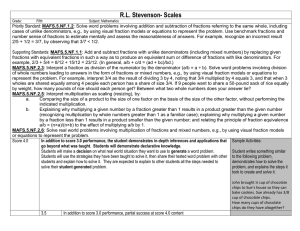
4.NF.B.3.D
advertisement

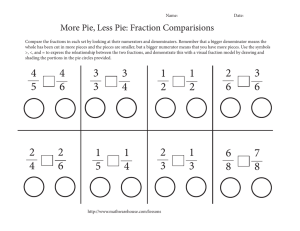
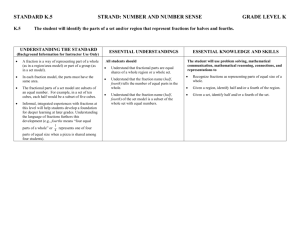
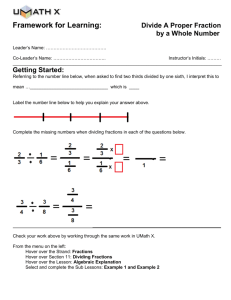
4.NF.B.3.D *This standard is part of a major cluster Standard: Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole and having like denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. Grade four expectations in this domain are limited to fractions with denominators 2,3,4,5,6,8,10,12, and 100. Standard Unpacked: This standard can and should be integrated as much as possible when working within the 4.NF.B.3 cluster. It is the application of word problems in context of these standards. Particular emphasis, as in the other standards in this cluster, with visual models and equations are relevant. Reference 4.NF.3.A, 4.NF.3.B, & 4.NF.3.C for additional information regarding those standards. As in the other standards in this cluster, this standard continues to stress the importance of using visual models and equations to represent the problems, while allowing students ample opportunity to create the models. There is substantial evidence to suggest that the effective use of models in fraction tasks is important (Cramer & Henry, 2002; Siebert & Gaskin, 2006). Unfortunately, textbooks rarely use manipulatives, and when they do, they tend to only be area models (Hodges, Cadey, & Collins, 2008). This means that students often do not get to explore fractions with a variety of models and/or do not have sufficient time to connect to the models to the related concepts. In fact, what appears to be critical in the learning is that the use of physical tools leads to the use of mental models, and this builds students’ understanding of fractions (Cramer & Whitney 2010; Petit, Laird & Marsden, 2010). Encouraging students to use models other than area models, as well as exposing them to tasks that call for students to use different models will be critical in their development of fractions. Questions to Check for Understanding and Increase the Rigor: • At noon, the bakery had 1 whole pumpkin pie and 5/12 of a pumpkin pie available to sell. At the end of the day, 3/12 of a pie was left. How much pumpkin pie did the bakery sell during the afternoon? Justify your thinking with a visual model. • Shelly needs 1 ⅜ cups of oats for a cookie recipe. How many cups of oats does Shelly need if she is tripling the recipe? (This question is not exclusive to multiplication of fractions, repeated addition can be used) Justify your thinking with a visual model. • The answer is 5 ⅙, write a story problem involving addition and/or subtraction to result in this answer. • • Jashae has 3 ¾ foot of yarn. She uses 1 ¼ foot of the yarn to make a bracelet. Then she gave her sister 1 ¼ foot of yard for her bracelet. How much yarn does she have left? Represent this problem visually. Don came home and found a fraction of a large pizza on the counter. He eats 3/8 of the pizza and now there is 2/8 of a pizza left. What fraction of the pizza was on the counter when he got home? Justify your thinking with a visual model.