X. Interrogatives/Question words
advertisement

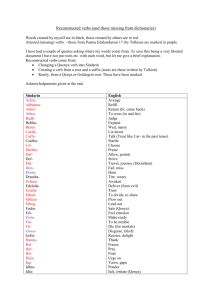
Latin I Midterm guide Test format: TBA I. Pronunciation Know that the following Latin letters differ in pronunciation from English. v ā g ē windy father get they c ae ī au cat aisle machine house II. Grammar Define the following terms. Term Definition Accusative DIRECT OBJECT Action verb a verb that shows a motion Adjective modifies or describes NOUNS, Adverb modifies verbs, adjectives and other adverbs NOUNS, PRONOUNS and ADJECTIVES have inflected endings that show their use in a sentence. Verb family (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th) (-āre, -ēre, -ere, īre) Case Conjugation Conjunction sed – but et - and Declension Noun family (1st, 2nd, 3rd) (-a, -us, anything) Direct object The person or thing being verbed Gender Latin has 3 genders: MASCULINE, FEMININE, and NEUTER Imperative command Indirect object ---------------------------- Indicative ---------------------------- Infinitive Linking verb the second principal part, “to verb” An ending on a word that shows its grammatical function in a sentence. a part of speech that is NOT connected to any other part. Usually shows great emotion: eheu, ecce, euge, salve, vale a verb that acts like an equal sign Macron indicates a long vowel Mood ---------------------------SUBJECT or PREDICATE NOMINATIVE/ADJECTIVE in a sentence. person, place, thing or idea Inflection Interjection Nominative Noun Number Object of preposition Revised 2/9/2016 SINGULAR = one PLURAL=more than one the noun (or pronoun) that comes after a preposition and completes the meaning of the preposition 1 Latin I Midterm guide Term Definition st Person Predicate nominative/noun, adjective nd rd 1 ,2 ,3 Follows a linking verb, and renames or defines the preceding subject. word that denotes relationships in time, space and location. It is followed by an OBJECT OF PREPOSITION. tu – you ego - I Preposition Pronoun commonly indicates what the subject is about or who performs the action of a sentence When the action or state of being is happening. [Latin I studies: PRESENT (now), IMPERFECT (ongoing in the past), PERFECT (completed in the past)] Subject Tense Vocative Voice ---------------------------- III. Nouns A. Cases & Grammatical functions Nominative is used for subjects and predicate nouns & adjectives. N.B. Predicate nouns and adjectives follow linking verbs, e.g. sum esse fui futurus “to be.” e.g. Caecilius est argentarius Caecilius is a banker e.g. Cerberus est iratus Cerberus is angry [Genitive provides noun stem, shows possession] Accusative is used for direct objects: direct objects answer the questions whom or what after the action verb. Complete the table with the correct endings. Nominative 1st Declension Singular Plural a ae 2nd Declension Singular Plural usually us ī 3rd Declension Singular Plural varies ēs Genitive ae ārum ī ōrum is um Dative ae īs ō īs ī ibus Accusative am ās um ōs varies ēs Ablative ā īs ō īs e ibus Vocative a ae see rules ī same as nom ēs Identify the case of each noun in the following sentences. puellae gladiatores in arenâ vident. Revised 2/9/2016 nominative accusative ablative 2 Latin I Midterm guide VI. Verbs A. Principal parts Most regular verbs have 4 principal parts and you should have a working knowledge of the first three. Principal part First principal part Second principal part Third principal part Example porto “I carry, do carry, am carrying” portare “to carry” portavi “I carried, did carry, have carried” Use First person singular present active Present active infinitive: yields the present active stem used for present and imperfect tenses active used for imperative active mood identifies the conjugation First person singular perfect: yields perfect active stem used for perfect active tense The second principal part has several grammatical functions. Its final three letters will determine to which conjugation the verb belongs. First conjugation verbs have infinitives which end in -āre. Second conjugation verbs have infinitives which end -ēre. Third conjugation verbs have infinitives which end in -ere. Fourth conjugation verbs have infinitives which end in -īre. e.g. e.g. e.g. e.g. laudāre vidēre dūcere audīre N.B. Not all verbs are placed into a specific conjugation. Those verbs which are not placed into a specific conjugation are called irregular verbs because their principal parts and/or tense forms do not change in a consistent and predictable manner. e.g. sum, esse, fui, futurus adsum, adesse, adfui, adfuturus absum, abesse, afui, afuturus Answer the following questions about navigo, navigare, navigavi, navigatus “to sail.” 1. What is the perfect stem? navigāv 2. What is the first person singular present active? navigō 3. What is the first person singular perfect active? navigāvī 4. What is the present active infinitive? navigāre 5. What is the present stem? navigā 6. To which conjugation does this verb belong? first B. Conjugating verbs Conjugate and translate the following tenses for amo, amare, amavi, amatus “love.” Revised 2/9/2016 3 Latin I Midterm guide Present Imperfect Perfect 1st singular amō amābam sensī translation I love I was loving I have loved/did love/loved 2nd singular amās amābās sensistī translation you love you were loving you have loved/did love/loved 3rd singular amat amābat sensit translation he loves he was loving you have loved/did love/loved 1st plural amāmus amābāmus sensimus translation we love we were loving we have loved/did love/loved 2nd plural amātis amābātis sensistis translation you pl love you pl were loving you pl have loved/did love/loved 3rd plural amant amābant sensērunt translation they love they were loving they have loved/did love/loved Conjugate and translate the following tenses for sum, esse, fui, futurus “be.” Present Imperfect Perfect 1 singular sum eram fuī translation I am I was I was/have been 2nd singular es erās fuistī translation you are you were you were/have been 3rd singular est erat fuit translation he is he was he was/has been 1st plural sumus erāmus fuimus translation we are we were we were/have been 2nd plural estis erātis fuistis translation you pl are you pl were you pl were/have been 3rd plural sunt erant fuērunt translation they are they were they were/have been st Identify the correct tense of the following verbs. Revised 2/9/2016 4 Latin I Midterm guide She kept leading. IMPERFECT We did lead. PERFECT I am leading. PRESENT You have led. PERFECT You lead. PRESENT They used to lead. IMPERFECT He does lead. PRESENT They led. PERFECT It leads. PRESENT ducebat IMPERFECT duco PRESENT duxistis PERFECT ducitis PRESENT ducit PRESENT ducebamus IMPERFECT ducebatis IMPERFECT ducis PRESENT duxit PERFECT Identify the imperfect tense sign for regular Latin verbs bā Identify the imperfect tense sign for the sum, esse, fui, futurus erā VII. Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. e.g. intentê intently ferōciter fiercely graviter seriously X. Interrogatives/Question words Latin questions can also be introduced by certain adverbs and pronouns. e.g. quis who ubi where quid what cur why Revised 2/9/2016 5