Neurology
advertisement

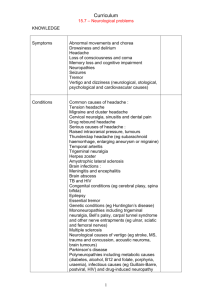
NEUROLOGY I. Name of the unit offering the course: Department of Neurology II. Head of the unit:/ course coordinator dr hab. n. med. Barbara Książkiewicz, prof. UMk III. Faculty of Medicine, 5th year IV. Form of classes: seminars, classes V. Form of crediting: exam, 5 p. ECTS VII. Hours: 20 h. seminars., 40 g. classes. A total of 60 h. TEACHERS: Dr n.med Magdalena Nowaczewska: magy_mat@by.onet.pl Dr n.med Piotr Rajewski Dr n.med. Krzysztof Nicpoń Lek. med. Wiktoria Rajczyk Lek. med Adam Wiśniewski I. Purpose of class: The goal is to learn theoretical and practical (clinical cases) of the symptomatology, diagnosis and treatment of common diseases of the nervous system with particular emphasis on life threatening neurological syndrome (increased intracranial pressure, status epilepticus, myasthenic crisis, cholinergic crisis, Guillain-Barre syndrome). II. Topics of the course (detailed plan): 1. Intracranial and spinal cord tumors. • Intracranial tumors: definition of brain tumor, the distribution of tumors, general and focal symptoms of intracranial tumors, histopathological classification. • Clinical symptoms and histopathological classification of epidural and spinal cord tumors. • Diagnostic tests and treatment. 2. Epilepsy and the other seizure states. • Epilepsy: classification of epilepsy, the causes of epilepsy, seizures morphology. • Diversification of epilepsy with other states of unconsciousness. EEG in epilepsy. • The treatment of epilepsy. 3. Life-threatening cases in neurology. • Syndrom of increased intracranial pressure, status epilepticus, myasthenic crisis, Guillain-Barre syndrome. • Diagnosis and therapeutic standards. 4. Stroke. • Blood supply of the brain, the mechanisms controlling blood flow (perfusion pressure, cerebral blood flow, self-regulation, chemical and metabolic regulation). • Definition of stroke, epidemiology, risk factors. • Causes of ischemic strokes, cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage. • Pathophysiology and pathology of stroke. 5. Stroke. • Clinical signs and symptoms of stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage. Supplemental diagnostic procedures and treatment. 6. Neuroinfections. • Clinical signs and symptoms of the meningitis and encephalitis. • Diagnostics and clinical differentiation of viral, bacterial, TB meningitis. • Treatment of neuroinfections. 7. Defect of the spine. Neurological rehabilitation. • A root compression syndrome. Cervical, lumbar root compression syndromes- etiology and clinical signs and symptoms. • Cervical myelopathy • Study of patients with neuralgia: subjective and objective symptoms. • Supplemental diagnostic procedures and treatment. 8. Multiple sclerosis, syringomyelia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. • The etiology, clinical symptoms, treatment. 9. Headache as a multidisciplinary approach. • Classification of headaches. • The cause and pathogenesis of headaches. • Migraine, cluster headaches, tension-type headaches - etiology, pathogenesis and treatment. • Neuralgies in the head with particular reference to nerve V. 10. Dementia and impairment of higher intellectual functions. • Dementia: definition, etiology, clinical manifestations, and treatment. • Aphasia: definition, classification, diagnosis. • Other disorders of higher brain activity. • Dysarthria. III. Scope of material for self-mastery by the student: neuroanatomy, neurophysiology, theoretical basis of neurological examination, symptomatology of the nervous system lesions. IV. Literature 1. Main book – Neurology and Neurosurgery Illustrated 5e Kenneth W. Lindsay Churchill Livingstone 01/10/2010 2. Additional book – neurological examination Neurological Examination Made Easy Geraint Fuller Churchill Livingstone 01/05/2008 3.Complementary book Netter's Neurology H.Royden Jones W.B. Saunders Company 01/10/2011 V. A detailed list of skills and confirmation of their method: Diagnosis- etiologic Treatment of intracranial hypertension Treatment of status epilepticus Treatment of myasthenic crisis Treatment of stroke Medical history- record keeping RULES AND REGULATIONS The student has to be present on seminars and exercises in order to pass. During exercises assistant shall verify student’s preparation to classes on a regular basis by means of oral questions, whereas during the practical the student shall be obliged to show his skills to perform neurological examination. It is also required to write a medical history. The practical and theoretical (test) examination shall verify the effects of students’ learning efforts. The practical part of the test shall take part during the last block of the exercises. The assisting physician, a specialist in neurology shall indicate a patient for each student, and the student has to examine the patient, indicate deviations concerning the examination, propose local, etiologic, syndrome diagnosis, as well as differentiation and recommended treatment. The student elaborates medical history that is to be approved by the assistant. The assistant evaluates the ability to perform neurological examination, proper naming of abnormalities observed during the examination, accuracy of the initial diagnosis, perception concerning differentiation with other ailments of the nervous system. The theoretical part has a form of a test – 100 questions All questions are statements with 5 possible answers – the student has to indicate the most appropriate answer (a test of choice – 1 proper answer).