HL Chemistry Definitions
advertisement

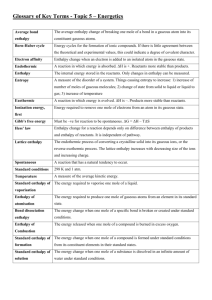
HL IB Chemistry Definitions You must learn these. You must be able to recall them word for word! Relative atomic mass - The relative atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes relative to 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Relative molecular mass - The relative molecular mass of a substance is the mass of one molecule of that substance relative to 1/12 of the mass of carbon – 12 atom. Mass Number - is equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom of that element. Atomic Number - is equal to the number of protons in an atom of that element. Isotope - are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. 1st Ionisation Energy - The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from one mole of gaseous atoms to produce 1 mole of gaseous ions. Electronegativity - Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. Ligand - An atom, ion or molecule that can donate a pair of electrons to form a dative covalent bond to a metal ion thereby forming a complex ion. Exothermic Reaction - An exothermic reaction is one that gives out heat to its surroundings. Endothermic Reaction - An endothermic reaction is one that takes in heat from its surroundings. Standard Conditions - Temperature = 298K, Pressure = 1atm & solutions 1 mol dm-3. Standard enthalpy change of a reaction - This is the enthalpy change that occurs for a reaction under standard conditions. Average Bond Enthalpy - Average enthalpy change per mole when the same type of bond is broken in the gas phase for many similar substances. Standard enthalpy change of Formation - The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is made from its elements in their standard states, under standard conditions. Standard enthalpy change of Combustion - the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance burns completely in oxygen under standard conditions. Lattice Enthalpy - the enthalpy change when 1 mole of the ionic lattice is formed from its ions in the gaseous state under standard conditions. Electron Affinity - the enthalpy change when 1 mole of electrons is added to 1 mole of gaseous atoms, under standard conditions (technically, this should be called the 1st electron affinity) Rate of Reaction - how fast a reaction takes place. Activation Energy - is the minimum energy required before a reaction can occur. Bronsted Lowry Acid - An acid is a proton (hydrogen ion) donor. Bronsted Lowry Base - A base is a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor. Lewis Acid - An acid is an electron pair acceptor. Lewis Base - A base is an electron pair donor. Oxidation - is electron loss. Reduction - is electron gain. Oxidising Agent - causes something else to be oxidised (to lose electrons). It gains the electrons that are lost by the substance being oxidised. Reducing Agent - causes something else to be reduced (to gain electrons). It gives away electrons to the substance that is being reduced. Standard Electrode Potential - The e.m.f (potential difference) of a half-reaction as a reduction relative to the standard hydrogen electrode, under standard conditions.