Living Donor Application - University of California | Office of
advertisement

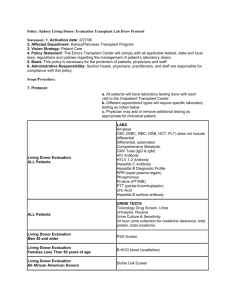
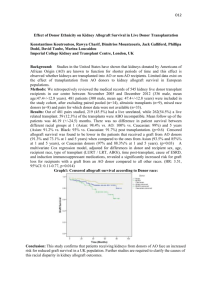
Application for 2015 University of California Larry L. Sautter Award for Innovation in Information Technology Date: May 16, 2015 Project Title: Living Donor Application University of California Davis Health System Submitted: Dan Cotton, Educational Technology & Application Development Manager UC Davis Health System IT daniel.cotton@ucdmc.ucdavis.edu (916) 734-2019 Michael Minear Chief Information Officer, UC Davis Health System mnminear@ucdavis.edu (916) 734-7131 I. Project Leaders and Team Members UC Davis strongly promotes a team science approach as a methodology for translational research. One of the key elements leading to the success of this project was the consistent partnering of individual experts throughout UC Davis Health System IT and the Living Donor Transplant Team to achieve team goals. Project Leadership Daniel Cotton, Educational Technology & Application Development Manager Information Technology Alesia Minyard, Analyst Peter Ruan, Development Supervisor David Haake, Senior Web Developer Vladimir Levin, Senior Web Developer Yujie Liu, Senior Web Developer Living Donor Transplant Team Luke Preczewski, Transplant Executive Director Michelle Sturges, RN BSN, CCTC, Transplant Coordinator Sharon Stencel, RN MSN, CCTC, Transplant Coordinator Rosemary Benefeito, Analyst Executive Sponsors Michael Minear, Chief Information Officer, UC Davis Health System Page 1 II. Summary The UC Davis Health System Information Technology department partnered with the Living Donor Transplant Team to create the Living Donor (LIDO) application. LIDO allows the Living Donor Transplant Team to manage individuals interested in donating a kidney from the time they first express interest in the program until the donation has taken place and beyond. III. Project Description Background The UC Davis Transplant center is a national leader in Kidney and other types of transplants. Sadly many patients across the world are on long waiting lists to receive this life saving surgery waiting for donated organs. In recent years, the living donor transplant program has advanced therapies in desensitization and paired-donor exchange to make it possible to transplant kidneys from living donors who previously would have been incompatible. By making living donor transplants possible, UC Davis clinicians helps the recipients of those organs, and also the patients behind them on the waiting list. UC Davis Medical Center - Waiting list and Kidney Transplant Activity 1 All donors must submit a “Living Kidney Donation Interest” questionnaire to initiate the donation process. In the past, potential donors submitted the questionnaire for consideration via a paper form; they would have to email, fax, mail or deliver form in person. Donors could also call the Living Donor Transplant Team directly and have a staff member fill out a questionnaire on their behalf. These methods of submitting donor information lacked the security this sensitive data required and were extremely inefficient. Basic donor information was entered into Transys, a home grown application primarily used to manage transplant recipients, all other information collected about donors was tracked on excel spreadsheets. Many steps are required to screen and qualify a donor for kidney donation. Each phase of the Living Donor Transplant Team’s business process was thoroughly analyzed and is accounted for in LIDO. The analysis and software development process took approximately two years resulting in an application customized for the Living Donor Transplant Team’s operational needs. 1 Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients (SRTR). (2014). Waiting list and Kidney Transplant Activity, University of California David Medical Center. Transplant Program (Organ): Kidney. Accessed from http://www.srtr.org/csr/current/Centers/centerdetail.aspx?facility=CASMTX1KI Page 2 Living Donor Application Overview LIDO was built with the intent of managing the donor data and processes from the time the initial questionnaire is submitted until the process was completed. All project participants collaborated weekly about the living donation business processes and developed a process map for current and desired workflows. Together, the team determined the high-level functionality the system should accomplish and designed a system that allowed a high degree of flexibility. Rather than staff adapting practices to software, the software was tailored to serve the Living Donor Transplant Team’s newly defined workflows. LIDO has radically changed, and improved the way the team processes and tracks donors. Implementation Timeframe 07/2011 – Business analysis began 09/2013 – Deployment to production environment Project Benefits 1. Electronic Questionnaire Submission – LIDO allows potential donors to submit an initial questionnaire electronically. This provides both convenience and security to the questionnaire submission process. Benefit: In the early months, after LIDO “went live” a total of 452 donors had been processed, and only approximately 34 donor questionnaires were entered manually by the Living Donor Transplant Team. This means that 92.48% of all questionnaires were entered electronically. Previously, 100% of the questionnaires were entered to the Excel spreadsheet and processed manually. 2. Customizable Questionnaire – LIDO provides the ability to change the questions appearing on the primary questionnaire, as well the sequence in which they appear. The feature allows the team to specify how each question on the questionnaire will be effected by the screening algorithm. Additionally, the instructions, privacy statement, and some of the text appearing on after a donor submits a questionnaire are all customizable. Benefit: Customization provides the Living Donor Transplant Team with the flexibility to change as much of the questionnaire as they require. The team can add, remove or change existing questions as the need arises. This ensures they capture the most critical information when the donor submits the questionnaire. 