File
advertisement

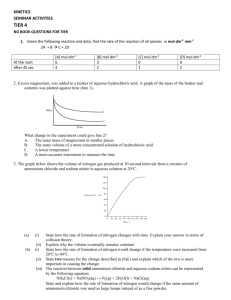
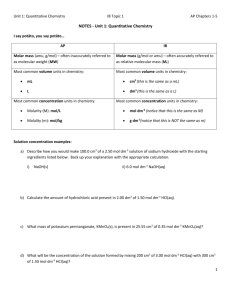
Unit 9 Worksheets 2 Oxidation & reduction 1. Consider the following four reactions: Mg(s) + Fe2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Fe(s) Fe(s) + Ni2+(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + Ni(s) Zn(s) + Fe2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Fe(s) Mg(s) + Zn2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Zn(s) (a) Place the metals in order of their decreasing reactivity (most reactive first). (b) Identify the strongest oxidizing agent among the species above. (c) Identify the strongest reducing agent among the species above. 2. A ‘tin’ can is actually a steel can coated with tin. When the can is dented and exposed to air and water it rusts much quicker than if the steel had been coated with zinc. Explain this fact and suggest why cans for storing food are coated with tin rather than zinc to protect them from rusting. 3. Consider the following three reactions: I. Cl2(aq) + 2Br−(aq) → 2Cl−(aq) + Br2(aq) II. Cl2(aq) + 2I−(aq) → 2Cl−(aq) + I2(aq) III. Br2(aq) + 2I−(aq) → 2Br−(aq) + I2(aq) (a) Identify the species that is the strongest oxidizing agent. _________________________________ (b) Identify the species that is the strongest reducing agent. _________________________________ (c) Explain how bromine is behaving in reactions I and III. ___________________________________ (d) Describe what will be observed when a yellow-brown aqueous solution of iodine is added to an aqueous solution of sodium chloride. 4. An excess of manganese(II) sulfate in alkaline solution was added to 250 cm3 of a sample of water taken from a local lake. The oxygen in the water reacts with manganese(II) sulfate according to the equation: 2Mn2+(aq) + 4OH−(aq) + O2(g) → 2MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l) The solution was then acidified and excess potassium iodide was then added which released iodine according to the equation: MnO2(s) + 2I−(aq) + 4H+ → Mn2+(aq) + I2(aq) + 2H2O(l) The iodine formed was then titrated with 1.00 x 10-2 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulfate solution using starch as an indicator: I2(aq) + 2S2O32−(aq) → S4O62−(aq) + 2I−(aq) The volume of thiosulfate solution required to react completely with the iodine was 20.0 cm3. (a) Calculate the solubility of the oxygen in the lake water in mol dm-3. (b) Calculate the solubility of the oxygen in the lake water in mg dm-3 which is the same as ppm. Answers 1. (a) Mg > Zn > Fe > Ni (Magnesium can displace zinc(II) ions and iron(II) ions from solution, zinc can displace iron(II) ions and iron can displace nickel(II) ions from solution.) (b) The strongest oxidizing agent is nickel(II) ions, Ni2+(aq), as it is the species that gains electrons the most readily. (c) The strongest reducing agent is magnesium metal, Mg(s), as it is the species that loses electrons the most readily. 2. Iron (steel) is more reactive than tin so once the can is dented it will be exposed to the atmosphere and it will react with tin metal to form iron(II) ions. Zinc is more reactive than iron so it protects the iron from rusting as if any iron(II) ions are formed they are converted back to iron metal by the zinc which forms zinc(II) ions in the process. Cans containing food are coated with tin to protect the iron from exposure to air and water. Although the iron would be better protected by coating with zinc, zinc cannot be used as it is poisonous. 3. (a) The strongest oxidizing agent is chlorine, Cl2(aq), as it gains electrons the most readily. (b) The strongest reducing agent is iodide ions, I−(aq) as they lose electrons the most readily. (c) In reaction I the oxidation state of bromine goes from -1 to 0 so it is being oxidized (loses an electron) and is acting as a reducing agent. In reaction III the oxidation state of bromine goes from 0 to -1 so it is being reduced (gains an electron) and it is acting as an oxidizing agent. (d) The yellow-brown colour would be slightly less intense as the solution of iodine is being diluted. However as no reaction occurs the solution will remain yellow-brown and no precipitate will be formed. 4. (a) Amount of S2O32- in 20.0 cm3 = (20.0/1000) x 1.00 x 10-2 = 2.00 x 10-4 mol Since 2 mol of S2O32- react with one mole of I2 Amount of I2 formed = ½ x 2.00 x 10-4 = 1.00 x 10-4 mol Since one mole of I2 is formed from one mole of MnO2 Amount of MnO2 produced = 1.00 x 10-4 mol Since 2mol of MnO2 are formed from one mole of O2 Amount of O2 present in 250 cm3 of the lake water = ½ x 1.00 x 10-4 = 5.00 x 10-5 mol Concentration of dissolved oxygen = (1000/250) x 5.00 x 10-5 = 2.00 x 10-4 mol dm-3 (b) Mr of O2 = 32.0 Concentration of O2 = (32.0 x 2.00 x 10-4) x 103 mg dm-3 = 6.40 x 10-3 mg dm-3 = 6.40 ppm