MRes Experimental Cancer Medicine
advertisement

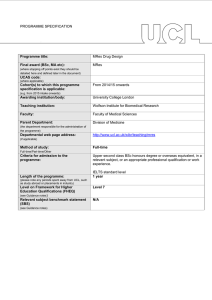
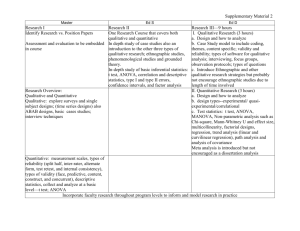
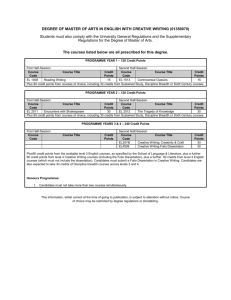
MRes Experimental Cancer Medicine The MRes Experimental Cancer Medicine comprises four taught modules (each of 15 credits) and two practical research projects (each of 60 credits). Students achieving 180 credits will be awarded the MRes; students may receive a PG Diploma in Experimental Cancer Medicine upon achievement of 120 credits. There is also an option for students to register for a PG Certificate in experimental cancer medicine and complete only the four taught modules on a part-time basis for 60 credits. In taught modules comprising a total of 7 weeks, students will learn the details of designing and delivering these types of studies, understanding the pre-clinical data which is required before a clinical programme can commence; and how to optimise the early clinical studies to provide the platform of evidence to progress a promising drug into Phase II/III clinical testing. For the remaining time, students will be allocated to one or more clinical studies in one or more of the above four categories. Student will be the named physician, nurse or clinical trials coordinator (as relevant to their background) for clinical trials allocated to them. Each student will have a named experienced member of The Christie experimental cancer medicine team as their “buddy”/trainer to allow the student to learn the practical procedures required to conduct a Phase 1 clinical trial to Good Clinical Practice. Students will elect two aspects of their direct clinical trial research experience as discrete research projects to write up in dissertation format which introduces students to the skills and knowledge required to critically report medical, scientific and clinically related sciences for peer review. Each of two practical research projects will be between 10-15,000 words with examples of suitable practical research projects being: Type of dissertation Research Proposal Publication based/Dissertation by publication Service development/professional report/ report based dissertation Adapted systematic (qualitative data) review Full systematic review that includes data collection (quantitative data) Example of practical research project • Compilation of a research proposal to research council/charity • Writing a protocol and trial costings for sponsor • Research and write a successful expression of interest selected by grant funder for full development • Writing a clinical study report • Authoring a peer-review journal review/original article • Public health report/outbreak report/health needs assessment/health impact assessment • Proposal for service development/organisational change • Audit/evaluate service delivery/policy • Implement recommended change from audit report • Compiling the platform of scientific evidence for a new drug indication from literature • Review of alternative research methodologies from literature Referral patterns for Phase 1 patients Qualitative empirical research Design, conduct, analyse and report an experiment Quantitative empirical research Qualitative secondary data analysis/analysis of existing quantitative data Quantitative secondary data analysis/analysis of existing qualitative data/theoretical study/narrative review Design, conduct, analyse and report an experiment Compilation, mining and analysis of existing clinical data sets • • Policy analysis or discourse analysis/content analysis A critical review of policy using framework analysis