3. Automatic Screening – LIDO automatically screens donor questionnaires into various online work queues when the donor submits a questionnaire. The donor gets immediate feedback if they are a possible candidate or not; this feedback helps to set the donors expectation as to what to expect next in the process. If they are not a possible candidate they are provided information on how to contact the Living Donor Transplant Team should they feel it is necessary. Benefit: This feature saved the team approximately 53 hours in the first couple of months of use. The Living Donor Transplant team estimates the initial contact with each donor takes 1 hour. Previously, ALL donors who submitted a questionnaire had to be contacted. With LIDO, Only donors who are screened and determined as suitable candidates are contacted by the Living Donor Transplant team. Additionally, the automatic screening algorithm determined that 53 potential donors were not suitable candidates. This allowed the teams to more quickly turn their attention to contacting donors who were more likely to be viable candidates. Page 3 4. Customizable Queues – In addition to the automatic screening process which places the donor into predefined queues’ after they submit their questionnaire, the Living Donor Transplant Team is able to make additional custom queues to indicate where the donor is in the donation process. The queues and corresponding dashboards allow real time views into the entire donation process. (Figure 1) Benefit: This enables the Living Donor Transplant Team to manually assign a donor to a custom queue as they deem necessary allowing them to more strategically organize their work. Previously the team was extremely challenged to locate donor’s case file and provide an accurate real-time status. Figure 1 - Active Donor Dashboard 5. Single Source of Donor Data – LIDO contains all the donor data collected by the Living Donor Transplant Team; it provides the ability to track all evaluation items, dates the evaluation was scheduled, date the evaluation was completed and provides the ability to upload documents specific to the evaluation. In addition to this critical donor data LIDO tracks the following data: (Figure 2 & 3) a. Donor Demographics b. Case Comments c. Other case documents d. Questionnaire data e. Administrative tasks f. Donor Status History Benefit: One of the single biggest advantages to the team is having all of the donor data in one, secure location. All data that pertains to a donor’s case in contained within a donor’s record in LIDO, and all members of the team with appropriate permissions may access the data by simply logging into LIDO and accessing the donor’s record. Previously, if a donors case file was not within the immediate grasp of the team member who needed to review the file, finding the case file was often very difficult and time consuming; due to many factors, it was not possible to have a central repository for donor case files. Figure 2 - Donor Details (Demographics) Page 4 Figure 3 - Donor Details (Evaluation Items) 6. Recipient Pairing – LIDO allows the Living Donor Transplant Team to pair a donor with a recipient, and allows the Living Donor Transplant Team to “push” that pairing to Transys; Transys is the recipient tracking system. Benefit: Pushing the Donor/Recipient paring removes the need for double entry into the Transys system. 7. Message Center – The message center feature within LIDO is role based. When a user sends a message, it is sent to a role not a specific person. Messages may only be sent to users within the LIDO system, and may NOT be sent to individuals outside the LIDO system. Benefit: Since messages are sent to a role, any user with the corresponding role may read and respond messages sent to that role. This prevents messages from sitting in individual team members “in boxes” potentially causing delays, if the intended team member was unavailable and/or out of the office. Additionally, it keeps the communication within the application eliminating the risk of sending electronic protected heath information (ePHI) accidently. 8. Paperless Case File – Since the system previously used was paper based, one of the significant problems was routing and tracking the paper “case file.” The team was challenged to keep all test results and other pertinent case information together and accessible to all staff when they needed it. Page 5 Benefit: LIDO is a role based system, which means that each user of the application with the appropriate role and permissions may access the donor record at any time from any location via the web eliminating the need to track down the packet. 9. Security – LIDO leverages the following authentication and authorization applications: a. Central Authentication Service (CAS) – CAS is an authentication service that utilizes the campus Lightweight Directory Service (LDAP) b. Central Role Management (CRM) – CRM is an application that was developed by UCDHS IT and provides authorization to an application via the use of “roles” Benefit: The application is compliant with existing security requirements for applications developed by Health System IT and relevant governmental regulations. With the use of CRM, the end user is able to grant permission to users of LIDO and assign them certain roles which grants them access to certain features. Technology Utilized in the Project The Living Donor application is completely built with Java Enterprise technologies. Java EE provides seamless integration of persistence, controller/service, presentation layers, security (authentication and authorization) and a Java EE certified application server. Java Persistence API (JPA) provides an object mapping facility that can correlate conceptualized object models in an enterprise environment and manage relational data in persistence layer. Enterprise Java Beans (EJB) provides services such as transactions, security, messaging and web services that encapsulates the business logic of an application. JavaServer Faces (JSF) is a server-side user interface component framework that provides the wiring of component-generated events to server-side application code. Java EE security services provide a robust security mechanism for authentication users and authorizing access to application functions and associated data. Glassfish is a Java EE certified application server that “ties” the above technologies together, so that developers can concentrate on building functions or features that satisfy business requirements. Eclipse is the primary development tool used to build the application. Eclipse is a one-stop shop that provides fluid development experience to implementing enterprise applications. The database backend is using MySQL. Conclusion The Living Donor Application is testament to the determination and collaboration between UCDSH IT and the Living Donor Transplant Team, which resulted in a highly functional application that meets all clinical needs of the Living Donor Transplant Team. LIDO provides an innovate approach to managing donor data and provides the Living Donor Transplant team a tool that allows them to continue to deliver excellent care to donors without excessive effort in managing donor data. The Living Donor Transplant team submitted an abstract – in the category of efficiency – to United Network of Organ Share (UNOS) for consideration for presentation at the ‘2015 UNOS Transplant Management Conference.’ The abstract detailed many of the benefits of LIDO that this application highlights. UNOS accepted the abstract and a member of the Living Donor Transplant team presented the abstract along with a corresponding poster to the conference held in April 2015. Page 6