Supplementary Table S1. Primers for TD-PCR.
advertisement

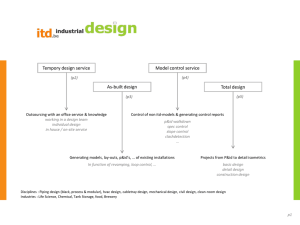
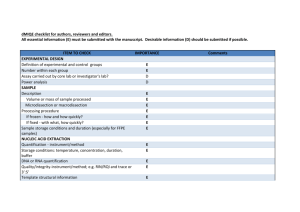
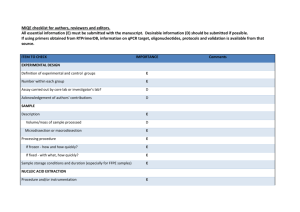
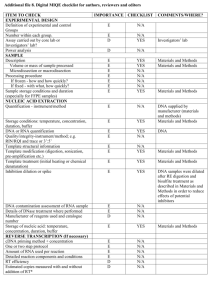
Supplementary Tables S1-S2 and Figures S1-S4 for Lin et al: A Novel Tandem Duplication Assay to Detect Minimal Residual Disease in FLT3/ITD AML 1 Supplementary Table S1. Primers for TD-PCR. Primer Sequencesa Label TD1F 5'-GACcagcatttcGtttccattgga-3' TD1R 5'-AGGaatggaaaaCaaatgctgcag-3' 6-FAM TD3 TD3F 5'-GtcaaatgggTgtttccaaga-3' TD3R 5'-ActtggaaTctcccatttgag-3' 6-FAM TD4 TD4F 5'-CatctcTaaAgggagtttcca-3' TD4R 5'-AggaaactcccaAAtgagatc-3' 6-FAM TD5 TD5F 5'-CTCATcttctTcgttgatttcagag-3' TD5R 5'-GAGACaaatcTacgtagaagtactc-3' 6-FAM TD6 TD6F 5'-GAGTCataatgTgtacttctacgttg-3' TD6R 5'-GTTGCtagaagAactcattatctgag-3' Hex TD7 TD7F 5'-ACTccggctcctcTgataatgag-3' TD7R 5'-GAGattatctgTggagccggtca-3' 6-FAM TD9 TD9F 5'-GagctacagTtggtacaggtg-3' TD9R 5'-GacctgtaccTtctgtagctg-3' Hex a Capitalized nucleotides: nucleotides altered to introduce mismatch. Primer pairs TD1 2 Supplementary Table S2. Early detection by TD-PCR of low level mutants in the initial diagnostic specimens that later became dominant mutations Initial diagnosis Blast percentage by flow cytometry ITD by standard assay positive replicates for TD5 TD-PCRb positive replicates for TD6 TD-PCRb Patient 1 AML 64% Negative 2/10c 0/10 Patient 2 MDS/MPNa 2% Negative 1/2 2/2 Relapse or AML transformation 6 months 5 months Blast percentage 89% 48% ITD by standard assay (bases)c 366 and 375c 387 a MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; MPN, myeloproliferative neoplasm. b Patient 3 AML 12% Negative 2/2 2/2 6 months 61% 379 TD-PCR using 50 ng DNA for each replicate. The numerator is the positive replicate number and the denominator is the total replicate number. c Migration of the wild-type allele at 328 + 1 bases by the standard PCR assay. TD-PCR detected the 366-base ITD but not the 375-base ITD in the initial diagnostic specimen. 3 Supplementary Fig. S1. Duplication-specific amplification of a long ITD by TD-PCR. Electropherogram of a large ITD shows amplification by adjacent primer sets because each lies within the ITD. The amplicon sizes are the same or differ slightly (1-5 bases) because of different primer spans. Given one amplicon size, a second amplicon size can be predicted, thus serving to confirm the duplication-specific amplification. TD-PCR was conducted with 1 ng DNA. TD-PCR products were diluted 40 fold before electrophoresis. Sizes in bases are in parentheses. RFU: relative fluorescence unit. PS: primer span (21-26 bases). 4 Supplemental Fig. S2. Estimation of TD-PCR amplicon sizes. By capillary electrophoresis of the standard PCR assay, the duplication length of an ITD is the observed mutant amplicon size minus the observed wild-type amplicon size (328+1 bases). The estimated TD-PCR amplicon size, corresponding to the ITD detected by the standard assay, is the duplication length plus the primer span (PS). 5 Supplementary Fig. S3. Linear correlation between the estimated and observed TD-PCR amplicon sizes. Amplification of the corresponding ITDs detected by the standard assay was supported by a consistent linear correlation between the estimated TD-PCR amplicon size (xaxis) calculated from the amplicon size determined by the standard assay (see the formula in Fig. 3) and the observed TD-PCR amplicon size (y-axis). 6 Supplementary Fig. S4. Minor ITD mutants detected by TD-PCR. In this specimen, the standard assay showed two dominant ITDs migrating at 348 and 354 bases and the wild-type allele migrating at 327 bases (a). A minor ITD mutant migrating at 195-199 bases was amplified by 5 TD-PCR primer pairs (b). Amplicons from this minor ITD mutant, if detectable by the standard assay, should migrate at approximately 502 bases. TD-PCR products were diluted 10fold before electrophoresis. Sizes in bases are in parentheses. RFU: relative fluorescence unit. PS: primer span. 7