Glaciers 2013 Invitational
advertisement

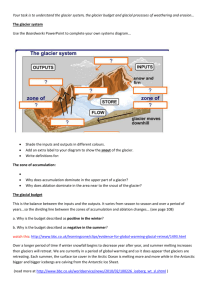
Dynamic Planet - Glaciers International Academy East – 2013 Science Olympiad 1. What is the name of the major ice sheet that impacted Michigan’s landforms? 2. What is the feature shown in the picture below labeled (A) In Picture A ? 3. What is the feature shown in Picture B? Picture A Picture B 4. How is a kame formed? 5. Are there sands and fine sediments deposited in a kame? 6. a. b. c. d. What glacial event forms an esker? Fast moving glacier Stagnant glacier Receding glacier Advancing glacier 7. a. b. c. d. What is the best description of a ground moraine? Rolling hill with fertile soil consisting of clay and loam Flat plain consisting of sand Rocky elongated hills with sand, round rocks and coarse sand Tall cone shaped mound of soil, sand, and rocks 8. a. b. c. d. An end moraine is : A flat surface surrounding the Saginaw Bay portion of Lake Huron A hill of sediment where a continental glacier rested for a period of time A ridge between two glaciers A series of small irregular hills that shows the direction of ice flow [Type text] Page 1 9. What is the name of the moraine that shows the farthest extent of a glacier? 10. A kettle lake is formed: a. At the front edge of a melting continental glacier b. It is a hole in the ice that fills with water c. By a giant ice block that is surrounded by outwash and then melts d. By putting a kettle of hot water on a glacier and watching it melt 11. What valuable resource is found in glacial drift? __________. 12. Describe the shape of a kettle lake? a. Round and deep b. Square c. Irregular d. Long and deep 13. What is glacial drift or till? a. An iceberg that breaks off a glacier into the water b. Material that is deposited by a glacier c. A large hole that is scoured through the land d. A lake that is made from a glacier melt water 14. When a glacier collects more snow and ice than it melts it is _____________. 15. When a glacier melts more snow and ice than it collects it is _____________. 16. What is the difference between a lateral moraine and an arête? a. An arête is French and a lateral moraine is English b. An arête is in mountain glaciation and a lateral moraine is continental c. An arête is a part of a mountain between two glaciers and a lateral moraine is debris carried by the glacier deposited along the sides d. An arête is a top of a mountain where four glaciers started and a lateral moraine is a deposit of glacial till at the bottom of the glacier 17. A valley carved by a mountain glacier is __________. 18. The debris trail created by the merging of two mountain glaciers is ___________. 19. Glacial movement is fastest a. Along the edges b. At the surface c. At the base close to the ground d. At the front and in the middle [Type text] Page 2 20. What is the name of an exposed smooth polished rock formation that has large scratch marks indicating the direction of glacier and exhibits cracking or pluck marks on the downhill side? Pick 8 Glacial Depositional Landforms from the list on the right 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. Pick 5 Fluvioglacial Depositional Landforms from the list on the right 29. 30 31. 32. 33. a. Braided streams b. drumlin c. erratics d. esker e. kame f. kettle hole/lake g. Lateral moraine h. Medial moraine i. outwash plain j. recessional moraine k. terminal moraine l. till plain m. varve 34. What is the name of a lake formed at the bottom of a cirque? What are the features identified on the following maps? 35. Feature A 36. Feature B 37. Feature C 38. Feature D 39. Feature E 403. Feature F [Type text] Page 3 [Type text] Page 4 A A’ 41-44. Draw a profile of the feature represented by the line A-----A” from the map above ( worth 4 points) [Type text] Page 5 45. Heavy oxygen isotopes condense water a. More quickly than light oxygen isotopes b. Slower than light oxygen isotopes c. Has no impact on condensation 46. Heavy oxygen isotopes have ____ neutrons. a. 4 b. 6 c. 8 d. 10 47. Light oxygen isotopes have ________neutrons a. 8 b. 10 c. 16 d. 22 48. The area above the Red line represents : a. b. Period of Glaciation Interglacial period 49. The area below the red line represents: a. Period of Glaciation b. Interglacial period Isotopes of Oxygen [Type text] Page 6 50.. How many glacial advances were recognized in North America during the Pleistocene? a. b. c. d. 3 4 5 8 51. Who was the person that developed the theory that climatic variations were caused in part by the tilt of the earth’s axis? 52. The Pleistocene Age was approximately ____ years ago? a. 10,000 to 25,000 years ago b. 11,000 to 2.5 Million years ago c. 11 billion to 15 billions years ago d. 2000 to 10,000 years ago 53. What technique enabled scientists to date glacial landforms? a. Oxygen isotopes b. Uranium -235 c. Carbon-14 d. measuring existing glaciers 54. What is a drumlin? a. a depression in the earth caused by big rocks stuck in the bottom of the glacier b. a ridge that extends for more than 1 mile c. a streamlined mound of glacial drift, rounded or elongated in the direction of the original flow of ice d. a type of stream that is created at the base of the glacier Use the following assumptions and draw on the graph paper provided. A drumlin with the following dimensions: 100 feet high the graph paper 1 square =20 feet 400 feet long contour interval = 20 ft 100 feet wide 55.Draw on the graph paper provided a profile view of a drumlin. 56.Draw on the graph paper provided a topographic view of a drumlin. 57. Draw an arrow pointing at the direction of movement [Type text] Page 7