________________ and ___________________ is also regarded as a powerful factor.
Thus, much less effect is demonstrated by loudness and quality.
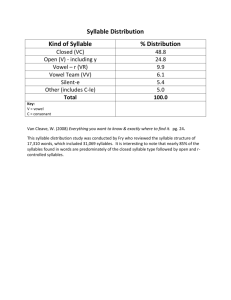
Levels of Stress
In some words, stress that is weaker than primary stress can be observed – secondary stress (low mark).
Examples:
The third level of stress can be called _________________ – the absence of any recognisable amount of prominence.
How to decide on stress placement?
It is necessary to take the following information into account:
1.
Whether a word is morphologically ______________ or _______________.
2.
What the ____________________________ of a word is
3.
How many __________________ a word has
4.
What the __________________________ of a word is
The rules
However, the rules are exceedingly complex and nearly all the rules have exceptions.
Proceduralization???
Many writers have said that English word stress is so difficult to predict that it is best to treat stress placement as a property of the individual word, to be learned when the word
itself is learned (Roach, 2009, p. 76)!
Dictionaries indicate the stress mark as a part of word entries!!!
Pronunciation teaching
Exposure
Noticing
Understanding
Practicing – giving learners opportunities to speak and giving them feedback also on the stress placement!
Exposure: watching movies, listening to songs
List of resources:
Cruttenden, A. Gimson’s Pronunciation of English. Hodder Education, 2008.
Crystal, D. A Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics. Blackvell Publishing, 2008.
Davenport M. – Hannahs S. Introducing Phonetics and Phonology. Hodder Arnold, 2005.
Richards, J. – Schmidt, R. Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics.
Longman, 2010.
Roach, P. English Phonetics and Phonology. Cambridge University Press, 2009.
Underhill, A. Learning and teaching pronunciation. Macmillan, 2005.