Chapter 1 Mineral Notes
advertisement

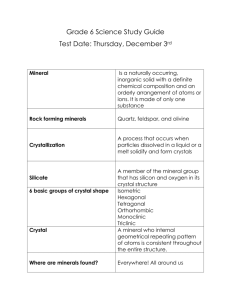
Name _____________________________ Date ____________ Period ________ Chapter 1 Minerals Section 1- What is a Mineral? Minerals: Naturally occurring __________________ (non-living) Solid Definite ____________________structure Crystal structure is a _______________________ shape pattern due to the ______________________ ___________________________ of the atoms that make it up Minerals make up rocks; rocks do not make up minerals The Atom The ____________________________ has the characteristics of that element _____________________ ________ _______ _____________________ that Element • Pure substance that _________________ __________ ____________________ ___________ into simpler substances • Pure substance: – only one type of particle Compounds • Two or more elements that are ______________________ ______________________ • Cannot be broken down by physical means Crystalline Structure • _____________________________ geometric pattern within a mineral due to the shape of the atoms that make it up Silicates • Contain _______________________ and ___________________________ • Make up more than _____________% of the earth’s _____________________ Non-Silicates • Do not contain a combination of silicon and oxygen Classes of Non-Silicate Minerals ____________________ ________________________ - Composed of only 1 element, Ex. Au, Ag, and Cu ________________________________ - Contain C and O ________________________________ - F, Cl, I, or Br combine with Na, K, or Ca ________________________________ - O with only 1 other element ________________________________ - S with only 1 other element ________________________________ -contains an SO4 group Section 2 Mineral Identification Color is not a reliable way to identify minerals due to impurities! Luster- The way the mineral reflect light o _________________________ Bright and reflective o _________________________Dull and not reflective (See figure 1 on page 8) o _________________________ Dull and reflective Streak The ___________________ of a mineral in ______________________________form Streak is often more reliable than color when identifying a sample. Cleavage refers to the natural ________________________ _________________________ in which a mineral will break __________________________, ______________________ surfaces Fracture refers to the tendency of a mineral to _________________________ ___________________ or along a ______________________________ Hardness A minerals ____________________________ to being __________________________ Moh’s Hardness Scale o Finger nail = 2.5 Penny = 3.5 Steel Nail = 4.5 Streak Plate = 6.5 Glass Slide = 5.5 Density How ___________________________ the mineral is ______________________ = Mass/Volume Specific Gravity • the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of __________________________ • SG = Density of substance /Density of water Special Properties of Some Minerals Section 3 Formation and Mining Metallic • ________________ • Good conductors of heat and electricity • _______________________ • Ductile Non-metallic • ____________________ (not shiny) • Poor conductors of heat and electricity • ______________________ • Unmalleable Gemstones • Highly _____________________ • Rarity, _______________________, ________________________ and _____________________determines how valuable it is • _______________________ is the unit of mass of a gemstone Mineral Formation the way in which a mineral forms determines it’s properties Mineral crystals _____________________ as _______________________ _________________ ___________________to its surfaces, edges, or corners Two main ways crystals are formed Crystallizing from elements and compounds in ___________________-- (underground lava) Crystallization of elements and compounds ___________________ in __________________ Size of crystals depends on cooling rate: ______________________ cooling= _____________________ crystals ______________________ cooling= ______________________crystals Crystallizing from Magma Molten material is a liquid mixture of freely moving crystals As molten material rises towards Earth’s surface it cools and crystalline solids form. Metamorphic o Changes in _____________________, ______________________ and/or ___________________ ___________________________ alter a rock and the minerals inside it o Ex. - calcite, garnet, graphite, hematite, magnetite, mica and talc Plutons o Magma that ____________________ ______________________, cools and solidifies o Ex. Mica, feldspar, magnetite and quartz Pegmatiteso ___________________ shaped ___________________ _____________________ o Ex. many gemstone, including topaz and tourmaline Crystallization of elements dissolved in water Elements in water are freely moving in _______________________________ When water ___________________________, solid crystals are left behind Can be above or below Earth’s surface Crystallizing from Hot Water Limestone o Crystallization of ___________________________ __________________________ carried by water and deposited on the bottom of lakes, seas Ex. Calcite and dolomite Evaporating salt water o Body of salt water dries up leaving behind minerals o • Ex. Halite and gypsum Hot water solutions o _________________________________ works its way downward and is heated by magma o Then it reacts with minerals to form hot liquid solutions o Dissolved metals and other elements crystallize when cools o Ex. Gold, copper, sulfur, pyrite, and galena Mining • extracting _________________________ from on top of and/or within the earth • Ore - rock and mineral deposits that are large and pure enough to be ______________________ once extracted • Two types of mining • – Surface – Subsurface The method used to reach mineral deposits depends on how deep it is from the surface Surface Mining • • • • When mineral deposits are located at or near the Earth’s surface – Types: open pits, surface coal mines, and quarries Open pit mine o Removes large _________________ - __________________ deposits of economically important minerals o Ex- gold and copper Quarry o Type of open pit mine in which building materials are extracted o Ex- limestone, marble, granite Surface Coal Mine o AKA _______________________ _____________________________ o Coal is removed in long wide strips Subsurface Mining • Minerals are extracted from deep within the earth • Different types of passageways can be dug to reach the ore • Types: _____________________, ________________________ and _______________________ Mines Harmful Effects of Mining • • • ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Solutions • • __________________________, _________________________, _________________________ _______________________ __________________________ - required by law since the 1970’s- to return land to its original condition after mining is completed ( or to a better state) Mine Reclamation Difficulties • Might never get species back even after land is restored • If wetlands are disturbed, new channels for water into the wetlands must be made which is untested • Natural peat lands are lost forever since it takes thousands of years for natural peat to develop