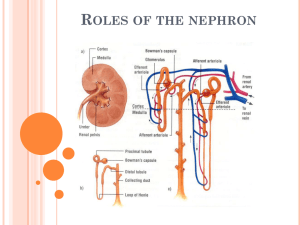
URINARY SYSTEM Chapter 25 Urinary System Organs : major
advertisement
URINARY SYSTEM Chapter 25 Urinary System Organs _______________ : major excretory organs _______________: transport urine from kidneys to urinary bladder _______________ _______________: temporary storage reservoir for urine _______________: transports urine out of body Kidney Anatomy _______________ _______________ atop each kidney Ureters, renal blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves enter and exit at _______________ Layers of surrounding supportive tissue o _______________ _______________: anchoring outer layer of dense fibrous connective tissue o _______________ _______________ _______________: fatty cushion o _______________ _______________: prevents spread of infection to kidney _______________ _______________: superficial region _______________ _______________: composed of cone-shaped medullary (renal) pyramids o Pyramids separated by _______________ _______________ (inward extensions of cortical tissue) _______________: tip of pyramid; releases urine into minor calyx _______________: medullary pyramid and its surrounding cortical tissue (approximately 8 per kidney) _______________ _______________: funnel-shaped tube continuous with ureter _______________ _______________: drain pyramids at papillae _______________ _______________: collect urine from minor calyces and empty urine into renal pelvis Urine flow: _______________ _______________ to minor calyx to _______________ _______________ to renal pelvis to _______________ to urinary bladder to _______________ Kidneys cleanse blood and adjust its composition Renal arteries deliver _______________ of blood to kidneys each minute _______________ to renal artery to _______________ _______________ to interlobar artery to _______________ _______________ to cortical radiate artery to _______________ _______________ to glomerulus to _______________ _______________ to peritubular capillaries or vasa recta to _______________ _______________ _______________ to arcuate vein to _______________ _______________ to renal vein to _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________: structural and functional units that form urine, composed of renal corpuscle and renal tubule _______________ _______________ o _______________: tuft of fenestrated capillaries; highly porous, allows filtrate formation o _______________ _______________ (Bowman's capsule): cup-shaped, hollow structure surrounding glomerulus _______________ _______________: simple squamous epithelium _______________ _______________: branching epithelial podocytes (extensions terminate in foot processes) _______________ _______________ between foot processes allow filtrate to pass into capsular space _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ (closest to renal corpuscle) o Functions in_______________ and _______________ o Confined to _______________ _______________ _______________ o _______________ and _______________ limbs _______________ _______________ _______________ (farthest from renal corpuscle) o Distal descending limb (_______________ limb) o _______________ ascending limb o Function more in _______________ than _______________ o Confined to _______________ Collecting Ducts Two cell types: o _______________ _______________: maintain water and Na+ balance (sparse, short microvilli) o _______________ _______________: maintain acid-base balance of blood (abundant microvilli) Receive filtrate from _______________ nephrons Fuse together to deliver urine through papillae into _______________ _______________ Classes of Nephrons _______________ _______________: 85% of nephrons; almost entirely in cortex _______________ _______________: long nephron loops deeply invade medulla o Ascending limbs have _______________ and _______________ segments o Important in production of _______________ urine Renal tubules associated with two capillary beds _______________: specialized for filtration o Fed by _______________ arteriole and drained by _______________ arteriole o Blood pressure in glomerulus high because afferent arterioles _______________ in diameter than efferent arterioles _______________ _______________: low-pressure, porous capillaries adapted for absorption of water and solutes o Arise from _______________ arterioles and empty into _______________ o Cling to adjacent renal tubules in _______________ _______________ _______________: long, thin-walled vessels parallel to long nephron loops of _______________ _______________ o Arise from _______________ arterioles serving juxtamedullary nephrons o Function in formation of _______________ urine Juxtaglomerular Complex (JGC) One per nephron Important in regulation of rate of _______________ _______________ and _______________ _______________ Three cell populations o _______________ _______________: located in ascending limb; chemoreceptors that sense NaCl content of filtrate o _______________ _______________: located in