Ecology
advertisement

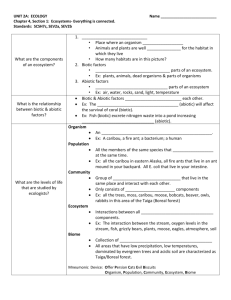
Ecology Keystone Eligible Content: Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organisms, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere) Describe characteristic biotic and abiotic components of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems Describe how energy flows through an ecosystem (e.g. food chains, food webs, energy pyramids) Describe biotic interactions in an ecosystem (e.g. competition, predation, symbiosis) Describe how matter recycles through an ecosystem (i.e. water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, and nitrogen cycle) Describe how ecosystems change in response to natural and human disturbances (e.g. climate change, introduction of nonnative species, pollution, fires) Describe the effects of limiting factors on population dynamics and potential species extinction Describe the levels of ecological organization. 1. Use the terms below to list the six levels of ecological organization in order of increasing complexity. Then define each term. Community Ecosystem Biosphere Population Species/Organism Biome A – _________________________ B – _________________________ C – _________________________ D – _________________________ E – _________________________ F – _________________________ - Describe characteristic biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem. 2. Identify four biotic and four abiotic components of the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems shown below. Biotic Factors Abiotic Factors Describe how energy flows through an ecosystem (e.g. food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids) Use the food chain below to answer the next two questions. 3. Identify the original source of energy in this food chain. 4. What percent of energy is transferred from the second trophic level (deer) to the third trophic level (lion)? 5. Energy in an ecosystem (flows in one direction / cycles). (circle one) 6. Nutrients in an ecosystem (flow in one direction / cycles). (circle one) Use the food web below to answer the next question. 7. If the size of the mouse population were to decrease, which of the following would most likely happen? a. b. c. d. The rabbit population will increase. The lion population will decrease. The owl population will increase. The snake population will decrease. Describe biotic interactions in an ecosystem (e.g. competition, predation, symbiosis) Use the food chain below to answer the next two questions. 8. If the size of the insect population were to decrease, what effect would that have on the size of the mouse population? Explain your answer. 9. If the size of the owl population were to decrease, what effect would that have on the size of the mouse population? Explain your answer. 10. Match each example with the correct type of community interaction. a. Competition b. Parasitism c. Mutualism d. Commensalism ______ A leech feeds on the blood of a human. ______ A clownfish lives among the sea anemone’s tentacles and protects the sea anemone by chasing away would-be attackers. A sea anemone, in turn, protects the clownfish from predators. ______ A cow and a sheep feed on the same grass. ______ A tree provides nutrients and a sunlit location for the orchid living on it. Describe how matter recycles through an ecosystem (i.e. water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, and nitrogen cycle) 11. Complete the diagram of the water cycle using the words below: Evaporation Transpiration Precipitation Condensation Condensation Runoff 12. Complete the diagram of the carbon cycle using the words below: Burning fossil fuels Plant Respiration Animal Respiration Photosynthesis Decomposition 13. Complete the diagram of the nitrogen cycle using the words below: Denitrification Nitrogen Fixation Ammonification Nitrification Atmospheric Nitrogen Describe how ecosystems change in response to natural and human disturbances (e.g. climate change, introduction of nonnative species, pollution, fires). 14. What is ecological succession? 15. Distinguish between primary and secondary succession. 16. Identify five ways that humans reduce biodiversity in an ecosystem. 17. How does the introduction of nonnative species threaten biodiversity? Describe the effects of limiting factors on population dynamics and potential species extinction. 18. What is a limiting factor? 19. Distinguish between density-dependent and density-independent limiting factors and give two examples of each type of limiting factor. Assessment Anchor – Ecology: Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organisms, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere). Use the list below to answer question 1. Observations • two grey wolves • five moose • several species of conifer trees • large granite rock • shallow pond 1. A student wrote several observations in a field notebook. Which term best classifies all of the student’s observations? a. population c. ecosystem b. food chain d. community Describe characteristic biotic and abiotic components of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. 2. A researcher observing an ecosystem describes the amount of sunlight, precipitation, and type of soil present. Which factors is the researcher most likely describing? a. biotic factors in a forest c. abiotic factors in a prairie b. biotic factors in a tundra d. abiotic factors in an ocean Describe how energy flows through an ecosystem (e.g. food chains, food webs, energy pyramids). Use the diagram below to answer question 3. 3. Which sequence correctly describes the flow of energy between organisms in the marine food web? a. from seals to penguins to krill c. from sea birds to seals to penguins b. from whales to krill to small fish d. from small fish to penguins to seals 4. Scientists observed that the populations of top-level consumers in a particular ecosystem were rapidly decreasing. Further studies revealed that there was also a decline in producer productivity. Which other changes did the scientists most likely observe in the ecosystem? a. increased producer diversity b. decreased population size at all levels c. decreased primary consumer populations only d. increased primary and secondary consumer diversity Describe biotic interactions in an ecosystem (e.g. competition, predation, symbiosis). 5. A species of snapping turtles has a tongue that resembles a worm. The tongue is used to attract small fish. Which best describes the interaction between the fish and the snapping turtle? a. predation b. symbiosis c. parasitism d. competition Describe how matter recycles through an ecosystem (i.e. water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, and nitrogen cycle). 6. Which statement correctly describes how nitrogen in the soil returns to the atmosphere? a. Soil bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. b. Decomposers directly convert ammonium into nitrogen gas. c. Plants assimilate nitrites and convert them into nitrogen gas. d. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in plant roots convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. Describe how ecosystems change in response to natural and human disturbances (e.g. climate change, introduction of nonnative species, pollution, fires). 7. Agricultural runoff can carry fertilizers into lakes and streams. This runoff can cause algae populations to greatly increase. Which effect does this change in the algae population sizes most likely have on affected lakes and streams? a. an increase in water level b. an increase in water clarity c. a reduction in dissolved oxygen needed by fish and shellfish d. a reduction in temperature variations near the water’s surface Describe the effects of limiting factors on population dynamics and potential species extinction. 8. A farmer observed that an increase in a field’s soil nitrogen content was followed by an increase in producer productivity. What does this observation most likely indicate about the relationship between nitrogen and the producers in the field? a. Nitrogen was a biotic factor. c. Nitrogen became a surplus resource. b. Nitrogen was a limiting factor. d. Nitrogen became a selection pressure. Use the graph below to answer question 9. 9. Isle Royale is located in Lake Superior. Isle Royale is home to populations of wolves and moose. The interactions between the wolves and moose, as well as the individual population sizes, have been studied since 1958. The graph shows the population sizes over time for both wolves and moose. A. Describe one limiting factor for the moose population. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ B. Explain one likely reason why the wolf population rapidly increased between 1975 and 1980. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ C. Predict what will happen to the moose population’s size after 1994 by describing the shape of the curve. In your answer, be sure to explain the reasoning behind your prediction. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________