Colleen Snow Lesson plans for Biology Week 16, April 23
advertisement

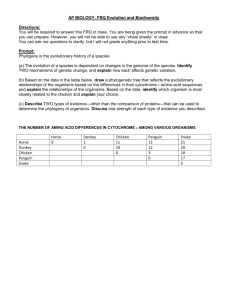
Colleen Snow Lesson plans for Biology Week 16, April 23-27, 2012 Unit 5-6: CLASSIFICATION April 23 Today’s assignment: Dichotomous key worksheet Activity: Read pp. 447-455 Vocabulary: Taxonomy: classifying organisms and assigning each organism a universally accepted name. Binomial nomenclature : each species is assigned a two-part scientific name (developed by Carolus Linnaeus). Genus: a group of closely related species. Taxon: a group or level of organization, taxonomic category. Family: genera that share many characteristics. Order: a broad category that is composed of similar families. Class: group composed of similar orders. Phylum: composed of several different classes that share important characteristics. Kingdom: Largest and most inclusive of Linnaeus’ taxonomy. Evolutionary classification: grouping organisms together based on their evolutionary history. Derived character: characteristics that appear in recent parts of a lineage, but not in older members. Cladogram: a diagram that shows evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms. Molecular clock: uses DNA comparisons to estimate the length of time that two species have been evolving independently. Objectives: At the end of this lesson, student will be able to: Objectives: At the end of this lesson (CLASSIFICATION)SWBAT: 1) 2) 3) 4) Classify organisms based on particular characteristics. Explain how living things are organized for study. Describe binomial nomenclature. Explain Linnaeus’ system of classification Standards: Concept 4: Biological Evolution Understand the scientific principles and processes involved in biological evolution. PO 6. Analyze, using a biological classification system (i.e., cladistics, phylogeny, morphology, DNA analysis), the degree of relatedness among various species. April 24, 2012 Today’s assignment: Quick lab pp.453 Today’s vocabulary: Domain: the most inclusive taxonomic category, larger than kingdom. Bacteria: unicellular and prokaryotic organisms that have cell walls containing peptidoglycan. Eubacteria: Kingdom that contains bacteria. Archae: : unicellular and prokaryotic organisms that lack peptidoglycans and contain lipids. Archaebacteria: Kingdom that contains Archae. Eukarya: domain of all organisms that have a nucleus. Protista: Kingdom of all nucleus organisms that cannot be classified as animals, plants or fungi. Fungi:Kingdom of all nucleus organisms that are heterotrophs. Plantae; kingdom of all nucleus organisms multicellular organisms that are photosynthetic autotrophs. Animalia: Kingdomof all nucleus organisms that are multicellular and heterotrophic. Read pp. : 457-463 Objectives: At the end of this lesson, student will be able to: Objectives: At the end of this lesson (CLASSIFICATION)SWBAT: 1) 2) 3) 4) Classify organisms based on particular characteristics. Explain how living things are organized for study. Describe binomial nomenclature. Explain Linnaeus’ system of classification Standards: Concept 4: Biological Evolution Understand the scientific principles and processes involved in biological evolution. PO 6. Analyze, using a biological classification system (i.e., cladistics, phylogeny, morphology, DNA analysis), the degree of relatedness among various species. April 25, 2012 Today’s assignment: Dichotomous key worksheet Today’s vocabulary: PO 6. Analyze, using a biological classification system (i.e., cladistics, phylogeny, morphology, DNA analysis), the degree of relatedness among various species. Objectives: At the end of this lesson, student will be able to: Objectives: At the end of this lesson (CLASSIFICATION)SWBAT: 1Classify organisms based on particular characteristics. 2Explain how living things are organized for study. 3Describe binomial nomenclature. 4)Explain Linnaeus’ system of classification Standards: Concept 4: Biological Evolution Understand the scientific principles and processes involved in biological evolution. PO 6. Analyze, using a biological classification system (i.e., cladistics, phylogeny, morphology, DNA analysis), the degree of relatedness among various species. April 26, 2012 Today’s assignment: T112 computer lab http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/evolution/brief-history-life.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/nature/classifying-life.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/evolution/how-did-life-begin.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/evolution/fossil-evidence.html Standards:Concept 4: Biological Evolution Understand the scientifi c principles and processes involved in biological evolution. PO 6. Analyze, using a biological classification system (i.e., cladistics, phylogeny, morphology, DNA analysis), the degree of relatedness among various species. Objectives: At the end of this lesson, student will be able to: Objectives: At the end of this lesson (CLASSIFICATION)SWBAT: 1) 2) 3) 4) Classify organisms based on particular characteristics. Explain how living things are organized for study. Describe binomial nomenclature. Explain Linnaeus’ system of classification Standards: Concept 4: Biological Evolution Understand the scientific principles and processes involved in biological evolution. PO 6. Analyze, using a biological classification system (i.e., cladistics, phylogeny, morphology, DNA analysis), the degree of relatedness among various species. April 27, 2012 Today’s assignment: T112 computer lab Standards: Concept 4: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/nature/pollination-game.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/nature/flowers-modern-ancient.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/nature/china-plants.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/evolution/does-race-exist.html Biological Evolution Understand the scientific principles and processes involved in biological evolution. PO 6. Analyze, using a biological classification system (i.e., cladistics, phylogeny, morphology, DNA analysis), the degree of relatedness among various species. Objectives: At the end of this lesson, student will be able to: Objectives: At the end of this lesson (CLASSIFICATION)SWBAT: 1) 2) 3) 4) Classify organisms based on particular characteristics. Explain how living things are organized for study. Describe binomial nomenclature. Explain Linnaeus’ system of classification Standards: Concept 4: Biological Evolution Understand the scientific principles and processes involved in biological evolution. PO 6. Analyze, using a biological classification system (i.e., cladistics, phylogeny, morphology, DNA analysis), the degree of relatedness among various species.