arteriole; mechanoreceptors that sense blood pressure in afferent arteriole (secrete renin) o _______________ _______________ _______________: between arteriole and tubule cells; may pass signals between macula densa and granular cells Mechanisms of Urine Formation _______________ fluid processed daily; only _______________ urine produced Three processes in urine formation and adjustment of blood composition o _______________ _______________: produces cell- and protein-free filtrate o _______________ _______________: selectively returns 99% of substances from filtrate to blood in renal tubules and collecting ducts o _______________ _______________: selectively moves substances from blood to filtrate in renal tubules and collecting ducts _______________: produced by glomerular filtration, blood plasma minus proteins _______________: composed of <1% of original filtrate, contains metabolic wastes and unneeded substances Glomerular filtration is _______________ process where _______________ metabolic energy is required _______________ _______________ forces fluids and solutes through _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________: porous membrane between blood and interior of glomerular capsule Composed of three layers o _______________ _______________ of glomerular capillaries o _______________ _______________ (fused basal laminae of two other layers) o Foot processes of _______________ with filtration slits Allows molecules smaller than 3 nm to pass (_______________, glucose, _______________ _______________, nitrogenous wastes) _______________ _______________ remain in blood to maintain _______________ _______________ _______________ which prevents loss of all water to capsular space Pressures That Affect Filtration _______________ pressures _______________ filtrate formation o _______________ pressure in glomerular capillaries (HPgc): glomerular blood pressure, _______________ Inward forces _______________ filtrate formation o _______________ pressure in capsular space (HPcs): pressure of filtrate in capsule, _______________ o _______________ _______________ pressure in capillaries (Opgc): “pull" of proteins in blood, _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ :sum of outward pressures that promote filtrate formation and inward forces that inhibit filtrate formation 55 mmHg forcing out; 45 mmHg opposing = net _______________ _______________ of 10 mmHg _______________ _______________ _______________ :volume of filtrate formed per minute by both kidneys (normal = 120–125 ml/min) GFR directly proportional to: o _______________ _______________ _______________ o _______________ _______________ _______________ available for filtration o Filtration membrane _______________ Glomerular Filtration Rate regulation via: _______________ _______________: maintains nearly constant GFR allowing _______________ to make filtrate and maintain extracellular homeostasis (______________________________) _______________ _______________: controls GFR via nervous and endocrine mechanism in response to changes in _______________ _______________ o _______________ GFR causes _______________ urine output which results in _______________ blood pressure, and vice versa Two Types of Intrinsic Controls (Renal Autoregulation): _______________ _______________: afferent arterioles reaction to changes in blood pressure in order to keep the blood flow within the glomerulus constant _______________ _______________ _______________: flow-dependent mechanism directed by macula densa cells in response to filtrate NaCl concentration Myogenic Mechanism (Intrinsic Control) Increased BP: Increased GFR o Increased _______________ _______________ in vessels o _______________ of afferent arterioles o Restricted _______________ _______________ into glomerulus o _______________ GFR Decreased BP: Decreased GFR o Reduced _______________ _______________ in vessels o _______________ of afferent arterioles o Increased _______________ _______________ into glomerulus o _______________ GFR Tubuloglomerular Feedback Mechanism (Intrinsic Control) Increased GFR: o Filtrate _______________ _______________ increase o Reabsorption time is _______________ o _______________ filtrate levels _______________, detected by _______________ _______________ _______________ o _______________ of afferent arteriole o GFR _______________ Decreased GFR: o Filtrate _______________ _______________ decrease o Reabsorption time is _______________ o _______________ filtrate levels _______________, detected by _______________ _______________ _______________ o _______________ of afferent arteriole o GFR _______________ Two Types of Extrinsic Controls: _______________ _______________: response to lowered blood pressure by _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________: main mechanism for increasing blood pressure via release of renin by _______________ _______________ (ReninAngiotensin- Aldosterone Mechanism) Neural Mechanism (Extrinsic Controls) _______________ blood pressure _______________ released by sympathetic nervous system; _______________ released by adrenal medulla Systemic _______________ resulting in _______________ blood pressure _______________ of afferent arterioles Restricted _______________ _______________ into glomerulus _______________ GFR Endocrine Mechanism: Renin-Angiotensin- Aldosterone Mechanism (Extrinsinc Control) Three pathways to_______________ release by _______________ _______________ o _______________ _______________ of granular cells by sympathetic nervous system o Stimulation by activated _______________ _______________ cells when filtrate NaCl concentration low o _______________ _______________ of granular cells _______________ _______________: most of tubular contents reabsorbed to _______________; all _______________ _______________ reabsorbed; water and ion reabsorption _______________ regulated and adjusted Two routes from tubule to peritubular capillary o _______________ route: pathway through the cells _______________ route: pathway between tubule cells _______________ tubular reabsorption: movement of _______________ across basolateral membrane via Na+-K+ ATPase pump o _______________ _______________ (glucose, amino acids, some ions, vitamins) reabsorbed by _______________ _______________ _______________ (facilitated diffusion mechanism) across apical; cotransported with Na+ o _______________ tubular reabsorption: movement of Na+ and other solutes creates _______________ _______________ for water; water reabsorbed by osmosis, aided by water- filled pores called _______________ Aquaporins always present in _______________ _______________ _______________: obligatory water reabsorption Aquaporins inserted in _______________ _______________ only if ADH present: facultative water reabsorption _______________ _______________ for every reabsorbed substance; reflects number of _______________ in renal tubules available When carriers saturated, excess excreted in _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________: site of most reabsorption All _______________ (glucose and amino acids) 65% of _______________ and _______________ Many _______________ All _______________ _______________; 1⁄2 _______________ Nephron loop _______________ _______________: H2O can leave; solutes cannot _______________ _______________: H2O cannot leave; solutes can _______________ _______________: passive movement _______________ _______________: active movement DCT and collecting duct: reabsorption _______________ regulated _______________ _______________ :insertion of aquaporins in collecting ducts; reabsorb water _______________: insertion of Na+ and K+ channels and Na+-K+ pump in collecting duct; Na+ reabsorption, water follows _______________ _______________ _______________: reduces blood Na+, reduced water reabsoprtion _______________ _______________: acts on DCT to increase Ca2+ reabsorption _______________ _______________: reabsorption in reverse; almost all in PCT _______________, H+, _______________, creatinine, _______________ _______________ and bases move from peritubular capillaries through tubule cells into filtrate Substances _______________ in tubule cells also secreted (HCO3-) Disposes of substances (drugs) bound to _______________ _______________ Eliminates _______________ _______________ passively reabsorbed (urea and uric acid) Rids body of excess potassium (______________________________) Controls _______________ _______________ by altering amounts of H+ or HCO3– in urine _______________: number of solute particles in 1 kg of H2O, reflects ability to cause osmosis (osmolality of body fluids expressed in _______________ _______________ maintain osmolality of plasma at by regulating urine concentration and volume via the _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________: occurs when fluid flows in opposite directions in two adjacent segments of same tubule with hair pin turn (establishes _______________ _______________ from renal cortex through medulla) o _______________ _______________: interaction of filtrate flow in ascending/descending limbs of nephron loops of juxtamedullary nephrons o _______________ _______________: blood flow in ascending/descending limbs of vasa recta Countercurrent Multiplier: _______________ _______________ _______________ limb is freely permeable to _______________ H2O passes out of filtrate into _______________ medullary interstitial fluid Filtrate osmolality _______________ to ~1200 mOsm _______________ limb is impermeable to _______________ and selectively permeable to _______________ Na+ and Cl– actively _______________ in thick segment; some passively _______________ in thin segment Filtrate osmolality _______________ to 100 mOsm Constant 200 mOsm _______________ between two limbs of nephron loop and between ascending limb and interstitial fluid Difference _______________ along length of loop to ~ 900 mOsm The Countercurrent Exchanger: _______________ _______________ Preserves _______________ _______________ by preventing the rapid