Forces Module - Temple University Sites
advertisement

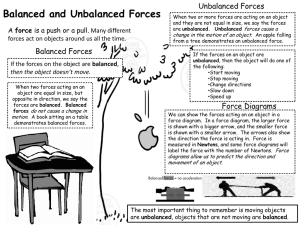
IES Grant Module Format Module – 9 Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Grade Level- 8th PA State Standard (# & short description) S8.A.1.3.3: Examine systems changing over time, identifying the possible variables causing this change, and drawing inferences about how these variables affect this change. Module Objective(s) Students will… Be able to explain the concept of balanced and unbalanced forces and how these forces relate to motion. Materials/Supplies- Rope (for tug of war) Picture Prompts- Notes Slide Show Big Idea: An object’s motion is the result of all forces acting on it. Essential Question(s): What causes objects to move? Module #1 1. Do Now: Pre-test (10 minutes) 2. Video Clip: http://www.engineeringinteract.org/resources/parkworldplot/flash/co ncepts/balancedandun.htm 3. Vocabulary: · Force- A force is a push or pull that causes an object to start moving, stop moving, or change direction. Bobbie used force to open the old rusty door. · Balanced forces- when forces are equal and opposite. The science book rested on the table because of balanced forces. · Unbalanced forces- when forces are not equal or not opposite. The blue team won the tug or war game because they were stronger and created an unbalanced force on the rope. · Gravity- force that pulls all things toward Earth. Rain falls from the sky because of gravity. · Friction- force acting in the opposite direction of motion. The friction of the gravel track helped me run faster. · Magnitude- is the difference between the forces- measured in Newtons (N). The magnitude of the force used to open the door was 10 N. · Direction- refers to the way an object is traveling. (left, right, up, away from, etc.) The ball was rolling towards the wall. 4. Lecture Part 1: What is a force? Write this down. A force is a push or a pull exerted on matter And a force causes an object to start moving, stop moving, or change direction. What are some examples of forces? One example of a force is gravity. You need to know that gravity forces all object towards the Earth. When you drop a ball, it falls to the ground. That is because the force of gravity. Something is pulling the ball towards the Earth. Gravity is a force working on all objects on Earth. Pushing a cart up a hill is another example of a force. When you push a cart up a hill, it might be a little more difficult because you are applying a force against the cart and are also working against the force of gravity and another force, the force of friction. Take note that the force of friction works in the opposite direction of a moving object. Friction occurs when two objects are in contact with each other. Therefore pushing furniture on an old rough carpet might be tough because there is a force working against you, the friction of moving the furniture on the rough carpet. Imagine pushing the same furniture on one of those smooth linoleum floors, its much easy- there is still friction, its just less friction. Another simple example of a force is a textbook resting on a desk. It may not seem there are any forces acting on the textbook, but gravity is actually forcing the book down, while the table is forcing the book up. Now that we know some examples of forces, we can discuss how forces can affect motion. You need to know that forces acting on objects occur in pairs and are either balanced or unbalanced. Forces also have magnitude and direction. You must know that when a pair of forces have equal strength and act in opposite directions, they are balanced forces. When we mention the strength of a force we are referring to its magnitude. Write this downthe magnitude of a force is the difference between all the forces acting on an object. Our unit for force is the Newton, because of Isaacs Newton’s work with forces. It would be like if you and I are pushing this book towards each other. So the direction of the forces in this case is towards each other. And basically, the magnitude is the size of the force we are pushing on the books. You must remember the direction is the way the force and/or object is moving. Lets try. If I pushed this book with a force of 3 N (magnitude) towards you (direction), and you pushed the book with a force of 3 N towards me, the forces would cancel out. The book wouldn’t move. The difference between the forces is zero- the magnitude of the forces acting on the book is zero. Three minus three equals zero. The word difference means we subtract. Therefore these two forces cancel each other out and the motion of the object they are acting on is unchanged. This book wasn’t moving, and its still not moving. You also must know that when one of the forces in a pair is greater than the other, they are considered to be unbalanced. And an unbalanced force results in a change in motion. For example, when an unbalanced force acts on an object at rest, the object will begin to move. Watch what happens to this textbook when I apply a greater force in this direction. The textbook changes its motion. So if I am pushing (forcing) the book at you with a force of 5 N, and you are pushing the book back at me with a force of 3 N, which way will the book move? And what is the magnitude of the force while the book is moving? Lets do the math. 5 N minus 3 N equals 2 N. Don’t forget that an unbalanced force may also cause a moving object to stop, change direction, or change speed. Lets review balanced and unbalanced forces. Balanced forces; the motion of object does not change, the forces are equal in size and opposite in direction. Unbalanced force; when the motion of an object does change in speed or direction, the forces are unequal in size Both gravity and friction are two forces that usually work against pushes and pulls. 5. Activity: Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Activity- Tug of War with students. Use rope and mix up student groups to show balanced and unbalanced forces and magnitude. 6. Review Notes: Address Note-taking students, “Go to the last page of your notes and write five lecture points, you may refer to your notes”, Address all other students, “Fill in any gaps in your notes”. 7. Post Test: (10 minutes) 8. Homework/Follow-up: Balanced and Unbalanced Reading Guide Q&A