removal of _______________ from interstitial space and removing reabsorbed _______________ Volume of blood at end of vasa recta _______________ than at _______________ Osmotic gradient used to raise urine concentration _______________: large volume dilute urine, ADH production decreases _______________: small volume concentrated urine, maximal ADH released _______________: chemicals that enhance urinary output _______________ _______________ (alcohol) _______________ _______________ _______________ resulting H2O reabsorption (caffeine, drugs for hypertension or edema) _______________ _______________ inhibit medullary gradient formation _______________ _______________: substance not reabsorbed so water remains in urine (high glucose of diabetic patient) _______________ _______________: volume of plasma kidneys clear of particular substance in given time Renal clearance tests used to o Determine_______________ o Detect _______________ damage o Follow progress of _______________ _______________ _______________ (plant polysaccharide): freely filtered; neither _______________ nor _______________ by kidneys; standard used for renal clearance (GFR = 125 ml/min) o If C < 125 ml/min, substance _______________ o If C = 0, substance completely _______________, or not filtered o If C = 125 ml/min, no net _______________ or _______________ o If C > 125 ml/min, substance_______________ (most drug metabolites) Physical characteristics of urine is normally_______________ and pale to deep yellow from _______________ (pigment from hemoglobin breakdown), slightly _______________ (~pH 6) Cloudy may indicate _______________ _______________ _______________ More _______________ urine has deeper color _______________ _______________ (pink, brown, smoky) from food ingestion, bile pigments, blood, drugs Develops _______________ odor upon standing as_______________ metabolize solutes Chemical Composition of Urine 95% _______________ and 5%_______________ Nitrogenous wastes o _______________ (from amino acid breakdown) largest solute component o _______________ _______________ (from nucleic acid metabolism) o _______________ (metabolite of creatine phosphate) Other normal solutes o _______________, Potassium, _______________ , Sulfate, _______________, Magnesium, _______________ Ureters: move urine from kidneys to bladder Enter _______________ of _______________ through posterior wall, as bladder pressure increases, distal ends of ureters close, preventing _______________ of urine Three layers of ureter wall from inside out o _______________: transitional epithelium o _______________: smooth muscle sheets, contracts in response to stretch o _______________: outer fibrous connective tissue _______________ _______________: kidney stones in renal pelvis (crystallized calcium, magnesium, or uric acid salts) _______________ _______________: muscular sac for temporary storage of urine Contains openings for _______________ and _______________ o _______________: smooth triangular area outlined by openings for ureters and urethra Layers of bladder wall o _______________: transitional epithelial mucosa o _______________ _______________: three layers of smooth muscle o _______________ _______________ Collapses when empty; _______________ appear Full bladder holds _______________ _______________: muscular tube draining urinary bladder Two sphincters o _______________ _______________ sphincter: _______________ (smooth muscle) at bladder-urethra junction o _______________ _______________ sphincter: _______________ (skeletal) muscle surrounding urethra as it passes through pelvic floor _______________ urethra (3 - 4 cm) carries _______________ o External urethral orifice: anterior to vaginal opening; posterior to clitoris _______________ urethra (19 – 20 cm) carries _______________ and _______________ o Three named regions _______________ _______________ (2.5 cm): within prostate _______________ _______________ (2 cm): passes through urogenital diaphragm from prostate to beginning of penis _______________ _______________ (15 cm): passes through penis; opens via external urethral orifice _______________: urination or voiding Three simultaneous events must occur o Contraction of _______________ _______________ of the bladder by ANS o Opening of _______________ _______________ sphincter by ANS o Opening of _______________ _______________ sphincter by somatic nervous system Reflexive urination (urination in infants) o Distension of bladder activates _______________ _______________ o Excitation of parasympathetic neurons in _______________ _______________ o Contraction of _______________ _______________ of the bladder by ANS o _______________ of internal urethral sphincter by ANS o _______________ of somatic pathways to external sphincter, allowing its _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ (located in the pons) mature between ages 2 - 3 o Pontine _______________ _______________: inhibits micturition o Pontine _______________ _______________: allow micturition